The introduction of Benzpyrimoxan
Feb 22,2024
Introduction
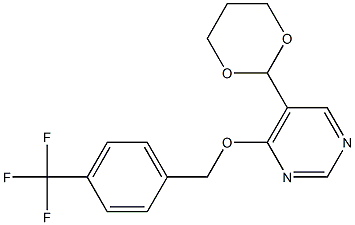
Benzpyrimoxan (5-(1,3-dioxan-2-yl)-4-{[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy}pyrimidine, NNI-1501) was discovered as a novel insecticide structurally characterized by a pyrimidine derivative substituted with 1,3-dioxanyl and 4-trifluoromethylbenzyloxy groups[1]. Nihon Nohyaku announced it as a new insecticide in 2017; it has been developed under the code NNI- 1501.
Uses
The compound showed remarkable activity against nymphs of rice planthoppers, including strains resistant to existing insecticides. Furthermore, it demonstrates molting inhibition differently from other existing insect growth regulators and does not impact non-target organisms such as pollinators and beneficial arthropods.
Symptoms of brown rice planthopper nymphs treated with benzpyrimoxan versus buprofezin
The Figure below shows the symptoms of nymphs affected by benzpyrimoxan versus buprofezin. Although the nymphs affected by both compounds died at the time of molting, the dead nymphs treated with benzpyrimoxan turned blackish compared to those treated with buprofezin and their exuviae were attached at the bottom of their bodies. This result indicated that the mode of action of benzpyrimoxan was the insect growth regulator, which is different from that of buprofezin.

Synthesis method
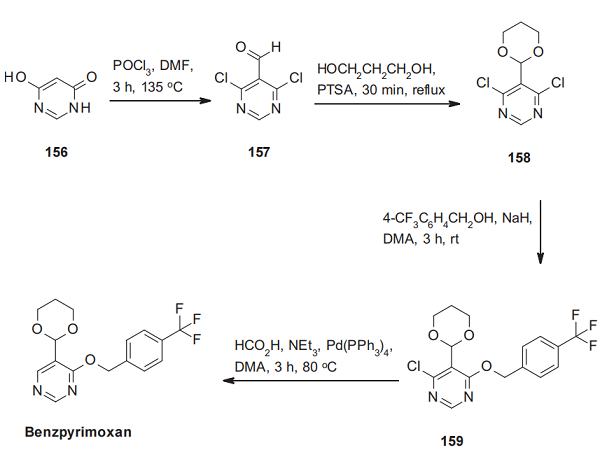
The synthesis of benzpyrimoxan starts with the trans-formation of 4,6-dihydroxypyrimdine (156) with in situ prepared Vilsmeier-Haack reagent, which directly leads to 4,6-dichloro-5-formyl- pyrimidine (157). This aldehyde is heated azeotropically to reflux with an excess of 1,3-propanediol in the presence of para-toluenesulfonic acid. One of the two chlorine atoms of the resulting acetal derivative 158 is then replaced by a reaction with 4-trifluoromethylbenzyl alcohol. Removing the remaining chlorine atom in 159 under palladium catalysis delivers benzpyrimoxan[2].
References
[1] Eikoh Satoh. “Benzpyrimoxan: Design, synthesis, and biological activity of a novel insecticide.” Journal of Pesticide Science (2021): 109–114.
[2] Stephane Jeanmart . “Synthetic approaches to the 2015–2018 new agrochemicals.” Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 39 (2021): Article 116162.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
The only difference between Aβ42 and Aβ40 is that Aβ42 has two extra residues at the C-terminus.....
Feb 22,2024Biochemical EngineeringDimpropyridaz is now classified by IRAC as a Pyridazine pyrazole carboxamides (PPCs) insecticide due to its unique mode of action, and it is the first member of this class of insecticides.....
Feb 22,2024Chemical pesticides ?Benzpyrimoxan
1449021-97-9You may like