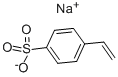
Sodium p-styrenesulfonate synthesis
- Product Name:Sodium p-styrenesulfonate
- CAS Number:2695-37-6
- Molecular formula:C8H7NaO3S
- Molecular Weight:206.19
54322-31-5
46 suppliers
$210.00/1g

2695-37-6
385 suppliers
$7.00/10g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with sodium hydroxide;sodium nitrite in water at 90; for 4 h;Autoclave;Large scale;
Steps:
6
A stainless steel reactor having a jacket and equipped with a stirrer was charged with 750 kg of a 11.7 wt % aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and 2.5 kg of sodium nitrite, and heated up to 90° C. At that temperature, 2,000 kg of a 73 wt % aqueous p-β-bromoethylbenzenesulfonic acid solution obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 and 950 kg of a 48 wt % aqueous sodium hydroxide solution were separately introduced at a constant rate over 4 hours (the sodium hydroxide concentration in the reactor gradually increased from 11.66 wt % at the start of the reaction to 14.69 wt % after 4 hours from the start of the reaction (at the end of the reaction), and the p-β-bromoethylbenzenesulfonic acid concentration gradually increased from 0.00 wt % at the start of the reaction to 39.43 wt % after 4 hours from the start of the reaction (at the end of the reaction)), followed by reaction crystallization of sodium p-styrenesulfonate. A slurry thereof was cooled to 40° C. over 2 hours. Thereafter, solid-liquid separation was performed by centrifugation. Separation was extremely easy, and 940 kg of a high-purity wet cake having a sodium styrenesulfonate content of 88.5 wt % was obtained by shaking for 30 minutes. Using a uniaxial screw blender, this wet cake was forcedly fluidized at 40° C. and a rotational speed of 20 rpm for 60 minutes. Sodium p-styrenesulfonate obtained had a median diameter of 63.1 μm, a content of small particles less than 10.00 μm of 1.50%, a water content of 7.1 wt %, a repose angle of 47 degrees and a dissolution time in water of 160 seconds. This was slightly inferior in fluidity to Comparative Example 8, but far superior in solubility. It is therefore clear that this is excellent in the balance between fluidity and solubility.Incidentally, the numerical values of sodium bromide and organic impurities such as isomers are as shown in Table 2. Further, for sodium p-styrenesulfonate obtained in Example 6, a Microtrac particle size distribution is shown in FIG. 4, an electron microscope image is shown in FIG. 5, and HPLC chromatogram is shown in FIG. 8.
References:
TOSOH ORGANIC CHEMICAL CO., LTD.;Ozoe, Shinji;Yamanoi, Kenichi;Matsunaga, Hideaki US2015/246876, 2015, A1 Location in patent:Paragraph 0269; 0270; 0271