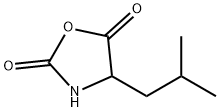
4-isobutyloxazolidine-2,5-dione synthesis
- Product Name:4-isobutyloxazolidine-2,5-dione
- CAS Number:51248-35-2
- Molecular formula:C7H11NO3
- Molecular Weight:157.17
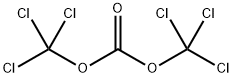
32315-10-9
411 suppliers
$10.00/1g
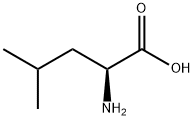
328-39-2
358 suppliers
$10.00/25g

51248-35-2
43 suppliers
$22.00/1g
Yield:51248-35-2 95%
Reaction Conditions:
with α-pinene in tetrahydrofuran;Inert atmosphere;
Steps:
3 2.3. Synthesis of leucine N-carboxyanhydride (Leu-NCA)
This NCA monomer was prepared as described by Smeets et al. [17] Leucine (8.02 g, 61.0 mmol) was suspended in anhydrous THF (100 mL).
α-pinene (25.0 mL, 157 mmol) and solid triphosgene (6.70 g, 22.2 mmol) were sequentially added under nitrogen atmosphere. The suspension was heated under reflux at 64 °C until it turned yellow and clear (~ 30 min).
The solution was then cooled down to room temperature and bubbled with nitrogen following the same procedure described above for the synthesis of γ-benzyl-glutamic acid NCA. The solvent was then removed under reduced pressure to yield a yellow oily residue.
Petroleum ether (300 mL) was added to induce the precipitation of Leu-NCA as a white solid.
This precipitate was filtered, washed with ice-cold petroleum ether (3 * 25 mL), and dried under reduced pressure, to give leucine N-carboxyanhydride (Leu-NCA) as a white solid (7.65 g, 48.6 mmol) with a recovery yield of 95% (mol/mol).
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 6.43 (bs, 1H, NHCH) 4.33 (dd, J = 8.9, 4.0 Hz, 1H, NHCH), 1.82 (m, 2H, CH2CH), 1.68 (m, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 0.99 (m, 6H, CH(CH3)2).
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.25 (1C, C(O)CH), 153.38 (1C, C(O)NH), 56.33 (1C, CHCH2), 40.88 (1C, CH2CH), 25.06 (1C, CH(CH3)2), 22.79 and 21.59 (2C, CH(CH3)2).
FT-IR: υ 2960, 1798, 1750, 1468, 1117, 1079 cm-1.
References:
Brunato, Silvia;Mastrotto, Francesca;Bellato, Federica;Bastiancich, Chiara;Travanut, Alessandra;Garofalo, Mariangela;Mantovani, Giuseppe;Alexander, Cameron;Preat, Veronique;Salmaso, Stefano;Caliceti, Paolo [Journal of Controlled Release,2021,vol. 335,p. 21 - 37]

61-90-5
775 suppliers
$10.00/25G

32315-10-9
411 suppliers
$10.00/1g

51248-35-2
43 suppliers
$22.00/1g
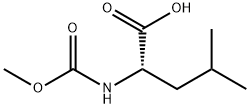
117919-56-9
4 suppliers
inquiry

51248-35-2
43 suppliers
$22.00/1g
