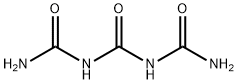
triuret synthesis
- Product Name:triuret
- CAS Number:556-99-0
- Molecular formula:C3H6N4O3
- Molecular Weight:146.1
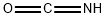
75-13-8
88 suppliers
inquiry
57-13-6
702 suppliers
$5.00/5g
108-19-0
361 suppliers
$14.14/5gm:

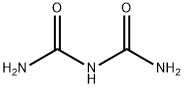
556-99-0
48 suppliers
$100.00/50mg
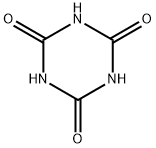
108-80-5
483 suppliers
$6.00/25g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
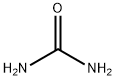
Stage #1:isocyanic acid;urea at 140 - 160;
Stage #2: with ammonia in water at 50 - 100; under 760.051 Torr; for 0.5 h;Product distribution / selectivity;
Steps:
1
Example 1Urea (produced by SigmaAldrich Co.) was dissolved in a urea melter at 140° C., and then injected to a thermal decomposition reactor at a predetermined loading rate. The temperature of the thermal decomposition reactor was maintained at 160° C. The thermal decomposition reactor was a continuous-type reactor consisting of three reactors connected in series. The air was injected to the thermal decomposition reactor through a lower portion of the thermal decomposition reactor in an amount of 1 mole of air per 1 mole of urea. Therefore, when the air passed out from the thermal decomposition reactor, the air included ammonia and unreacted isocyanic acid. The resultant air was transferred to the urea melter so that the unreacted isocyanic acid reacted with urea. The product obtained from thermal decomposition reactor was continuously injected to a cooling tank to precipitate a crude biuret crystal. At this time, the average residual time of the product in the cooling tank was controlled to be about 150 minutes. The product obtained from the thermal decomposition reactor was recovered to measure a conversion rate of urea. As a result, the conversion rate of urea was about 35%. The product of the thermal decomposition reaction was identified using liquid chromatography. Based on 100 parts by weight of urea injected, the amount of biuret was 29.8 parts by weight, the amount of urea was 50.9 parts by weight, the amount of cyanuric acid was 3.0 parts by weight, and the amount of triuret was 1.3 parts by weight. That is, the total weight of biuret, urea, cyanuric acid, and triuret was 85 parts by weight. The 100 parts by weight of urea injected minus the total weight of the generated product was 15 parts by weight, and such loss was caused since the unreacted isocyanic acid and the ammonia escaped from the thermal decomposition reactor. Hereinafter, the amount of each component was measured in a unit of parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of urea injected.85 parts by weight of water was injected to 85 parts by weight of the thermal decomposition product and cooled to 15° C. while mixing, and then the reaction product was centrifugally dehydrated. A dehydrated cake containing crystal was washed with 15 parts by weight of water to remove the remaining urea. As a result, the amount of the cake obtained was 28 parts by weight. The cake excluding water was identified using a liquid chromatography. As such, the amount of biuret was 85.7 wt %, the amount of urea was 1.8 wt %, the amount of cyanuric acid was 8.9 wt %, and the amount of triuret was 3.6 wt %. In addition, the mother liquor obtained by dehydrating was identified using liquid chromatography. As a result, the amount of biuret was 4.1 wt %, the amount of urea was 35.5 wt %, the amount of cyanuric acid was 0.3 wt %, the amount of triuret was 0.2 wt % and the amount of water was 59.9 wt %. The mother liquor obtained by dehydrating was heated at a temperature of 110 to 130° C. under a pressure of 200 mmHg and then reinjected to the urea melter. The composition of the resultant solution right before being reinjected to the urea melter was identified. As a result, the amount of biuret was 12.2 wt %, the amount of urea was 86.5 wt %, the amount of cyanuric acid was 0.9 wt %, and the amount of triuret was 0.4 wt %. Then, urea was additionally injected to the urea melter. Through such processes, in the composition of a thermal decomposition product of the thermal decomposition reactor, a conversion rate of biuret was increased to reach an equilibrium state. In the equilibrium state, the composition of the thermal decomposition product included 37.3 wt % of biuret, 57 wt % of urea, 4.2 wt % of the cyanuric acid, and 1.5 wt % of triuret.72 parts by weight of water was further added to a dehydrated crude biuret cake, and then 2.5 mole that is equivalent to 1 mole of NaOH aqueous solution with respect to the mole of the cyanuric acid was added thereto and heated at 70° C. for 20 minutes to decompose all of the thermal decomposition product. At this time, the cyanuric acid reacted with the NaOH aqueous solution to form a cyanuric acid salt which is very soluble in water. The resultant solution prepared by dissolving with the NaOH aqueous solution was injected to a cooling tank and cooled to 10° C. At this time, biuret was crystallized and precipitated. The resultant solution was dehydrated using a centrifuge, and washed with water to obtain a purified biuret. As a result, as high as 99.5 weight percent biuret was obtained.Furthermore, the dehydrated mother liquor was injected to a neutralizing tank and then HCL was added thereto until the pH of the solution in the neutralizing tank was decreased to 4. At this time, a cyanuric acid was precipitated. The resultant solution was dehydrated at 50° C. and washed with water to obtain a purified cyanuric acid. At this time, as high as 99 weight percent cyanuric acid was obtained.; Comparative Example 1122 parts by weight of water, and 28.6 parts by weight of ammonia (19% ammonia water) were added to 85 parts by weight of a crude biuret cake obtained through thermal decomposing, cooling, and filtering processes according to Example 1 and then mixed together. The resultant solution was heated to a temperature of 90° C. to 100° C. and left to sit for 30 minutes, and then, cooled to 50° C. and the pressure in the reactor used was gradually reduced was reduced to atmospheric pressure to precipitate a biuret crystal. At this time, a cyanuric acid was combined with ammonia and as such became soluble with respect water. Therefore, the cyanuric acid was not precipitated. The resultant slurry was filtered and the mother liquor cake was washed with water and dried. The dried product was identified using liquid chromatography. As a result, the amount of biuret was 98%, the amount of urea was 0.5%, the amount of the cyanuric acid was 0.3%, and the amount of triuret was 1.2%.
References:
Lee, Chun Hyuk;Shin, Min Seung;Lee, Hoon US2008/39623, 2008, A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 5

108-19-0
361 suppliers
$14.14/5gm:

57-13-6
702 suppliers
$5.00/5g

556-99-0
48 suppliers
$100.00/50mg
69-93-2
227 suppliers
$30.00/20mg

556-99-0
48 suppliers
$100.00/50mg
![Ethanamine, N-[(3,5-dichlorophenyl)methylene]-2,2-diethoxy-](/CAS/20210305/GIF/1000210-73-0.gif)
1000210-73-0
0 suppliers
inquiry

556-99-0
48 suppliers
$100.00/50mg

6498-10-8
0 suppliers
inquiry

556-99-0
48 suppliers
$100.00/50mg