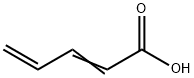
TRANS-2,4-PENTADIENOIC ACID synthesis
- Product Name:TRANS-2,4-PENTADIENOIC ACID
- CAS Number:626-99-3
- Molecular formula:C5H6O2
- Molecular Weight:98.1
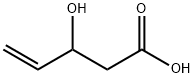
81357-28-0
5 suppliers
inquiry

626-99-3
93 suppliers
$41.00/100mg
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with 3-hydroxypent-4-enoate dehydrataseEnzymatic reaction;
Steps:
1.2R
Figure 2 also shows pathways derived from the 4-hydroxy 2- oxovalerate intermediate. 4-hydroxy 2-oxovalerate is dehydrated to 2-oxopent-4- enoate (also called 2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate) by 4-hydroxy-2-oxopentanoate dehydratase, also called 2-oxopent-4-enoate hydratase (2C). An alcohol dehydrogenase with 2-oxopent-4-enoate reductase activity forms 2-hydroxypent-4- enoate. Multiple enzymatic routes are shown in Fig 2 for converting 2-hydroxypent- 4-enoate to butadiene and butadiene precursors. One route entails isomerization of 2-hydroxypent-4-enoate to 5-hydroxypent-2-enoate (2E). This intermediate is then decarboxylated to 3-buten-l-ol (2P) and dehydrated to butadiene (2Q). Alternately, the 5-hydroxypent-2-enoate is further dehydrated to pentadienoate (2F) and subsequently decarboxylated to butadiene (2G). In yet another pathway, the 5- hydroxypent-2-enoate intermediate is activated to its corresponding acyl-CoA (21), dehydrated to pentadienoyl-CoA (2N), and further hydrolyzed to 2,4-pentadienoate (2J). Yet another set of pathways results when 2-hydroxypent-4-enoate is converted to 3-hydroxypent-4-enoate (abbreviated as 3FTPE) by a mutase (2H). Direct conversion of 3HPE to butadiene is catalyzed by an oxidative decarboxylase (2K). The two-step conversion of 3HPE to butadiene via 2,4-pentadienoate entails dehydration (2R) followed by decarboxylation (2G). In yet another route, 3HPE is activated to its acyl-CoA by a CoA synthetase or transferase. Conversion of 3-HPE- CoA to 2,4-pentadienoyl-CoA is catalyzed by an acyl-CoA dehydratase (20) or an isomerase and dehydratase (2M, 2 ). Useful products shown in Figure 2 include butadiene, 3-buten-l-ol, 4-hydroxy-2-oxovaIerate, 2-oxopent-4-enoate, 2- hydroxypent-4-enoate, 4-hydroxypent-2-enoate, 3HPE and 2,4-pentadienoate. Enzymes for catalyzing each step are described below.
References:
GENOMATICA, INC.;CULLER, Stephanie J.;BURK, Mark J.;OSTERHOUT, Robin E.;PHARKYA, Priti WO2016/4334, 2016, A1 Location in patent:Paragraph 0015; 00101

141-82-2
760 suppliers
$5.00/25g

107-02-8
4 suppliers
$38.60/4s8501

626-99-3
93 suppliers
$41.00/100mg
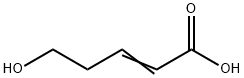
23251-44-7
0 suppliers
inquiry

626-99-3
93 suppliers
$41.00/100mg
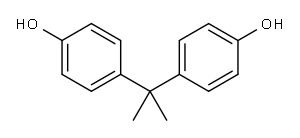
80-05-7
681 suppliers
$13.00/100g

3588-17-8
144 suppliers
$32.89/1g

626-99-3
93 suppliers
$41.00/100mg
20406-62-6
5 suppliers
inquiry

626-99-3
93 suppliers
$41.00/100mg