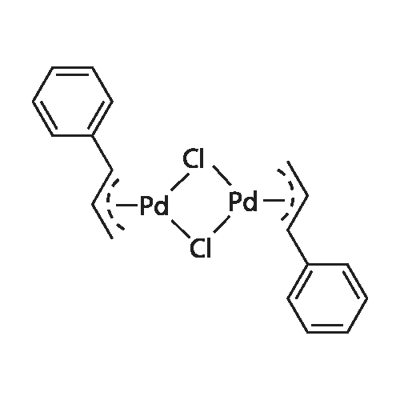
What is di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(ii)?
Feb 12,2020
Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(ii) is an important organic regant for the use of transition-metal-mediated organic syntheses. Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(ii) can be used as a catalyst for the ammonia cross-coupling reactions to synthesize arylamines and conversion of aryl triflates to fluorides.

In addition, di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(ii) is an important organic intermediate to synthesize (π-Allyl)Pd complexes containing N-heterocyclic carbene and pseudohalogen ligands. In transition-metal-mediated organic syntheses, Pd-catalyzed C–C cross-coupling reactions are widely utilized. In particular, palladium compounds containing labile ligands such as C,N-donor ligands have emerged as efficient precatalysts for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. Furthermore, to enhance catalytic efficiency in the catalytic reactions, several studies on cyclopalladated compounds containing N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs), one of the many sterically and/or electronically beneficial ligands, were used. Pseudohalogen ligands are known to be better leaving groups than halogen ligands in catalytic reactions. Their catalytic activity was dependent on the supporting ligand, a tertiary phosphane or an NHC ligand. For example, compounds with an NHC ligand showed higher catalytic activity for aryl chlorides than those with a combinationof C,N-donor and tertiary phosphane ligands [1].

In using [{Pd (cinnamyl)Cl}2]/Mor-DalPhos precatalyst mixtures, electron-rich, electron-poor, and heterocyclic products of ammonia monoarylation were prepared (50–110OC) in high isolated yields. Mor-DalPhos has also been found to be useful in facilitating the Pd-catalyzed monoarylation of hydrazine, acetone, and other carbonyl compounds in chemoselective and aqueous BHA chemistry, as well as in the Au-catalyzed hydroamination of internal alkynes with dialkylamines. Whereas the room-temperature BHA of aryl chlorides with ammonia was not successful when using [{Pd (cinnamyl)Cl}2]/Mor-DalPhos precatalyst mixtures, unprecedented room-temperature transformations of a small number of aryl chlorides were achieved with good monoarylation selectivity by use of the chlorobenzene oxidative addition product [(k2-P,N-Mor-Dal-Phos)Pd(Ph)Cl] as a precatalyst. It is possible to overcome the limitations of other catalysts which include substrate-scope challenges with respect to the monoarylation of electronically deactivated and sterically unhindered aryl chloride substrates, the frequent requirement of relatively high reaction temperatures.[2]
References
1.Kim HK et al. (π-Allyl)Pd Complexes Containing N-Heterocyclic Carbene and Pseudohalogen Ligands – Synthesis, Reactivity toward Organic Isothiocyanates and Isocyanides, and Their Catalytic Activity in Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Couplings[J]. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 4958–4969
2. Alsabeh PG et al. An Examination of the Palladium/Mor-DalPhos Catalyst System in the Context of Selective Ammonia Monoarylation at Room Temperature[J]. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2131 – 2141.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
See also
(-)-di-p-toluoyl-l-tartaric acid can be used as a chiral resolving agent for the resolution of the racemic bases to isolate the (-)-enantiomeric forms.....
Feb 12,2020Carboxylic acids and derivativesKaempferol (3,5,7‐trihydroxy‐2‐[4‐hydroxyphenyl]‐4H‐1‐benzopyran‐4‐one) is a yellow bioactive flavonoid, which is present inmany edible plants such as tea, cabbage, broccoli, endive, kale, beans, tomato, strawberries, leek, and grapes.....
Feb 12,2020Natural ProductsYou may like
- Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium: uses and Health effect
May 9, 2024
- polypropylene vs polycarbonate
Mar 18, 2024
- What is sodium chlorite used for?
Mar 16, 2024
Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(II) manufacturers
- Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(II)
-
![12131-44-1 Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(II)](/ProductImageEN/2023-01/Small/e5013789-c6e1-45e5-9ca4-f703de0175e8.jpg)
- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2023-01-17
- CAS:12131-44-1
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 98%min
- Supply Ability: 30tons/month
- Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(II)
-
![12131-44-1 Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(II)](/ProductImageEN/2022-09/Small/c18dac70-4adf-4b70-8713-082516f7970b.png)
- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2022-09-24
- CAS:12131-44-1
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg
- Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(II)
-
![12131-44-1 Di-chlorobis[(1,2,3-)-1-phenyl-2-propenyl]dipalladium(II)](/ProductImageEN/2020-11/Small/40efc31f-3860-4bbc-9f8d-e1fcffb532d9.jpg)
- $20.00 / 1KG
- 2020-11-16
- CAS:12131-44-1
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000KG