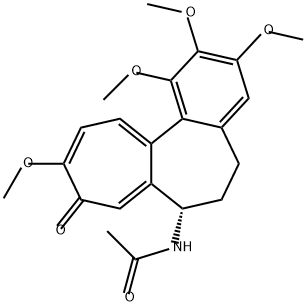
콜키신
|
|
콜키신 속성
- 녹는점
- 150-160 °C (dec.)(lit.)
- 알파
- -250 º (c=1, alcohol)
- 끓는 점
- 522.37°C (rough estimate)
- 밀도
- 1.2770 (rough estimate)
- 굴절률
- 1.5614 (estimate)
- 저장 조건
- 2-8°C
- 용해도
- H2O: 10 mg/mL
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 12.36(at 20℃)
- 물리적 상태
- 가루
- 색상
- 녹색을 띤 흰색에서 노란색까지
- 수용성
- 45g/L(20℃)
- 감도
- Light Sensitive
- Merck
- 14,2471
- BRN
- 2228813
- BCS Class
- 3
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 빛에 민감합니다. 강한 산화제와 호환되지 않습니다.
- InChIKey
- IAKHMKGGTNLKSZ-INIZCTEOSA-N
- LogP
- 1.300
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 64-86-8(CAS DataBase Reference)
- NIST
- Colchicine(64-86-8)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | T+,T,Xi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 26/28-41-46 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 13-45-36/37/39-28-26-53 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 1544 6.1/PG 1 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | GH0700000 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| 위험 등급 | 6.1 | ||
| 포장분류 | I | ||
| HS 번호 | 29399990 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 64-86-8(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LD50 in rats (mg/kg): 1.6 i.v. (Rosenbloom, Ferguson); in mice (mg/kg): 4.13 i.v. (Beliles) |
콜키신 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Colchicine is a pale-yellow powder that is obtained from various species of Colchicum, primarily Colchicum autumnale L. Its total chemical synthesis has been achieved, but the primary source of colchicine currently remains alcohol extraction of the alkaloid from the corm and seed of C. autumnale L. It darkens on exposure to light and possesses화학적 성질
Colchicine is a pale yellow powder. It has little or no odor. It darkens on contact with light.물리적 성질
Appearance: colchicine exists in white or light-yellow crystal powder with no smell, and it is seldom prone to absorb moisture. Melting point: it becomes dark when it is exposed to light, and it melts at 87–89?°C. Solubility: this product is soluble in chloroform or ethanol and it dissolves in water. However, the semihydrate crystal can form in certain concentrations. The product is hardly soluble in ether. Specific optical rotation: ?121° (0.9?g/100?mL, chloroform, 589.3?nm, 17?°C).역사
Meadow saffron (Colchicum) is recorded to treat rheumatic swelling on ancient Egyptian medical papyrus in 1500 B.C.. According to De Materia Medica written by Pedanius Dioscorides in the first century, extract of Meadow saffron is used in treating gout. London Pharmacopoeia in 1618 recorded that colchicine is also applied to treat gout.In 1820, the ingredient was first isolated by the French chemist P.S. Pelletier and J.B. Caventou. In 1833, it was purified and named by Geiger. Michael Dewar guessed that there are two seven-membered rings in colchicine in 1945. Murray Vernon King et al. determined the structure of colchicine by X-ray diffraction in 1952. In 1959, Albert Eschenmoser integrated the product successfully
Colchicine tablet and raw material are approved mostly in domestic in 2010. The tablet produced by Taiwan manufacturers is approved for being listed in mainland of China in 2012. The raw material made by Indian obtained the approval in 2013. There are three kinds of colchicine approved by FDA: with the combination of probenecid, it is prior to be approved. The others are tablet (2009) and capsule (2014).
