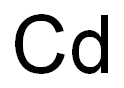카드뮴분
|
|
카드뮴분 속성
- 녹는점
- 320.9 °C (lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 765 °C (lit.)
- 밀도
- 8.65 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- 증기압
- 1.3 hPa (394 °C)
- 저장 조건
- Store below +30°C.
- 용해도
- 8.2mg/l 불용성
- 물리적 상태
- 철사
- Specific Gravity
- 8.642
- 색상
- 은백색
- 냄새
- 냄새 없는
- 비저항
- 7.27 μΩ-cm, 22°C
- 수용성
- 물에 불용성; 묽은 HNO3와 반응하고 뜨거운 HCl과 천천히 반응함 [MER06]
- Merck
- 13,1613
- BRN
- 8137359
- 노출 한도
- TLV-TWA 0.05 mg/m3 (for dusts and salts) (ACGIH), 0.2 mg/m3 (MSHA), 0.1 mg/m3 (OSHA), lowest feasible level in air (NIOSH); ceiling 0.3 mg/m3 (OSHA).
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 강한 산화제, 질산염, 질산, 셀레늄, 아연과 호환되지 않습니다. 가연성. 분말 금속은 자연발화성일 수 있습니다.
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 7440-43-9(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 1 (Vol. 58, 100C) 2012
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | T,N,T+,F,Xi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 45-50/53-68-63-62-48/23/25-26-17-36/38-20/21/22 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 53-45-61-60-43-7/8-26 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 3082 9/PG 3 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | EU9800000 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS 번호 | 8107 20 00 | ||
| 위험 등급 | 8 | ||
| 포장분류 | III | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 7440-43-9(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | A metal that is used for electroplating and in batteries, as a color pigment for paints and as a stabilizer in plastics. The oral LD50 in rats is about 0.88 mg/kg and the LC50 in fathead minnows is about 3.06 mg/L. Cadmium is a nephrotoxicant and hepatotoxicant, probably acting by displacement and substitution of essential metals in proteins and enzymes. In humans acute poisoning can cause nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, headache, muscular aches, salivation, abdominal pain, and shock. In acute poisoning, unabsorbed cadmium is removed by catharsis. | ||
| IDLA | 9 mg Cd/m3 | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-04397 | ||
| 유해화학물질 필터링 | 06-5-9 | ||
| 중점관리물질 필터링 | 별표1-123 | ||
| 함량 및 규제정보 | 물질구분: 제한물질; 혼합물(제품)함량정보: 카드뮴 및 이를 0.1% 이상 함유한 혼합물 |
카드뮴분 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
물성
금속 광택이 나는 청색을 띤 은백색의 부드러운 금속이며, 칼로 깎을 수도 있다. 연성·전성이 풍부하여 가공하기 쉽다. 수은과는 아말감을 잘 만들며, 공기 중에서는 표면만이 산화되고 내부는 침식당하지 않는다. 또, 공기 중에서 강하게 가열하면 적색 불꽃과 갈색 연기를 내면서 연소하여 산화물이 된다. 가열하면 할로겐과 잘 반응하나, 수소나 질소·탄소 등과는 직접 반응하지 않는다. 묽은 질산에는 쉽게 녹고, 뜨거운 염산에는 서서히 녹는다. 차가울 때는 황산에 용해되지 않지만, 가열하면 녹는다. 아연과 달리 알칼리 용액에 녹지 않는다.개요
순수한 카드뮴은 부드럽고 은백색의 금속으로 공기, 물, 토양 등에 자연적으로 소량 존재하며 독성이 있는 전이 금속으로서 전지를 만드는데 주로 쓰이고 명확한 맛이나 향이 없다.용도
카드뮴은 니켈-카드뮴 재충전가능한 전지, 금속 판금시 사용된다. 또한, 페인트, 플라스틱, 금속 합금 등에도 사용되며, 얼음 트레이, 피쳐, 도자기용기 등에 소량 포함되어 있을 수 있다. 카드뮴을 사용하는 주 산업은 금속제련, 전자, 핵연료, 안료제품 등이다.개요
Cadmium is a grey-white, soft, blue-white malleable, lustrous metal. It is insoluble in cold water, hot water, methanol, diethyl ether, and n-octanol. It is stable and incompatible with strong oxidising agents, nitrates, nitric acid, selenium, and zinc, and the powdered metal may be pyrophoric and flammable.
Cadmium is associated with occupations such as industrial processes, metal plating, and production of nickel– cadmium batteries, pigments, plastics, and other synthetics. Cadmium metal is produced as a by-product from the extraction, smelting, and refining of the non-ferrous metals zinc, lead, and copper. In view of the unique properties, cadmium metal and cadmium compounds are used as pigments, stabilisers, coatings, specialty alloys, and electronic compounds.
