| Aladdin Scientific | |
|---|---|
| Country: | United States |
| Tel: | 400-620-6333 |
| E-mail: | sales@aladdinsci.com |
| QQ: | |
| Skype: | Chat Now! |
【Aladdin】Methods for Counting Cells Using a Hemocytometer
Release time: 2025-01-21
Methods for Counting Cells Using a Hemocytometer

Licia Miller Product Manager
Cell counting with a hemocytometer is a cornerstone of in vitro and in vivo experiments. It improves the precision and reproducibility of your research and increases the reliability of your results. Whether your research focuses on microbiology, hematology, oncology, or other diseases, accurate manual counts with a hemocytometer are essential if cell cultures are involved.
This protocol covers how to use a hemocytometer for cell counting, from preparing samples to calculating cell viability using trypan blue staining, so that you can confidently use a hemocytometer in your experiments.
Phase 1 Prepare the hemocytometer
1. If using a glass hemocytometer and coverslip, clean them with alcohol before use. Wet the coverslip with water and attach it to the hemocytometer.
2. If using a disposable hemocytometer, simply remove it from the package before use.
Phase 2 Preparation of cell suspension
Quantities of DPBS and trypsin-EDTA required for trypsinization of adherent cells.
|
Experimental Steps
1. Gently swirl the flask to ensure that the cells are evenly distributed.
2. Before the cells settle, take out 0.5 mL of the cell suspension using a 5 mL sterile pipette and place it into an EP microcentrifuge tube.
3. Take 100 µL of cells and place them into a new EP centrifuge tube. Add 400 µL of 0.4% Trypan blue (final concentration 0.32%) and stir gently.
Phase 3 Count
Experimental Steps
1. Use a pipette to draw 100 µL of the trypan blue-treated cell suspension into a hemacytometer.
If using a glass hemocytometer, very gently fill the two chambers beneath the coverslip so that the cell suspension is drawn out by capillary action.
If using a disposable hemacytometer, pipette the cell suspension into the wells of the counting chamber, allowing capillary action to draw it inside.
2. Using a microscope, focus on the grid lines of the hemocytometer using the 10× objective.
3. Using a manual counting counter, count the unstained live cells (live cells do not absorb Trypan blue) in a set of 16 squares (Figure 1).
When counting, use fixed rules, such as "record the top and not the bottom, count the left and not the right."
Following the same guidelines, dead cells stained with trypan blue can also be counted to assess viability if desired.
Figure 1. Hemocytometer diagram showing one of the 16-square grids used for counting.
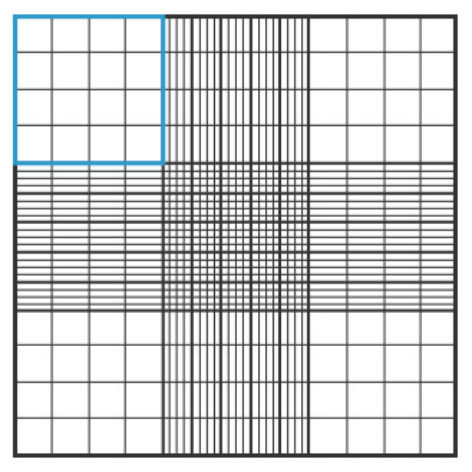
4. Move the hemocytometer to the next set of 16 corner squares and continue counting until all 4 sets of 16 corners have been counted.
Phase 4 Cell Viability
1. Calculate the number of viable cells/mL.
The average cell number from each set of 16 corner squares was taken and multiplied by 10,000 (104) and then multiplied by 5 to correct for the 1:5 dilution after the addition of trypan blue. The final value is the number of viable cells/mL in the original cell suspension.
For example, if the number of cells in each of the 16 squares is 54, 42, 49, and 56, then the average number of cells is:
(54+42+49+56) ÷ 4 = 50.25
50.25 × 10,000 (104) = 502,500
502,500 × 5 = 2,512,500 viable cells/mL in the original cell suspension
2. Calculate cell viability
If the number of live and dead cells is recorded for each set of 16 corner squares, estimated viability can be calculated.
The number of live cells and the number of dead cells were added together to obtain the total number of cells, and then the number of live cells was divided by the total number of cells to calculate the cell viability.
The calculation formula is: number of live cells/(number of live cells + number of dead cells)
For more product details, please visit Aladdin Scientific website.