용도
Colchicine is present in the poisonous autumncrocus (meadow saffron). It is the major alkaloid of Colchicum autumnale L. and Liliaceae. It was used in poison potions in theancient kingdom of Colchis (Greece). It isused therapeutically as an antineoplast, for thesuppression of gout, and in the treatment ofMediterranean fever. It is used in plant studiesfor doubling chromosome groups.정의
colchicine: An alkaloid derivedfrom the autumn crocus, Colchicumautumnale. It inhibits cell division.Colchicine is used in genetics, cytology,and plant breeding research andalso in cancer therapy to inhibit celldivision.Indications
Colchicine, an alkaloid obtained from the autumn crocus, has long been used and is relatively selective for the treatment of acute gouty arthritis. Unlike many of the newer agents for use in gout, colchicine has minimal effects on uric acid synthesis and excretion; it decreases inflammation associated with this disorder. It is thought that colchicine somehow prevents the release of the chemotactic factors and/or inflammatory cytokines from the neutrophils, and this in turn decreases the attraction of more neutrophils into the affected area .The ability of colchicine to bind to leukocyte microtubules in a reversible covalent complex and cause their depolymerization also may be a factor in decreasing the attraction of the motile leukocytes into the inflamed area.Biological Functions
Acting on polymorphonuclear leukocytes and diminishing phagocytosis, it inhibits the production of lactic acid, causing an increase in the pH of synovial tissue and, thus, a decrease in urate deposition, because uric acid is more soluble at the higher pH. Additionally, colchicine inhibits the release of lysosomal enzymes during phagocytosis that also contributes to the reduction of inflammation. Because colchicine does not lower serum urate levels, it has been found to be beneficial to combine colchicine with a uricosuric agent, particularly probenecid. It is a potent drug, being effective at doses of approximately 1 mg, but doses as small as 7 mg have caused fatalities.일반 설명
Colchicine is an alkaloid isolated from the dried corns andseeds of Colchicum autumnale L., commonly known as autumncrocus or meadow saffron.It is specifically indicated for acute treatment of goutyarthritis because of its ability to block the production and releaseof the CCF that mediates the inflammatory responsebecause of urate crystals, a mechanism different fromcolchicine’s antimitotic action, which is being investigatedfor its anticancer properties. It is often quite effective inaborting an acute gouty attack if given within the first 10 to12 hours after the onset of arthritis.공기와 물의 반응
Slowly hydrolyzed in acidic solution, but unbuffered solutions are stable at 68°F for at least six months. Isomerizes on exposure to ultraviolet radiation.반응 프로필
Colchicine darkens on exposure to light. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Also incompatible with mineral acids .위험도
As little as 20 mg may be fatal if ingested.건강위험
Colchicine is classified as super toxic. Probable oral lethal dose in humans is less than 5 mg/kg, i.e. less than 7 drops for a 70 kg (150 lb.) person. Death results from respiratory arrest. The fatal dose varies considerably; as little as 7 mg of Colchicine has proved fatal.화재위험
Stable.생물학적 활성
Plant-derived alkaloid that binds to tubulin and depolymerizes microtubules.Mechanism of action
Colchicine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration and tends to concentrate in the spleen, kidney, liver, and gastrointestinal tract. Leukocytes also avidly accumulate and store colchicine even after a single intravenous injection. Since colchicine can accumulate in cells against a concentration gradient, it is postulated that an active transport process may be involved in its cellular uptake. The drug is metabolized, primarily in the liver, by deacetylation. Fecal excretion plays a major role in colchicine elimination, since it and its metabolites are readily secreted into the bile. Only about 15 to 30% of the drug is eliminated in the urine except in patients with liver disease; urinary excretion is more important in these individuals.Pharmacokinetics
