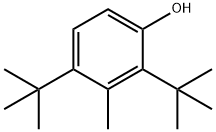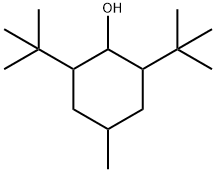
2,6-Bis-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexanol synthesis
- Product Name:2,6-Bis-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexanol
- CAS Number:163119-16-2
- Molecular formula:C15H30O
- Molecular Weight:226.4
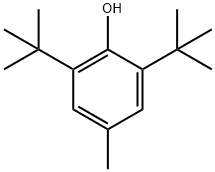
128-37-0
1098 suppliers
$5.00/25g

163119-16-2
71 suppliers
$9.00/1g
Yield:163119-16-2 95.3%
Reaction Conditions:
with palladium on activated charcoal;potassium tert-butylate;hydrogen in ethyl acetate at 90; under 3000.3 Torr; for 0.25 h;Autoclave;Temperature;Pressure;
Steps:
1-5 Example 5: This example is different from Example 1 is
In this example, in a 500 ml autoclave, add 150 grams of ethyl acetate and 50 grams of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol at room temperature and stir for 15 minutes until all is dissolved, then add 2.5 grams of palladium carbon and tert-butanol Potassium is 25.5 grams, the autoclave is closed; nitrogen is introduced to fully replace the oxygen in the autoclave to ensure that there is no oxygen and avoid hydrogen explosion, and then hydrogen is introduced. The hydrogenation reaction is carried out at a temperature of 90 and a hydrogen pressure of 0.4Mpa. Stop hydrogenation when hydrogen is no longer absorbed in the kettle, filter out the palladium carbon, add dilute hydrochloric acid solution to the filtrate, adjust to neutral, and separate the lower water.The upper layer was first at normal pressure and then evaporated to dry the ethyl acetate under reduced pressure to obtain a colorless and transparent liquid of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexanol.The yield was 95.3%, and the gas chromatography content was 96.5%.
References:
CN111348986,2020,A Location in patent:Paragraph 0017-0028

23790-39-8
37 suppliers
$60.00/1g

163119-16-2
71 suppliers
$9.00/1g