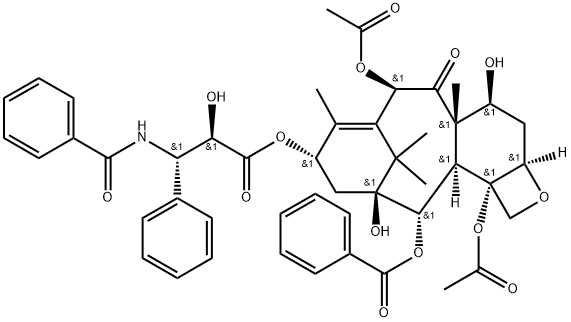
파클리탁셀
|
|
파클리탁셀 속성
- 녹는점
- 213 °C (dec.)(lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 774.66°C (rough estimate)
- 알파
- D20 -49° (methanol)
- 밀도
- 0.200
- 굴절률
- -49 ° (C=1, MeOH)
- 인화점
- 9℃
- 저장 조건
- 2-8°C
- 용해도
- 메탄올: 50 mg/mL, 투명, 무색
- 물리적 상태
- 가루
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 11.90±0.20(Predicted)
- 색상
- 하얀색
- 수용성
- 0.3mg/L(37 ºC)
- 최대 파장(λmax)
- 227nm(MeOH)(lit.)
- Merck
- 14,6982
- BRN
- 1420457
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 강한 산화제와 호환되지 않습니다. 타기 쉬운.
- InChIKey
- RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-N
- LogP
- 3.950 (est)
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 33069-62-4(CAS DataBase Reference)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | Xn | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 37/38-41-42/43-62-68-40-48-20/21/22-68/20/21/22 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 22-26-36/37/39-45 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | 1544 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | DA8340700 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 10-21 | ||
| 위험 등급 | 6.1(b) | ||
| 포장분류 | III | ||
| HS 번호 | 29329990 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 33069-62-4(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LD50 intraperitoneal in mouse: 128mg/kg |
파클리탁셀 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Paclitaxel, a natural product isolated from the bark of the Pacific yew, is effective in treating refractory metastatic ovarian cancer. Unlike any other antineoplastic agents, paclitaxel appears to have several possible mechanisms of action, including an antimicrotubule action through the promotion of tubulin polymerization and stabilization of microtubules, thereby, halting mitosis and promoting cell death. The supply of paclitaxel is limited by its low natural abundance and currently it is being manufactured by a semi-synthetic route from deacetylbaccatin Ⅲ that is isolated from the needles of the yew tree. Recent completion of two total syntheses of taxol conquered the structural complexity of the title compound and may be useful in obtaining certain closely related analogs, some of which have been found to have antitumor activity. Paclitaxel has potential uses in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, and malignant melanoma.화학적 성질
White Powder물리적 성질
Appearance: Odorless and tasteless white or kind of white crystal powder. Solubility: Poorly soluble in water but slightly soluble in ether. Soluble in methanol, acetonitrile, chloroform, acetone, and other organic solvents. Melting point: 213–216?°C. Specific optical rotation: ?49° (C?=?1, MeOH); Curl: 20° to D?=?49.0–55.0° (10?mg/mL of methanol solution) in anhydrous dry goods without solvents.역사
The toxic ingredients in branches and leaves of Taxus chinensis were separated in 1856 and named “taxine,” which was identified as a kind of white alkaloid’s component. Currently, among all the antitumor drugs, the sale of paclitaxel becomes the first in the world as a well-recognized anticancer drug with potent broad-spectrum activity. In October of 1995, China became the second country with formal production of paclitaxel and its injection in the world. The achievement was gained under the unremitting efforts of researchers in the Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences.용도
Paclitaxel is an antineoplastic that used to treat patients with lung, ovarian, breast cancer, head and neck cancer, and advanc ed forms of Kaposi's sarcoma. Paclitaxel is a mitotic inhibitor used in cancer chemotherapy. It is also used in the study of structure and function of microtubles into tubulin.제조 방법
The total synthesis of paclitaxel (Taxol) is described. Double Rubottom oxidation of the bis(silyl enol ether) derived from a tricarbocyclic diketone effectively installed a bridgehead olefin and C-5/C-13 hydroxy groups in a one-step operation. The novel Ag-promoted oxetane formation smoothly constructed the tetracyclic framework of paclitaxel.Total Synthesis of Paclitaxel
The biosynthesis of paclitaxel involves the condensation of the three isoprenyl diphosphate (IPP) units with dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). Plants are unique in producing IPP and DMAPP by both the mevalonic pathway (MVA) in the cytosol or via the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway in the plastids.