화학적 성질
Calmium is an odorless, silver-white lustrous metal with a bluish tinge, which is ductile and highly malleable with a melting point of 321 °C. The metal is soft enough to cut with a knife and will tarnish in air; as a powder, cadmium is flammable. Burning cadmium results in an odorless yellowbrown cadmium fume (cadmium monoxide or cadmium oxide fume) composed of finely divided particles dispersed in air. Both cadmium and cadmium oxide are insoluble in water and have a vapor pressure of approximately 0 mmHg. Cadmium is insoluble in water but can be solubilized in acid. Cadmium salts (e.g., cadmium sulfate and cadmium chloride) are soluble in water.물리적 성질
Cadmium is a soft, blue-white metal that is malleable and ductile although it becomesbrittle at about 80°C. It is also found as a grayish-white powder. It is considered rare and isseldom found by itself as an ore. Its melting point at 320.9°C is considered low. Its boilingpoint is 765°C, and its density is 8.65 g/cm3. Certain alloys of cadmium have extremely lowmelting points at about 70°C.Isotopes
There are 52 isotopes of cadmium. Forty-four are radioactive and artificiallyproduced, ranging from Cd-96 to Cd-131. Of these 52 isotopes, there are five stableisotopes plus three naturally occurring radioactive isotopes with extremely long half-livesthat are considered as contributing to the element’s natural occurrence in the Earth’scrust. The three naturally radioactive isotopes (Cd-106, Cd-113, and Cd-116) are thelongest known beta emitters. They are two million years older than when the solar systemwas formed about 4.5 billion years ago. The five stable isotopes and their proportionalcontributions to the element’s existence on Earth are as follows: Cd-108 = 0.89%,Cd-110 = 12.49%, Cd-111= 12.80%, Cd-112 = 24.13%, and Cd-114 = 28.73%.Origin of Name
The word cadmium is from the Latin word cadmia or the Greek word kadmeia, meaning the zinc oxide ore “calamine” that contains the element cadmium.출처
Cadmium is considered a rare element even though it is widely distributed over the Earth’scrust. Its estimated abundance in the Earth’s crust is 1.10-1 milligrams per kilogram. It is consideredthe 65th most abundant element, but it does not occur as a free metal in nature. It isusually found in relationship with other metallic ores. Its abundance is only about 1/1000ththat of zinc. It is found in an ore called greenockite, which is cadmium sulfite (CdS). This oredoes not have a high enough concentration of cadmium to be mined profitably. Cadmiumis found along with zinc, lead, and copper ores. Today, most cadmium is obtained as a byproductfrom the processing and refining of zinc ores. In addition, dust and fumes from roastingzinc ores are collected by an electrostatic precipitator and mixed with carbon (coke) andsodium or zinc chloride. This residue is then treated to recover the cadmium. Other refiningprocesses can obtain up to 40% recovery of cadmium from zinc ores.Greenockite ore, as well as zinc and other ores, which produce cadmium as a by-product,are found in many countries, including Australia, Mexico, Peru, Zaire, Canada, Korea, andBelgium-Luxembourg and in the central and western United States.
Characteristics
Although cadmium is not considered a transition element in some periodic tables, it is thecentral element of the triad with zinc and mercury. Zinc is just above it and mercury is below itin group 12 of the periodic table. Cadmium’s chemical and physical properties are similar to itsgroup 12 mates. Their electronegativity is very similar: Zn = 1.6, Cd = 1.7, and Hg = 1.9.Cadmium is resistant to alkalis, but is soluble in acids, mainly nitric acid. Although it isused to electroplate steel to prevent corrosion, it will tarnish in moist air.
용도
A soft bluish metal, cadmium is extremely toxic, particularly in the compounds used for photography. It is found in zinc ores and in the mineral greenockite (CdS).정의
cadmium: Symbol Cd. A soft bluishmetal belonging to group 12 (formerlyIIB) of the periodic table; a.n.48; r.a.m. 112.41; r.d. 8.65; m.p.320.9°C; b.p. 765°C. The element’sname is derived from the ancientname for calamine, zinc carbonateZnCO3, and it is usually found associatedwith zinc ores, such as sphalerite(ZnS), but does occur as themineral greenockite (CdS). Cadmiumis usually produced as an associateproduct when zinc, copper, and leadores are reduced. Cadmium is used inlow-melting-point alloys to make solders,in Ni–Cd batteries, in bearingalloys, and in electroplating (over50%). Cadmium compounds are usedas phosphorescent coatings in TVtubes. Cadmium and its compoundsare extremely toxic at low concentrations;great care is essential wheresolders are used or where fumes areemitted. It has similar chemical propertiesto zinc but shows a greater tendencytowards complex formation.The element was discovered in 1817by F. Stromeyer.일반 설명
Silver-white blue tinged lustrous metallic solid.공기와 물의 반응
The finely divided metal is pyrophoric. Slowly oxidized by moist air to form CADMIUM oxide. Insoluble in water.반응 프로필
A violent explosion occurred 30 minutes after placement of a CADMIUM rod into hydrazoic acid [Mellor 8 Supp. 2:50 1967]. Fused ammonium nitrate with powdered metal often produces a violent explosive reaction. Reactivity similar to zinc. May be incompatible with oxidants.위험도
Cadmium powder, dust, and fumes are all flammable and toxic if inhaled or ingested.Cadmium and many of its compounds are carcinogenic.Severe illness and death can occur from exposure to many cadmium compounds. It isabsorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. However, it can be eliminated in the urine and fecesin young, healthy people.
