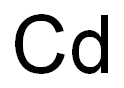
CADMIUM synthesis
- Product Name:CADMIUM
- CAS Number:7440-43-9
- Molecular formula:Cd
- Molecular Weight:112.41
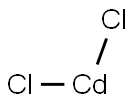
10108-64-2
197 suppliers
$10.00/5g
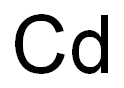
7440-43-9
243 suppliers
$34.00/50g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in not givenElectrolysis; electrodeposition of Cd from EDTA/Cd salt electrolyte (100 - 200 A/m**2);
References:
Kovyazina, L. I.;Timanyuk, V. M.;Ovchinnikova, T. M. [Journal of applied chemistry of the USSR,1982,vol. 55,p. 1096 - 1098][Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii (Sankt-Peterburg, Russian Federation),1982,vol. 55,p. 1183 - 1185]
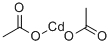
543-90-8
143 suppliers
$60.00/25 gm
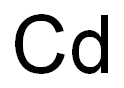
7440-43-9
243 suppliers
$34.00/50g
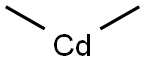
506-82-1
25 suppliers
$476.00/5g
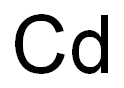
7440-43-9
243 suppliers
$34.00/50g