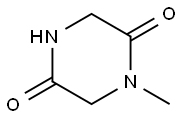
1 - Methylpiperazine - 2,5 - dione synthesis
- Product Name:1 - Methylpiperazine - 2,5 - dione
- CAS Number:5625-52-5
- Molecular formula:C5H8N2O2
- Molecular Weight:128.13
![Glycine, N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]glycyl-N-methyl-, ethyl ester](/CAS/20210111/GIF/145590-97-2.gif)
145590-97-2
0 suppliers
inquiry

5625-52-5
25 suppliers
$175.00/50mg
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
Stage #1: N-tert-butoxycarbonylglycylsarcosine ethyl esterwith trifluoroacetic acid in dichloromethane;water; for 0.5 h;
Stage #2: with potassium carbonate in ethanol; pH=8;Product distribution / selectivity;Heating / reflux;
Steps:
2
Example 2; General Procedure for the Synthesis of 1-Methyl-2,5-Diketopiperazine (FIG. 1); A solution of 1:1 trifluoroactetic acid (TFA):DCM containing 0.5% water was prepared. This solution was added to the column purified product (3) of the condensation reaction (10 mL/g starting material). The resulting solution was stirred for 30 minutes and then the solvents removed by rotoevaporator. Ethanol (10 mL/g starting material) was then added to the reaction flask and this solution was again striped to dryness. The procedure was repeated with toluene. The product was again dissolved in ethanol in the reaction flask and anhydrous potassium carbonate (4 eq) was added. The solution bubbled vigorously for a short period following the addition of the potassium carbonate. A drop of the reaction mixture was removed, diluted with water, and the pH of the solution was determined. If the pH was below 8, more potassium carbonate was added. Once the pH was confirmed to be greater than 8, the reaction was allowed to reflux overnight. The warm reaction mixture was then passed through a plug of Celite to remove the excess salts. The cake was rinsed twice with anhydrous ethanol. The filtrate was transferred to a larger flask and stripped to dryness. The product foam was redissolved in 9:1 ethyl acetate-methanol and passed through a plug of silica-gel. The silica-gel was then washed with 4 column volumes of 9:1 ethyl acetate-methanol. All fractions were evaporated to dryness. Notes and alternative procedures: Deprotection of the t-boc group with the TFA/DCM/H2O solution can be followed by TLC (ninhydrin/heat shows conversion of the spot at Rf 0.85 to a dark red-brown spot at origin). After deprotection, it is also acceptable to add methanol, concentrate and re-treat with methanol followed by a second concentration and drying in vacuo to remove excess TFA. In some reactions, concentrated ammonium hydroxide (large excess 60 mL per 16 mmol of starting material) was substituted for potassium carbonate. (When concentrated ammonium hydroxide was added to the reaction at room temperature, it generated a white insoluble material and a slightly milky reaction mixture.) After the addition of concentrated ammonium hydroxide, the flask was sealed with septum to prevent loss of ammonia. Cyclization appeared to be complete after overnight (12 hrs) reaction although in some cases heating to 60° C. over several hours was sufficient. The reaction was monitored by TLC (10% MeOH/DCM visualized with 10% phosphomolybdic acid (PMA) in MeOH with heat). The product appeared as a blue spot at Rf=0.54. Since the deblocked material (red-brown spot at origin) could not be visualized with PMA, another TLC was performed as a cross-reference using ninhydrin/heat. When cyclization was deemed complete by TLC analysis, the mixture was filtered and the flask and solids were rinsed with DCM. The filtrate was concentrated and redissolved in 10% MeOH/DCM before chromatography. The white waxy solids were partially insoluble in the 10% MeOH/DCM so the material was sonicated. Sonification successfully dissolved the mixture that was then applied to the column. The first fraction eluted was mainly the white waxy solid. The major fraction (the dione product (4)) eluted next and was followed by another minor impurity (Rf 0.3). It was observed that in cases where incomplete TFA removal resulted in formation of ammonium triflate, this impurity co-eluted with the product and the secondary material. A second column could be used to completely purify the desired product. The melting points of the dione (4): 116,117: 138-139 for model compound: lit: 136-139 (J. Het. Chem 18,423, 1981); 142-143 (J. Biol. Chem 61, 445, 1924). TLC Condition: 9:1 Ethyl Acetate-Methanol (Develop with Phosphomolybdic Acid and Heat) Product Rf0.2 Alternative TLC Condition: 10% MeOH/DCM; Develop with Heat Product (blue spot) Rf=0.54
References:
US2005/148771,2005,A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 9-10
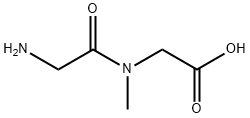
29816-01-1
117 suppliers
$24.00/250mg

5625-52-5
25 suppliers
$175.00/50mg
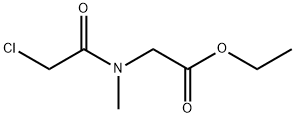
24515-53-5
10 suppliers
inquiry

5625-52-5
25 suppliers
$175.00/50mg

38082-72-3
14 suppliers
$200.00/100mg

5625-52-5
25 suppliers
$175.00/50mg
![Glycine, N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]glycyl-N-methyl-, methyl ester (9CI)](/CAS/20200611/GIF/174311-10-5.gif)
174311-10-5
0 suppliers
inquiry

5625-52-5
25 suppliers
$175.00/50mg