Paclitaxel: biosynthesis, production and future prospects
Indications
Paclitaxel (Taxol) is a highly complex, organic compound isolated from the bark of the Pacific yew tree. It binds to tubulin dimers and microtubulin filaments, promoting the assembly of filaments and preventing their depolymerization. This increase in the stability of microfilaments results in disruption of mitosis and cytotoxicity and disrupts other normal microtubular functions, such as axonal transport in nerve fibers. The major mechanism of resistance that has been identified for paclitaxel is transport out of tumor cells, which leads to decreased intracellular drug accumulation. This form of resistance is mediated by the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein.일반 설명
Paclitaxel (commercial name, Taxol) a complex diterpene alkaloid isnaturally obtained from Taxus species (family Taxaceae). Paclitaxel has been provedas highly effective in the treatment of various types of cancers, since it acts as amicrotubule-stabilizing agent to protect against disassembly. Paclitaxel was developed by the National Cancer Institute, USA, as a drug for cancer therapy andused for the treatment of refractory ovarian cancer, metastatic breast and lung cancer,and Kaposi’s sarcoma (Srivastava et al. 2005). The natural source of paclitaxelis the bark of several Taxus species; however, the cost of extraction is very highsince the concentration of paclitaxel accumulation is very low (0.02% of dry weight)and also entails the destruction of natural resources (Cusido et al. 2014). Eventhough, paclitaxel can be chemically synthesized, but this process is not commerciallyviable. Plant cell cultures have been developed for the production of paclitaxelby Phyton Biotech in 1995, and in 2004 the FDA has approved the use of plantculture supply of paclitaxel/Taxol (Leone and Roberts 2013).공기와 물의 반응
May be sensitive to prolonged exposure to moisture. .건강위험
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.화재위험
Flash point data for Paclitaxel are not available. Paclitaxel is probably combustible.생물학적 활성
Antitumor agent; promotes and stabilizes tubulin polymerization, causing cell cycle arrest. Induces autocatalytic activation of caspase-10 in CCRF-HSB-2 cells, triggering apoptosis.Mechanism of action
Paclitaxel is currently the only known drug that can promote microtubule polymerization and stabilize polymerized microtubules. It can only form on polymerized microtubules and does not react with non-polymerized microtubule protein dipolymers. After coming in contact with paclitaxel, cells will accumulate a large number of microtubules within themselves, which disrupts cell functions, especially cell division, which is forced to cease at the mitotic stage.Pharmacology
Paclitaxel is mainly used for the treatment of ovarian cancer and breast cancer. The mechanism of it includes:1. The effects on cell microtubules/tubulin: Inhibition of microtubule depolymerization results in abnormal micro tube bundle arrangement and makes the spindle lose normal function and then induces cell death.
2. In the absence of bird triphosphate (GTP) and microtubule associated protein (MAP), it induces cells to form microtubule lack of function.
3. It significantly sensitized cancer cells to radiotherapy through blocking the cell cycle in the stage of G2 and M .
Paclitaxel is mainly metabolized through the liver and enters into the intestine with bile and then eliminated from the body by the feces (90%).
Clinical Use
Paclitaxel is among the most active of all anticancer drugs, with significant efficacy against carcinomas of the breast, ovary, lung, head, and neck. It is combined with cisplatin in the therapy of ovarian and lung carcinomas and with doxorubicin in treating breast cancer.부작용
Myelosuppression is the major side effect of paclitaxel. Alopecia is common, as is reversible dose-related peripheral neuropathy. Most patients have mild numbness and tingling of the fingers and toes beginning a few days after treatment. Mild muscle and joint aching also may begin 2 or 3 days after initiation of therapy. Nausea is usually mild or absent. Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur. Cardiovascular side effects, consisting of mild hypotension and bradycardia, have been noted in up to 25% of patients.Toxicology
The major toxicity seen with paclitaxel is a dose-limitingmyelosuppression that normally presents as neutropenia. Thepreviously mentioned hypersensitivity reactions occur but aregreatly reduced by antihistamine pretreatment. Interactionwith the axonal microtubules such as that seen for the vincasalso occurs and leads to numbness and paresthesias (abnormaltouch sensations including burning and prickling). Theagent is also available as an albumin-bound formulation(Abraxane) to eliminate the need for the solubilizing agentsassociated with the hypersensitivity reactions. Other adverseeffects include bradycardia, which may progress to heartblock, alopecia, mucositis, and/or diarrhea. Paclitaxel producesmoderate nausea and vomiting that is short-lived.신진 대사
Paclitaxel is highly plasma protein bound (>90%) anddoes not penetrate the CNS. Metabolism involves CYPmediatedoxidation to give 6 -hydroxypaclitaxel (CYP2C8)and para hydroxylation of the phenyl group attached to the3'-position (CYP3A4). The 6α-hydroxy metabolite normallypredominates, but the para hydroxy metabolite mayoccur to a greater degree in those patients with liver diseaseor when CYP3A4 has been induced. Both metabolites areless active than the parent and do not undergo phase II conjugationreactions. Elimination occurs primarily in the feces,and the elimination half-life is 9 to 50 hours depending onthe infusion period.주의 사항
1. Hermatological toxicity: the main factor in increased dosage limitations; when white blood cells are below 1500/mm3, supplement with G-CSF; when platelets are below 30000/mm3, transfuse component blood.2. Allergic reaction: Aside from preconditions, if there are only minor symptoms such as flushed face, skin reactions, slightly increase heart rate, slightly lowered blood pressure, etc., do not stop treatment and decrease injection speed. If there are serious reactions such as hypotension, vascular edema, difficulty breathing, measles, etc., stop treatment and treat accordingly. Patients with serious allergic reactions should not use paclitaxel in the future.