화재위험
Flammable in powder form. Combustible.공업 용도
Cadmium (symbol Cd) is a silvery-white crystallinemetal that has a specific gravity of 8.6,is very ductile, and can be rolled or beaten intothin sheets. It resembles tin and gives the samecharacteristic cry when bent, but is harder thantin. A small addition of zinc makes it very brittle.It melts at 320°C and boils at 765°C. Cadmiumis employed as an alloying element insoft solders and in fusible alloys, for hardeningcopper, as a white corrosion-resistant platingmetal, and in its compounds for pigments andchemicals. It is also used for Ni–Cd batteriesand to shield against neutrons in atomic equipment;but gamma rays are emitted when theneutrons are absorbed, and these rays requirean additional shielding of lead.Most of the consumption of cadmium is forelectroplating. For a corrosion-resistant coatingfor iron or steel a cadmium plate of 0.008 mmis equal in effect to a zinc coat of 0.025 mm.The plated metal has a silvery-white color witha bluish tinge, is denser than zinc, and harderthan tin, but electroplated coatings are subjectto H2 embrittlement, and aircraft parts are usuallycoated by the vacuum process. Cadmiumplating is not normally used on copper or brasssince copper is electronegative to it, but whenthese metals are employed next to cadmium-plated steel a plate of cadmium may beused on the copper to lessen deterioration.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, tumorigenic, and neoplastigenic data. A human poison by inhalation and possibly other routes. Poison experimentally by ingestion, inhalation, intraperitoneal,Carcinogenicity
Cadmium and cadmium compounds are known to be human carcinogens based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans, including epidemiological and mechanistic studies. Cadmium and cadmium compounds were first listed as reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens in the First Annual Report on Carcinogens in 1980, based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals. The listing was revised to known to be human carcinogens in the Ninth Report on Carcinogens in 2000.환경귀착
Cadmium inhibits plasma membrane calcium channels and Ca2t-ATPases. It also inhibits repair of DNA damaged by various chemicals, an effect which is believed to be associated with the induction of tumors. Although cadmium forms a metallothionein, the preformed cadmium metallothionein is nephrotoxic (toxic to the kidneys); it is suggested that effects occur when, at some stage in the kidney, the cadmium is dissociated from the metallothionein. In Itai-Itai disease (see Human under Chronic Toxicity section), patients were found to have chromosome abnormalities.Cadmium has an affinity for sulfhydryl groups, and hence can inhibit enzymes; however, cells treated with cadmium showed proliferation of peroxisomes, which contain catalase, an enzyme. It appears that cadmium at first inhibits catalase activity and then, after a time, enhances that activity. In addition, cadmium inhibits enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis (the generation of glycogen for energy production from noncarbohydrate precursors). It also inhibits oxidative phosphorylation (energy production) and depresses trypsin inhibitor capacity.
저장
Cadmium should be kept stored in a tightly closed container in a cool place. It should be kept stored in a separate locked safety storage cabinet운송 방법
UN2570 Cadmium compounds, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.Purification Methods
Any oxide contaminant is removed by filtering the molten metal, under vacuum, through quartz wool. Its solubility in Hg is 5.2% (18o), and it is soluble in mineral acids. [Wagenknecht & Juza in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1092 1965.]Structure and conformation
The space lattice of Cadmium belongs to the hexagonal system, and its closely-packed hexagonal lattice has lattice constants of a=0.2973 nm and c=0.5607 nm.비 호환성
Air exposure with cadmium powder may cause self-ignition. Moist air slowly oxidizes cadmium forming cadmium oxide. Cadmium dust is incompatible with strong oxidizers, ammonium nitrate; elemental sulfur; hydrazoic acid; selenium, zinc, tellurium. Contact with acids cause a violent reaction, forming flammable hydrogen gas.폐기물 처리
With cadmium compounds in general, precipitation from solution as sulfides, drying and return of the material to suppliers for recovery is recommended. Cadmium may be recovered from battery scrap as an alternative to disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.주의 사항
On exposures to cadmium, wash the skin immediately with plenty of water and a nonabrasive soap. Workers should cover the exposed skin with an emollient.카드뮴분 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
카드뮴분 공급 업체
글로벌( 254)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21689 | 55 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 |
sales@coreychem.com | China | 29914 | 58 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28180 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22968 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-61398051 +8613650506873 |
sales@chemdad.com | China | 39916 | 58 |
| Antai Fine Chemical Technology Co.,Limited | 18503026267 |
info@antaichem.com | CHINA | 9641 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | 0551-65418671 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34572 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 |
1026@dideu.com | China | 9126 | 58 |
| Zhuoer Chemical Co., Ltd | 02120970332; +8613524231522 |
sales@zhuoerchem.com | China | 3005 | 58 |
| changzhou huayang technology co., ltd | +8615250961469 |
2571773637@qq.com | China | 9821 | 58 |