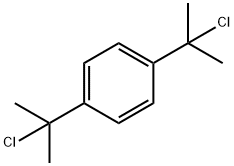
2,2'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis(2-chloropropane) synthesis
- Product Name:2,2'-(1,4-Phenylene)bis(2-chloropropane)
- CAS Number:7374-80-3
- Molecular formula:C12H16Cl2
- Molecular Weight:231.16
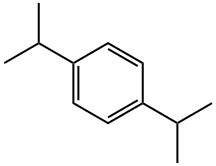
100-18-5
146 suppliers
$9.00/5g

7374-80-3
8 suppliers
inquiry
Yield:7374-80-3 45%
Reaction Conditions:
Stage #1: 1,4-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenewith hydrogenchloride;sodium hypochlorite in water;chlorobenzene at 0; for 1 h;
Stage #2: with sodium hydroxide in hexane;water;chlorobenzene at 50 - 60; for 5 - 8 h;
Stage #3: with hydrogenchloride in water;toluene;Product distribution / selectivity;
Steps:
3; 4; 5
(EXAMPLE 3) To a glass separable flask, having a capacity of 0.002 m3, equipped with a thermometer, a baffle, and a stirrer were added 1,4-diisopropylbenzene (0.045 kg), monochlorobenzene (0.03 kg), and an aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite (1.2 kg, 0. 9 mol/kg) under stirring and cooling in an ice bath. Subsequently, concentrated aqueous hydrochloric acid (0.08 kg, 35 percent by weight) was slowly added dropwise to the solution through a dropping funnel over a period of 3 minutes and stirring was continued for 60 minutes. After the reaction, the organic layer and the aqueous layer was separated by standing. To the separated organic layer was added concentrated hydrochloric acid (0. 03 kg, 35 percent by weight), and then the resulting mixture was vigorously stirred for about 5 minutes to deactivate the hypochlorous acid finely dispersed in the organic layer. The resulting organic layer was separated to obtain a monochlorobenzene solution of the reaction product. The yield of 1,4-bis(2-chloro-2-propyl)benzene in the product was determined by gas chromatography (hereinafter, referred to as "GC") analysis (yield: 60.0%). To the same flask that was cleaned were added the separated monochlorobenzene solution, 0.04 kg of hexane, and 1 kg of an aqueous solution containing 2 wt% sodium hydroxide, and then stirring was continued for 5 hours at 60°C. The aqueous layer was alkaline through the reaction. This hydrolysis reaction provided 1,4-bis(2-hydroxy-2-propyl)benzene with a selectivity of about 90%. Subsequently, the resulting solid was washed with hexane and pure water and then stirred in the presence of 0.3 kg of 35 wt% concentrated hydrochloric acid and 0.05 kg of toluene to yield 1,4-bis(2-chloro-2-propyl)benzene. The purity determined by NMR was 95%. The ultimate yield was 45%; (EXAMPLE 4) The target compound was produced as in EXAMPLE 3 except that, in alcoholization, the reaction temperature was 50°C, and the reaction time was 8 hours. The alcoholization provided 1,4-bis(2-hydroxy-2-propyl)benzene with a selectivity of about 90%. The subsequent operation was performed as in EXAMPLE 3 to yield 1,4-bis(2-chloro-2-propyl)benzene at the end. The purity determined by NMR was 95%. The ultimate yield was 45%; (EXAMPLE 5) The target compound was produced as in EXAMPLE 3 except that the aqueous solution of 1 wt% sodium hydroxide was first added and the aqueous solution of 25 wt% sodium hydroxide was added in an amount of 0.04 kg after the confirmation that the aqueous layer showed acidic pH. The alcoholization provided 1,4-bis(2-hydroxy-2-propyl)benzene with a selectivity of about 90%. The subsequent operation was performed as in EXAMPLE 3 to yield 1,4-bis(2-chloro-2-propyl)benzene at the end. The purity determined by NMR was 95%. The ultimate yield was 45%.
References:
EP1553072,2005,A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 11-12