Colchicine is absorbed on oral administration, with peak plasma levels being attained within 0.5 to 2 hours after dosing. Plasma protein binding is only 31%. It concentrates primarily in the intestinal tract, liver, kidney, and spleen and is excreted primarily in the feces, with only 20% of an oral dose being excreted in the urine. It is retained in the body for considerable periods of time, being detected in the urine and leukocytes for 9 to 10 days following a single dose.Pharmacology
The drug can be given intravenously as well as orally, but care must be exercised, since extravasated drug may result in local sloughing of skin and subcutaneous tissues. Relief of pain and inflammation usually occurs within 48 hours. Small doses of colchicine can be used during asymptomatic periods to minimize the reappearance or severity of acute attacks. It should be used with caution in patients with preexisting compromised heart, kidney, gastrointestinal tract, and liver disease. Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain are the major limiting side effects that ultimately determine the tolerated dosage. These symptoms occur in approximately 80% of patients who take colchicine, especially in those taking high dosages. The hepatobiliary recycling of colchicine and its antimitotic effect on cells that are rapidly turning over, such as those of the intestinal epithelium, account for its gastrointestinal toxicity. Gastrointestinal symptoms generally intervene before the appearance of more serious toxicity and thereby provide a margin of safety in drug administration. Ingestion of large doses of colchicine may be followed by a burning sensation in the throat, bloody diarrhea, shock, hematuria, oliguria, and central nervous system (CNS) depression.Anticancer Research
It is a natural toxic secondary metabolite, extracted from Colchicum genus plants. Itprevents gastric cancer by upregulating the dual specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1)gene. It is also reported to upregulate transforming growth factor beta 2 (TGF-β2)and A-kinase anchoring protein 12 (AKAP12) in hepatocellular carcinoma (Singhet al. 2016b).Clinical Use
The major use of colchicine is as an antiinflammatory agent in the treatment of acute gouty arthritis; it is not effective in reducing inflammation in other disorders. It also can be used to prevent attacks. Since colchicine is so rapidly effective in relieving the acute symptoms of gout (substantial improvement is achieved within hours), it has been used as a diagnostic aid in this disorder. Therapy with colchicine is usually begun at the first sign of an attack and is continued until symptoms subside, adverse gastrointestinal reactions appear, or a maximum dose of 6 to 7 mg has been reached.부작용
Colchicine may produce bone marrow depression, with long-term therapy resulting in thrombocytopenia or aplastic anemia. At maximum dose levels, GI disturbances (e.g., nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain) may occur. Acute toxicity is characterized by GI distress, including severe diarrhea resulting in excessive fluid loss, respiratory depression, and kidney damage. Treatment normally involves measures that prevent shock as well as morphine and atropine to diminish abdominal pain. A number of drug interactions have been reported. In general, the actions of colchicine are potentiated by alkalinizing substances and are inhibited by acidifying drugs, consistent with its mechanism of action of increasing the pH of synovial fluid. Responses to CNS depressants and to sympathomimetic drugs appear to be enhanced. Clinical tests may be affected; most notably, elevated alkaline phosphatase and SGOT (serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase) values and decreased thrombocyte values may be obtained.Safety Profile
