N,N-Dimethylformamide: The application and metabolism
Apr 11,2023
General description
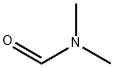
N,N-Dimethylformamide is a common polar solvent that has a worldwide annual production, and is used in a wide variety of industrial processes. Often used as a common solvent for chemical reactions and utilized widely in industry as a reagent, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) has played an important role in organic synthesis for a long time. The primary use of DMF is as an effective polar solvent for various chemical reactions. Additionally, DMF is a multipurpose reagent widely used in chemistry. For instance, DMF can be utilized as an effective ligand in the preparation of metallic complexes. Furthermore, it can also participate in reactions as a dehydrating agent, as a source for a reducing agent, or even as a catalyst.4 More importantly, because of its structure, DMF can participate in many reactions by serving as a multipurpose building block for various units, such as O, -CO, -NMe2, -CONMe2, -Me, -CHO, etc. Its appearance is as follows:

Figure 1 Appearance of N,N-Dimethylformamide.
Application
N,N-Dimethylformamides has many uses in the organic chemistry. It can serve as a precursor in formylation reactions. The formylation of numerous substrates, such as electron-rich aromatic or heteroaromatic compounds, as well as electron-rich alkenes and 1,3-dienes, has been achieved by utilizing Vilsmeier reagents, which are usually prepared from N,N-Dimethylformamides and acid chlorides [1]. Moreover, N,N-Dimethylformamides can serve as a precursor in aminocarbonylation reactions. In 2001, the group of Indolese observed the formation of dimethylamide in the reductive carbonylation of 3-bromobenzotrifluoride in DMF. With the employment of imidazole, which is known as a powerful Lewis base and acylating catalyst, and the adjustment of the Pd/P ratio, an 89 % yield of the amide was obtained. Since this reaction was conducted under CO (5 bar), DMF was considered to be the amine source [2].
In addition, N,N-Dimethylformamides can serve as a Source of dimethylamine in mmination reactions. DMF has been utilized widely in the amination of aryl halides by serving as an important and convenient source of dimethylamine, which results from facile decomposition of DMF under various reaction conditions [3]. Besides, N,N-Dimethylformamides can serve as a source of dimethylamine in amidation reactions. There have been some reports on the synthesis of amides just by heating DMF solutions of acyl chlorides, esters, or anhydrides. Recently, Kumagai et al. reported an effective synthesis of N,N-dimethylamides from carboxylic acids and DMF in the presence of thionyl chloride [4].
Metabolism
The major pathway of metabolic disposition of DMF involves the hydroxylation of its methyl moieties. The primary product of this metabolic route is N-(hydroxymethy1)-N-methylformamide [HMMF, CH3(CH2OH)NCHO. HMMF, in turn, can decompose to NMF chemically with concomitant elimination of formaldehyde at a rate which depends on the pH and temperature of the environment. HMMF is the major urinary excretion product of DMF in humans. Volunteers who were exposed for 8 h to 30 mg/m-3 DMF vapor excreted only 0.3% of the absorbed dose as DMF, but 22.3% as HMMF [5]. In an investigation of the plasma disposition of DMF and its metabolites in rats and mice which had inhaled DMF vapor, discrimination between NMF and HMMF was achieved. NMF constituted between 30% and 60 % of HMMF plasma levels, depending on exposure and sampling time [6].
Toxicity
The original studies on DMF metabolism related its adverse effects to its biotransformation to NMF. Consistent with this notion, monoalkylformamides such as NMF are clearly more potently toxic than DMF.
References
[1]G. Jones, S. P. Stanforth, Org. React. 2000, 56, 355– 659.
[2]A. Schnyder, M. Beller, G. Mehltretter, T. Nsenda, M. Studer, A. F. Indolese, J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 4311– 4315.
[3]A. Sharma, V. P. Mehta, E. Van?der?Eycken, Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 2605– 2610.
[4]T. Kumagai, T. Anki, T. Ebi, A. Konishi, K. Matsumoto, H. Kurata, T. Kubo, K. Katsumoto, C. Kitamura, T. Kawase, Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 8968– 8973.
[5] J. MrAz and H. Nohova. Int. Arch. Occup. Enuiron. Health. 1992, 64, 85-92.
[6] J. R. Barnes and K. E. Ranta. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1972, 23, 271-276.
[7]Gate,E. N.,Threadgill,M. D., Stevens,M. F. G.,Chubb, D.,Vickers, L. M., Langdon, S. P., Hickman, J. A., and Gescher, A. J. Med. Chem. 1986, 29, 1046-1052.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- N,N-Dimethylformamide: Uses and Safety Data Sheet Mar 15, 2024
N,N-Dimethylformamide is a colourless or light yellow transparent liquid with an amine-like odour, which can dissolve most organic and many inorganic substances, and is therefore widely used as an industrial solvent, and is known as an all-
- N,N-Dimethylformamide: Polarity and Application Jan 3, 2024
N,N-Dimethylformamide is a colourless, odourless liquid solvent. It is miscible with water and many organic liquids. It has a polarity index of 6.4, a dipole moment of 3.86, and a dielectric constant of 37.
- What is N,N-Dimethylformamide? Feb 21, 2020
N,N-Dimethylformamide, or dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NC(O)H. Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate).
The Isovaleraldehyde is an intermediate in the production of fragrances and other organic chemicals, and naturally exists in essential oils such as citrus and lemon.....
Apr 11,2023Organic Solvents(1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid is prepared from camphor by sulfonation reaction. It is a Chinese herbal reference and chemical intermediates.....
Apr 11,2023Natural ProductsN,N-Dimethylformamide
68-12-2You may like
- γ-Valerolactone:synthesis and chemical recovery
Dec 15, 2025
- Application research of 4,4'-Dibromobiphenyl
Nov 18, 2025
- Application research of Octadecyl acrylate
Nov 18, 2025
N,N-Dimethylformamide manufacturers
- N,N-Dimethylformamide
-

- $10.00 / 1kg
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:68-12-2
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%min
- Supply Ability: 200tons
- N,N-Dimethylformamide
-

- $0.00 / 230kg
- 2025-12-05
- CAS:
- Min. Order: 230kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20 ton
- N,N-Dimethylformamide
-

- $0.00 / 230kg
- 2025-12-05
- CAS:
- Min. Order: 230kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20 ton