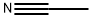아세토나이트릴
|
|
아세토나이트릴 속성
- 녹는점
- ?45 °C (lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 81-82 °C (lit.)
- 밀도
- 0.786 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- 증기 밀도
- 1.41 (vs air)
- 증기압
- 72.8 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
- 굴절률
- n
20/D 1.344(lit.)
- 인화점
- 48 °F
- 저장 조건
- Store at +5°C to +30°C.
- 용해도
- 유기용매: 에 용해됨(lit.)
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 25(at 25℃)
- 물리적 상태
- 액체
- 색상
- <10(APHA)
- Specific Gravity
- approximate 0.78(20/20℃)
- 냄새
- 40ppm에서 감지 가능한 방향족 에테르 같은 냄새
- 상대극성
- 0.46
- 폭발한계
- 3.0-17%(V)
- Odor Threshold
- 13ppm
- 수용성
- 혼용 가능
- 최대 파장(λmax)
- λ: 195 nm Amax: ≤0.12
λ: 200 nm Amax: ≤0.032
λ: 230 nm Amax: ≤0.0044
λ: 235 nm Amax: ≤0.0044
λ: 250 nm Amax: ≤0.0044
λ: 400 nm Amax: ≤0.0044
- Merck
- 14,70
- BRN
- 741857
- Henry's Law Constant
- 7.30 at 5 °C, 8.90 at 10 °C, 11.6 at 15 °C, 14.6 at 20 °C, 17.6 at 25 °C (headspace-GC, Ji and Evans, 2007)
- 노출 한도
- TLV-TWA 70 mg/m3 (40 ppm) (ACGIH and OSHA); STEL 105 mg/m3 (60 ppm) (ACGIH); IDLH 4000 ppm (NIOSH).
- Dielectric constant
- 37.5(21℃)
- 안정성
- 알칼리 금속, 산, 염기, 환원제 및 산화제와 호환되지 않습니다. 가연성이 높습니다.
- LogP
- -0.340
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 75-05-8(CAS DataBase Reference)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | F,Xi,Xn,T | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 11-36-20/21/22-10-36/37/38-23/24/25-41-24-20/22 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 16-36/37-45-36/37/39-27-26-36 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 1993 3/PG 3 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 2 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | AL7700000 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 9 | ||
| 자연 발화 온도 | 524 °C | ||
| 위험 참고 사항 | Highly Flammable/Harmful/Irritant | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| 위험 등급 | 3 | ||
| 포장분류 | II | ||
| HS 번호 | 29269095 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 75-05-8(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LD50 orally in rats: 3800 mg/kg (Smyth) | ||
| IDLA | 137 ppm | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-00067 |
아세토나이트릴 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Acetonitrile is a liquid with an etherlike odor. It is a highly polar, volatile solvent used in many different industrial applications. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical, photographic, chemical, and analytical industries. It is useful as an industrial solvent for the separation of olefins, polymers, spinning fibers, and plastics. Other uses include the extraction and refining of copper and by-product ammonium sulfate; used for dyeing textiles and in coating compositions; used as a stabilizer for chlorinated solvents; manufacture of perfumes and cosmetics; and as a general reagent in a wide variety of chemical processes.화학적 성질
Acetonitrile (methyl cyanide), CH3CN, is a colorless liquid with a sweet, ethereal odor. It is completely miscible with water and its high dielectric strength and dipole moment make it an excellent solvent for both inorganic and organic compounds including polymers. it is commonly applied to the development and manufacturing of cosmetics, pharmaceutical and agricultural products.Acetonitrile has been banned in cosmetic products in the European Economic Area (EEA) since early 2000 and acetone and ethyl are often preferred as safer for domestic use.물리적 성질
Colorless liquid with an ether-like or pungent odor of vinegar. A detection odor threshold concentration of 1,950 mg/m3 (1,161 ppmv) was experimentally determined by Dravnieks (1974). An odor threshold concentration of 13 ppmv was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).용도