experimentally by most routes. Human systemic effects: aplastic anemia, blood pressure depression, body temperature decrease, changes in kidney tubules, dyspnea, flaccid paralysis without anesthesia, gastrointestinal effects, kidney damage and hemorrhaging, muscle contraction or spasticity, muscle weakness, nausea or vomiting, respiratory stimulation, and somnolence. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. A severe eye irritant. Human mutation data reported. Inhibits the formation of microtubules and thus impairs cell division. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.잠재적 노출
Colchicine is a drug used to treat gouty arthritis, pseudogout, sarcoidal arthritis; and calcific tendonitis.환경귀착
Colchicine binds to tubulin and prevents its polymerization into microtubules, subsequently disrupting microtubule function. Consequently, it alters nuclear structure, intracellular transport, and cytoplasmic motility, ultimately causing cell death. Colchicine is a potent inhibitor of cellular mitosis.신진 대사
Metabolism occurs primarily in the liver, with the major metabolite being the amine resulting from amide hydrolysis.운송 방법
UN1544 Alkaloids, solid, n.o.s. or Alkaloid salts, solid, n.o.s. poisonous, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1- Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3249 Medicine, solid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materialsPurification Methods
Commercial material contains up to 4% desmethylcolchicine. Purify colchicine by chromatography on alumina and eluting with CHCl3 [Ashley & Harris J Chem Soc 677 1944]. Alternatively, an acetone solution on alkali-free alumina has been used, and eluting with acetone [Nicholls & Tarbell J Am Chem Soc 75 1104 1953]. It crystallises as yellow needles from EtOAc or CHCl3 with solvent of crystallisation which can be removed at ~70o. It is soluble in Et2O (0.5%), *C6H6 (1%) and H2O (4%). It is sold as “Colgout” for the treatment of gout and binds to tubulin. [Schreiber et al. Helv Chim Acta 44 540 1961, Scott et al. Tetrahedron 21 3605 1965, van Tamelen et al. Tetrahedron 14 8 1961, Beilstein 14 IV 946.]비 호환성
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, mineral acids. Keep away from light.콜키신 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
Acetamide, N,N'-[(7S,7bR,8aS,8bS,9aR,10S,16cS,16dR,16eR,16fS)-5,6,7,7b,8,8a,8b,9,9a,10,11,12,16c,16d,16e,16f-hexadecahydro-1,2,3,8a,8b,14,15,16-octamethoxy-8,9-dioxobisbenzo[3',4']cyclohepta[1',2':3,4]cyclobuta[1,2-c:1',2'-c']cyclobuta[1,2-a:4,3-a']dicyclopentene-7,10-diyl]bis-
GAMMA-LUMICOLCHICINE
씨오콜치신
콜키신 공급 업체
글로벌( 699)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12471 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531190177 |
peter@yan-xi.com | China | 6000 | 58 |
| Anhui Ruihan Technology Co., Ltd | +8617756083858 |
daisy@anhuiruihan.com | China | 994 | 58 |
| Ouhuang Engineering Materials (Hubei) Co., Ltd | +8617702722807 |
admin@hbouhuang.com | China | 3001 | 58 |
| Hangzhou FandaChem Co.,Ltd. | 008657128800458; +8615858145714 |
fandachem@gmail.com | China | 9341 | 55 |
| Nanjing Finetech Chemical Co., Ltd. | 025-85710122 17714198479 |
sales@fine-chemtech.com | CHINA | 885 | 55 |
| ATK CHEMICAL COMPANY LIMITED | +undefined-21-51877795 |
ivan@atkchemical.com | China | 32686 | 60 |
| Shanxi Naipu Import and Export Co.,Ltd | +86-13734021967 +8613734021967 |
kaia@neputrading.com | China | 1011 | 58 |
| SHANDONG ZHI SHANG CHEMICAL CO.LTD | +86 18953170293 |
sales@sdzschem.com | China | 2931 | 58 |
| Chengdu Biopurify Phytochemicals Ltd. | +8618080483897 |
sales@biopurify.com | China | 3424 | 58 |
콜키신 관련 검색:
매트린 디하이드로미르세놀
Rotundine
Sophoricoside
META-TOPOLIN
Crane top red
COLCHICOSIDE
colchiceine
N-Deacetyl-N-methyl(deutero)colchicine,N-METHYL-N-DEACETYL-COLCHICINE,COLCHICINE,N-DEACETYL-N-METHYL-,DEMECOLCINE/COLCEMIDE/COLCHICINE
cornigerine
GLORIOSINE
GAMMA-LUMICOLCHICINE
N-TRIFLUOROACETYL-N-METHYL-DEACETYLCOLCHICINE
N-TRIFLUOROACETYL DEACETYLCOLCHICINE
COLCHICINE METHANETHIOSULFONATE
COLCHICINE-D6
COLCHICINE, [RING C, METHOXY-3H]
COLCHICINE, [RING C, METHOXY-14C]