3. Nervous system: Common reactions include numb toes. Approximately 4% patients, especially with high dosage, experience significant sensory and motor difficulty and decreased tendon reflex. There have been individual reports of epilepsy.
4. Cardiovascular: Transient tachycardia and hypotension are common and do not usually require attention. However, monitor closely during first hour of injection. Afterwards, only patients with serious injection difficulty require hourly check-ins.
5. Join and muscle: Approximately half of the patients will experience some joint and muscle pain within the first 2-3 days following injection, which is related to dosage, and usually subsides after a couple days. Patients who are also administered G-CSF will experience heightened muscle pain.
6. Liver and gall: As paclitaxel is mainly excreted through bile, patients with liver and gall diseases must be monitored carefully. Among thousands of cases, 8% of patients experienced increased bilirubin, 23% experienced increased alkaline phosphatase, and 18% experienced increased glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase. However, there is currently no evidence indicating that paclitaxel causes any severe liver damage.
7. Other: Digestive tract reactions are common but rarely severe, with few cases of diarrhea and mucosa infection. Slight alopecia is also common.
참고 문헌
Wani et al.,J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 93,2325 (1971)파클리탁셀 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
실리카겔
Column
초산에틸
규조토
불화 트리에틸암모늄
염화벤조일
hydrogen fluoride
삼차-뷰틸 아이소시아네이트
중탄산나트륨(중조)
4-나이트로벤젠설포닐 염화물
벤즈알데히드디메틸아세탈
트리에틸아민
트리메틸클로로실란
티오페놀
P-톨루엔설폰 산
포타슘터셔리부톡사이드
불산
준비 용품
파클리탁셀 공급 업체
글로벌( 1098)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing Mesochem Technology Co.,Ltd | +8613651027935 |
rachel@mesochem.com | China | 191 | 58 |
| Hubei Ipure Biology Co., Ltd | +8613367258412 |
ada@ipurechemical.com | China | 10326 | 58 |
| Hebei baicao biology science and technology co., ltd | +86-19131911055 +8617824879454 |
zhang@hbbocao.com | China | 1035 | 58 |
| Wuhan senwayer century chemical Co.,Ltd | +undefined-27-86652399 +undefined13627115097 |
market02@senwayer.com | China | 885 | 58 |
| Lewoo Pharmatech(Shanghai)Co.,Ltd | +86-15800805830 +86-15800805830 |
miao@lewoopharma.com.cn | China | 156 | 58 |
| Taizhou Creating Bio-pharm co., ltd. | +8613586099526 |
post@creatingbiopharm.com | China | 217 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12468 | 58 |
| Wuhan Haorong Biotechnology Co.,ltd | +8618565342920 |
sales@chembj.net | China | 270 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +undefined18602966907 |
qinhe02@xaltbio.com | China | 1000 | 58 |
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 |
info@fdachem.com | China | 18219 | 58 |
파클리탁셀 관련 검색:
지베렐린산 파클리탁셀
Docetaxel
Docetaxel trihydrate
Irinotecan
Irinotecan hydrochloride
Benzenepropanoic acid, β-aMino-α-hydroxy-, Methyl ester, (αR,βR)-
DIHYDRO CUMINYL ALCOHOL
(-)-PERILLALDEHYDE
(4S,5R)-3-Benzoyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-5-oxazolidinecarboxylic acid
Shikonin
Perillartine
Pterostilbene
ELEUTHEROSIDE B
Murexide
Taxifolin
Perilla oil
CASTICIN