Acetonitrile is the simplest organic nitrile. It is a by-product of the manufacture of acrylonitrile, and acetonitrile has, in fact, replaced acrylonitrile. Acetonitrile has a number of uses, primarily as an extraction solvent for butadiene; as a chemical interme- diate in pesticide manufacturing; as a solvent for both inorganic and organic compounds; to remove tars, phenols, and coloring matter from petroleum hydrocarbons not soluble in acetonitrile; in the production of acrylic fi bers; in pharmaceuticals, perfumes, nitrile rubber, and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) resins; in high-performance liquid and gas chro- matographic analysis; and in extraction and refi ning of copper. It is used as a starting material for the produc- tion of acetophenone, alpha-naphthalenacetic acid, thiamine, and acetamidine.주요 응용
Acetonitrile is used as a solvent for polymers, spinning fibers, casting and molding plastics, and HPLC analyses; for extraction of butadiene and other olefins from hydrocarbon streams; in dyeing and coating textiles; and as a stabilizer for chlorinated solvents. It occurs in coal tar and forms as a by-product when acrylonitrile is made. Although acetonitrile is one of the more stable nitriles, it undergoes typical nitrile reactions and is used to produce many types of nitrogencontaining compounds.Acetonitrile also is used as a catalyst and as an ingredient in transitionmetal complex catalysts.생산 방법
Acetonitrile is mainly prepared by dehydration of acetamide (CH3CONH2) with glacial acetic acid (Turner 1950) or by reacting acetic acid with ammonia at 400-500°C in the presence of a dehydration catalyst (Anon 1978).정의
ChEBI: Acetonitrile is a nitrile that is hydrogen cyanide in which the hydrogen has been replaced by a methyl group. It has a role as a polar aprotic solvent and an EC 3.5.1.4 (amidase) inhibitor. It is an aliphatic nitrile and a volatile organic compound.일반 설명
A colorless limpid liquid with an aromatic odor. Flash point 42°F. Density 0.783 c / cm3. Toxic by skin absorption. Less dense than water. Vapors are denser than air.공기와 물의 반응
Highly flammable. Water soluble.반응 프로필
Acetonitrile decomposes when heated to produce deadly toxic hydrogen cyanide gas and oxides of nitrogen. Strongly reactive [Hawley]. May react vigorously with strong oxidizing reagents, sulfuric acid, chlorosulfonic acid, sulfur trioxide, perchlorates, nitrating reagents, and nitric acid. [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 20]. Potentially explosive in contact with nitrogen-fluorine compounds (e.g., tetrafluorourea) [Fraser, G. W. et al., Chem. Comm., 1966, p. 532].건강위험
Acetonitrile liquid or vapor is irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. Acetonitrile has only a modest toxicity, but it can be metabolized in the body to hydrogen cyanide and thiocyanate. Acetonitrile causes delayed symptoms of poisoning (several hours after the exposure) that include, but are not limited to, salivation, nausea, vomiting, anxiety, confusion, hyperpnea, dyspnea, respiratory distress, disturbed pulse rate, unconscious- ness, convulsions, and coma. Cases of acetonitrile poisoning in humans (or, more strictly, of cyanide poisoning after exposure to acetonitrile) are rare but not unknown, by inha- lation, ingestion, and (possibly) by skin absorption. Repeated exposure to acetonitrile may cause headache, anorexia, dizziness, weakness, and macular, papular, or vesicular dermatitis.인화성 및 폭발성
Acetonitrile is a flammable liquid (NFPA rating = 3), and its vapor can travel a considerable distance to an ignition source and "flash back." Acetonitrile vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 4 to 16% (by volume).Hazardous gases produced in a fire include hydrogen cyanide, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and oxides of nitrogen. Carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used for acetonitrile fires.
