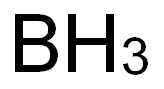
Boron synthesis
- Product Name:Boron
- CAS Number:7440-42-8
- Molecular formula:B
- Molecular Weight:10.81
B2O3 + 3Ca → 2B + 3CaO
The metal is obtained as a black amorphous product.
2BCl3 + 3H2 → 2B + 6HCl
High purity grade boron may be prepared by such hydrogen reduction at high temperatures using a hot filament.
Electrolytic reduction and thermal decomposition have not yet been applied in large scale commercial methods. Electrolysis of alkali or alkaline earth borates produces boron in low purity. Electrolytic reduction of fused melts of boron trioxide or potassium tetrafluroborate in potassium chloride yield boron in high purity. Also, boron tribromide or boron hydrides may be thermally dissociated by heating at elevated temperatures.
Impurities from boron may be removed by successive recrystallization or volatilization at high temperatures. Removal of certain impurities such as oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen or carbon from boron are more difficult and involve more complex steps.
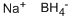
16940-66-2
8 suppliers
$21.21/100ml
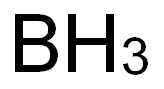
7440-42-8
335 suppliers
$43.00/10g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with sodium azide;dinitrogen monoxide in water;Kinetics;other Radiation; N2O satd. soln. of NaN3 and NaBH4 at pH 11.1 (molar ratio 200:3), pulse radiolysis;
References:
Horii, Hideo;Taniguchi, Setsuo [Journal of the Chemical Society. Chemical communications,1986,# 12,p. 915 - 916]