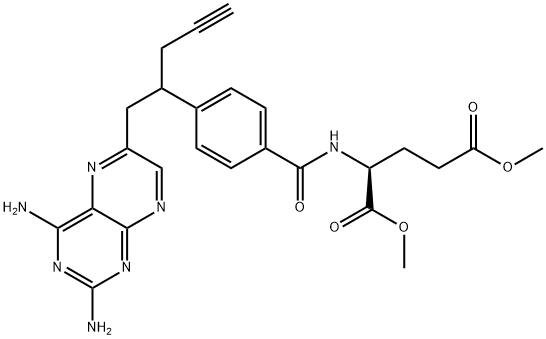
L-GlutaMic acid, N-[4-[1-[(2,4-diaMino-6-pteridinyl)Methyl]-3-butyn-1-yl]benzoyl]-, 1,5-diMethyl ester synthesis
- Product Name:L-GlutaMic acid, N-[4-[1-[(2,4-diaMino-6-pteridinyl)Methyl]-3-butyn-1-yl]benzoyl]-, 1,5-diMethyl ester
- CAS Number:374777-77-2
- Molecular formula:C25H27N7O5
- Molecular Weight:505.53
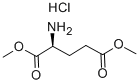
23150-65-4
328 suppliers
$6.00/10g
![Benzoic acid, 4-[1-[(2,4-diamino-6-pteridinyl)methyl]-3-butyn-1-yl]-](/CAS2/GIF/146464-93-9.gif)
146464-93-9
43 suppliers
inquiry
![L-GlutaMic acid, N-[4-[1-[(2,4-diaMino-6-pteridinyl)Methyl]-3-butyn-1-yl]benzoyl]-, 1,5-diMethyl ester](/CAS/GIF/374777-77-2.gif)
374777-77-2
14 suppliers
inquiry
Yield:374777-77-2 50%
Reaction Conditions:
with (benzotriazo-1-yloxy)tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate;triethylamine in DMF (N,N-dimethyl-formamide) at 20 - 25; for 3 h;
Steps:
1
EXAMPLE 1; FIG. 4 shows a synthetic scheme useful in preparing 10-propargyl-10-dAM in accordance with the invention. A mixture of 60% NaH in oil dispersion (1.06 g, 26.5 mmol) in 18 mL of sieve-dried THF was cooled to 0° C. The cold mixture was treated with a solution of homoterephthalic acid dimethyl ester (5.0 g, 24 mmol. compound 1 in FIG. 4) in dry THF (7 mL), and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour at 0° C. Propargyl bromide (26.4 mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at 0° C. for an additional 1 hour, and then at room temperature for 16 hours. The resulting mixture was treated with 2.4 mL of 50% acetic acid and then poured into 240 mL of water. The mixture was extracted with ether (2×150 mL). The ether extracts were combined, dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated to an orange-yellow oil. Chromatography on silica gel (600 mL of 230-400 mesh) with elution by cyclohexane-EtOAc (8:1) gave the product α-propargylhomoterephthalic acid dimethyl ester (compound 2) as a white solid (4.66) which appeared by TLC (cyclohexane-EtOAc, 3:1) to be homogeneous. Mass spectral data on this product, however, showed it to be a mixture of the desired product 2, and the dipropargylated compound. No starting material 1 was detected. HPLC shows the ratio of mono- to di-propargylated products to be about 3:1. Since the dipropargylated product, unlike compound 1, cannot produce an unwanted coproduct in the next step of the reaction, this material was suitable for conversion to compound 3. Absence of starting compound 1 in the product used to proceed in the synthesis is very important in order to avoid the sequential formation of 10-dAM during the transformations lading to the final product, because complete removal from 10-dAM from 10-propargyl-1-dAM is very difficult. A mixture was formed by combining 0.36 g of a 60% NaH (9 mmol) in oil dispersion with 10 mL of dry DMF and cooled to 0-5° C. The cold mixture was treated drop-wise with a solution of the product of the first reaction (compound 2) (2.94 g, 12 mmol) in 10 mL dry DMF and then stirred at 0° C. for 30 minutes. After cooling to -25° C., a solution of 2,4,diamino-6-(bromomethyl)-pteridine hydrobromide-0.2 2-propanol (1.00 g, 2.9 mmol) in 10 mL dry DMF was added drop-wise while the temperature was maintained near -25° C. The temperature of the stirred mixture was allowed to rise to -10° C. over a period of 2 hours. After an additional 2 hours at -10° C., the temperature was allowed to rise to 20° C.; stirring at room temperature was continued for 2 hours longer. The reaction was then adjusted to pH 7 by addition of solid CO2, After concentration in vacuo to remove solvent, the residue was stirred with diethyl ether and the ether insoluble material was collected, washed with water, and dried in vacuo to give 1.49 g of a crude product. This crude product was dissolved in CHCl3-MeOH (10:1) for application to a silica gel column. Elution by the same solvent system afforded 10-propargyl-10-carbomethoxy-4-deoxy-4-amino-10-deazapteroic acid methyl ester (compound 3) which was