공업 용도
Acetonitrile is used as a solvent both in industry and in the laboratory, as a rodenticide, and in the denaturation of alcohol. Because of both its solvent properties and volatility, it is useful for extracting vegetable and animal oils and dissolving hydrocarbons, oils, and greases. Acetonitrile is used for the purification of acetylene and artificial textile fibers, and as an antioxidant for rubber (Dequidt et al 1974). It has also been used to extract herbicide residues from soils (Smith 1980), to remove tars and other compounds from petroleum hydrocarbons, and to extract fatty acids from vegetable and fish liver oil. Acetonitrile is now a standard solvent component in reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. It is the starting point for the syntheses of a number of organic compounds such as carboxylic acids and various nitrogen derivatives (Smiley 1981).Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by several routes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. A skin and severe eye irritant. Human systemic effects by ingestion: convulsions, nausea or vomiting, and metabolic acidosis. Human respiratory system effects by inhalation. Mutation data reported. Dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. Explosion Hazard: See also CYANIDE and NITRILES. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of CNand NOx,. Potentially explosive reaction with lanthanide perchlorates and nitrogen-fluorine compounds. Exothermic reaction with sulfuric acid at 53°C. Will react with water, steam, acids to produce toxic and flammable vapors. Incompatible with oleum, chlorosulfonic acid, perchlorates, nitrating agents, inchum, dinitrogen tetraoxide, N-fluoro compounds (e.g., perfluorourea + acetonitrile), HNO3, so3. To fight fire, use foam, Con, dry chemical잠재적 노출
Acetonitrile is used as an extractant for animal and vegetable oils, as a solvent; particularly in the pharmaceutical industry, and as a chemical intermediate in pesticide manufacture; making batteries and rubber products. It is present in cigarette smokeCarcinogenicity
Under the conditions of these 2- year inhalation studies by NTP, there was equivocal evidence of carcinogenic activity of acetonitrile in male F344/N rats based on marginally increased incidences of hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma. There was no evidence of carcinogenic activity of acetonitrile in female F344/N rats exposed to 100, 200, or 400 ppm. There was no evidence of carcinogenic activity of acetonitrile in male or female B6C3F1 mice exposed to 50, 100, or 200 ppm. Exposure to acetonitrile by inhalation resulted in increased incidences of hepatic basophilic foci in male rats and of squamous hyperplasia of the forestomach in male and female mice.신진 대사
Acetonitrile metabolism in dogs was demonstrated by Lang (1894), who reported that about 20% of the nitrile administered was converted to thio-cyanate in the urine, while guinea pigs metabolized acetonitrile to a greater extent (50% of dose excreted as thiocyanate). When the animals were pre-treated with ethanol, acetonitrile metabolism was induced (Tanii and Hashimoto 1986). In rats, acetone was found to potentiate acetonitrile toxicity and elevate cyanide concentrations in the blood (Freeman and Hays 1985). Baumann et al (1933) found that rabbits injected with acetonitrile excreted 27-35% of the dose as thiocyanate, while in thyroidectomized rabbits, the excretion decreased significantly (3-5% of the dose). Thiocyanate excretion was increased notably upon feeding dessicated thyroid to these animals. Hunt (1923) found that powdered sheep thyroid protected mice against acetonitrile toxicity. However, the role played by the thyroid in the detoxication of cyanide to thiocyanate is unclear. It has been suggested that the thyroid may have a role in the microsomal cleavage of cyanide from acetonitrile other than its direct effect on sulphation of cyanide to thiocyanate.저장
Acetonitrile should be used only in areas free of ignition sources, and quantities greater than 1 liter should be stored in tightly sealed metal containers in areas separate from oxidizers.운송 방법
UN1648 Acetonitrile, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid비 호환성
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, chlorosulfonic acid, oleum, epoxides. May accumulate static electrical charges, and may cause ignition of its vapors. Nitriles may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompatible with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reactions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxidizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids). These reactions generate heat. Peroxides convert nitriles to amides. Nitriles can react vigorously with reducing agents. Acetonitrile and propionitrile are soluble in water, but nitriles higher than propionitrile have low aqueous solubility. They are also insoluble in aqueous acids폐기물 처리
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Incineration with nitrogen oxide removal from effluent gases by scrubbers or incinerators아세토나이트릴 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
수소화칼슘
나트륨 디에틸디티오카르밤산 염
모리큘라시브 3A
수산화칼륨
아세트아마이드
모리큘라시브
과망간산칼륨
아세트산 암모늄
아크릴로나이트릴
황산
탄소
산화알루미늄
암모니아(가스)
준비 용품
2-THENOYLACETONITRILE
CIS-2-AMINOCYCLOHEXANOL HYDROCHLORIDE
METHYL 3-((PYRROLIDIN-1-YL)METHYL)BENZOATE
1,1'- 비스 (디 페닐 포스 피노) 페로센 - 팔라듐 (Ⅱ) 디 클로라이드 디클로로 메탄 착물
1-(1-TERT-BUTYL-3-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)-1H-PYRAZOL-4-YL)-2,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHANONE
BIS(DIISOPROPYLAMINO)CHLOROPHOSPHINE
4-Methyl-3-nitroanisole
2-Amino-5-chlorobenzonitrile
(E)-METHYL 3-(4-BROMOPHENYL)ACRYLATE
클로로넵
ISOPROPYLSULFONYL CHLORIDE
2,2,2-TRIFLUORO-1-(3-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)-1-METHYL-1H-PYRAZOL-4-YL)ETHANONE
2-Hydroxy-5-bromopyridine
6-CHLORO-[1,2,4]TRIAZOLO[4,3-B]PYRIDAZINE
1-Phenylimidazole
3-AMINO-1-PHENYL-PROPAN-1-OL
1-Naphthalenesulfonyl chloride
2-퀴놀린카르보니트릴
6-(BOC-AMINO)-HEXYL BROMIDE
Boron trifluoride acetonitrile complex
Bis(2,4-pentanedionato-O,O')palladium(II)
Methyl 3-(morpholinomethyl)benzoate ,98%
시스-9-테트라데센-1-OL
1-Boc-piperazine acetate
[1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane]dichloropalladium(II)
디클로로(1,5-시클로옥타딘)팔라디움(II)
1-BENZYL-2-IMIDAZOLECARBOXYLIC ACID
Benzoylacetonitrile
Dimethyl acetylmethylphosphonate
4-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)benzaldehyde
1-(3-Aminopropyl)piperidine
1-PIPERIDINEPENTANOL
6-Bromopurine
수산화 세트리모늄
5-BROMO-2-(PYRROLIDIN-1-YL)PYRIMIDINE
N-Cyano etrhl ethyl midxite
Bis(acetonitrile)dichloropalladium(II)
4-AMINO-2-BUTANOL
5-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)-1-PHENYL-1H-PYRAZOLE
TRIETHANOLAMINE BORATE
아세토나이트릴 공급 업체
글로벌( 998)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai Yaokan Chemical Co., LTD | +86-021-60956847 +8613524860067 |
ni.chen@yaokanchem.com | China | 3 | 58 |
| Anhui Royal Chemical Co., Ltd. | +86-25-86655873 +8613962173137 |
marketing@royal-chem.com | China | 145 | 55 |
| Shandong Yanshuo Chemical Co., Ltd. | +86-18678179670 +86-18615116763 |
sales@yanshuochem.com | China | 101 | 58 |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-833-552-7181 |
sales@aladdinsci.com | United States | 57511 | 58 |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-833-552-7181 |
sales@aladdinsci.com | United States | 52927 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12471 | 58 |
| Hebei Guanlang Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +8619930503252 |
daisy@crovellbio.com | China | 5962 | 58 |
| Nanjing Deda New Material Technology Ltd. | +8613223281135 |
niki@njdeda.com | China | 75 | 58 |
| Yujiang Chemical (Shandong) Co.,Ltd. | +86-17736087130 +86-18633844644 |
catherine@yjchem.com.cn | China | 351 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21689 | 55 |