homogenous to TLC in 40% yield (485 mg). A stirred suspension of compound 3 (400 mg, 0.95 mmol) in 2-methoxyethanol (5 mL) was treated with water (5 mL) and then 10% sodium hydroxide solution (3.9 mL). The mixture was stirred as room temperature for 4 hours, during which time solution occurred. The solution was adjusted to pH 8 with acetic acid and concentrated under high vacuum. The resulting residue was dissolved in 15 mL of water and acidified to pH 5.5-5.8 resulting in formation of a precipitate. The precipitate was collected, washed with water and dried in vacuo to recover 340 mg of compound 4 (91% yield). HPLC analysis indicated a product purity of 90%. Compound 4 (330 mg) was decarboxylated by heating in 15 mL DMSO at 115-120° C. for 10 minutes. A test by HPLC after 10 minutes confirmed that the conversion was essentially complete. DMSO was removed by distillation in vacuo (bath at 40° C.). The residue was stirred with 0.5 N NaOH to give a clear solution, Acidification to pH 5.0 with 1N HCl gave 10-propargyl-4-deoxy-4-amino-10-deazapteroic acid (compound 5) as a yellow solid in 70% yield. HPLC indicated product purity at this stage as 90%. Compound 5 (225 mg, 0.65 mmol) was coupled with dimethyl L-glutamate hydrochloride (137 mg, 0.65 mmol) using BOP reagent (benzotriazole-1-yloxytris(dimethylamino) phosphonium hexafluorophosphate (287 mg, 0.65 mmol, Aldrich Chemical Co.) in DMF (10 mL) containing triethylamine (148 mg, 1.46 mmol). The mixture was stirred for 3 hours at 20-25° C. and then evaporated to dryness. The residue was stirred with water, and the water-insoluble crude product was collected and dried in vacuo. The crude product (350 mg) was purified by silica gel chromatography with elution by CHCl3-MeOH (10:1) containing triethylamine (0.25% by volume) to recover 165 mg of 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin dimethyl ester (compound 6, 50% yield) which was homogeneous to TLC (CHCl3-MeOH 5:1). Compound 6 (165 mg, 0.326 mmol) was suspended in 10 mL stirred MeOH to which 0.72 mL (0.72 meq) 1N NaOH was added. Stirring at room temperature was continued until solution occurred after a few hours. The solution was kept at 20-25° C. for 8 hours, then diluted with 10 mL water. Evaporation under reduced pressure removed the methanol, and the concentrated aqueous solution was left at 20-25° C. for another 24 hours. HPLC then showed the ester hydrolysis to be complete. The clear aqueous solution was acidified with acetic acid to pH 4.0 to precipitate 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin as a pale yellow solid, The collected, water washed and dried in vacuo product weighed 122 mg (79% yield). Assay by elemental analysis, proton NMR and mass spectroscopy were entirely consistent with the assigned structure. HPLC analysis indicated purity of 98% and established the product to be free of 10-deazaaminopterin.
References:
US2005/267117,2005,A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 3; 4; Sheet 2
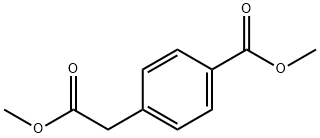
52787-14-1
144 suppliers
$12.00/1g
![L-GlutaMic acid, N-[4-[1-[(2,4-diaMino-6-pteridinyl)Methyl]-3-butyn-1-yl]benzoyl]-, 1,5-diMethyl ester](/CAS/GIF/374777-77-2.gif)
374777-77-2
14 suppliers
inquiry
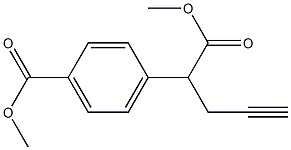
146464-90-6
64 suppliers
inquiry
![L-GlutaMic acid, N-[4-[1-[(2,4-diaMino-6-pteridinyl)Methyl]-3-butyn-1-yl]benzoyl]-, 1,5-diMethyl ester](/CAS/GIF/374777-77-2.gif)
374777-77-2
14 suppliers
inquiry
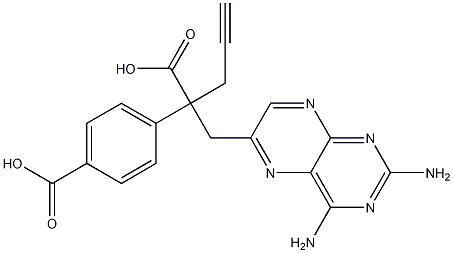
146464-92-8
31 suppliers
$505.42/5MG
![L-GlutaMic acid, N-[4-[1-[(2,4-diaMino-6-pteridinyl)Methyl]-3-butyn-1-yl]benzoyl]-, 1,5-diMethyl ester](/CAS/GIF/374777-77-2.gif)
374777-77-2
14 suppliers
inquiry
![6-Pteridinepropanoic acid, 2,4-diaMino-α-[4-(Methoxycarbonyl)phenyl]-α-2-propyn-1-yl-, Methyl ester](/CAS/20150408/GIF/146464-91-7.gif)
146464-91-7
17 suppliers
inquiry
![L-GlutaMic acid, N-[4-[1-[(2,4-diaMino-6-pteridinyl)Methyl]-3-butyn-1-yl]benzoyl]-, 1,5-diMethyl ester](/CAS/GIF/374777-77-2.gif)
374777-77-2
14 suppliers
inquiry