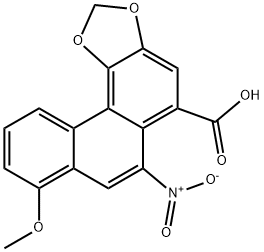
아리스토로크산 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Aristolochic acid first appeared in Chinese medicine in the fifth century AD, while it was used to treat kidney and urinary diseases, as well as gout, snakebites, and a variety of other ailments. In many of these cases, aristolochic acid was just one of the main components of the salves. In the first century, aristolochic acid was first described as a composition of ingested medicine to treat symptoms such as asthma, hiccups, pains, and spasms.
화학적 성질
Shiny brown leaflets or a yellow or white
powder.
물리적 성질
Appearance: brown sheet crystal or yellow powder. Solubility: practically insoluble in water and soluble in ethanol, chloroform, ethyl ether, acetone, glacial acetic acid, and aniline. Melting point: 260–265?°C (500–509?°F; 533–538?K).
역사
At a clinic in Brussels, Belgium, a group of women who had all taken the same weight loss supplement, Aristolochia fangchi, which contained aristolochic acid, was first diagnosed with aristolochic acid poisoning. Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN) was later found to be also the result of aristolochic acid (AA) consumption. Balkan endemic nephropathy is likely caused by low-level AA exposure, possibly from the contamination of wheat flour seeds by Aristolochia clematitis. BEN falls under the umbrella of what is now known as aristolochic acid nephropathy, the prevalent symptom of AA poisoning .
용도
Aristolochic acids occur in Aristolochiaceae and in butterflies feeding on these plants. One of a group of fourteen known, substituted 1-phenanthrenecarboxylic acids
정의
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is phenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid that is substituted by a methylenedioxy group at the 3,4 positions, by a methoxy group at position 8, and by a nitro group at position 10. It is the most abundant of the aristolochic acids and is
found in almost all Aristolochia (birthworts or pipevines) species. It has been tried in a number of treatments for inflammatory disorders, mainly in Chinese and folk medicine. However, there is concern over their use as aristolochic acid is b
th carcinogenic and nephrotoxic.
Indications
Due to the widely associated kidney problems and urothelial cancers, the FDA has issued warnings regarding consumption of AA-containing supplements.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Extracts of aristolochiaceae have traditionally been used as a
bitter for which a broad range of therapeutic effects has been claimed. Aristolochic
acid is claimed to promote phagocytosis and to have immunostimulant activity.
However, in 1981, a three-month toxicity study in rats revealed the carcinogenic
potential of aristolochic acid and preparations containing this substance have
since been withdrawn in several countries.
일반 설명
This substance is a primary reference substance with assigned absolute purity (considering chromatographic purity, water, residual solvents, inorganic impurities). The exact value can be found on the certificate. Produced by PhytoLab GmbH & Co. KG
Pharmacology
In 1992, some cases of women present with a rapidly progressive renal failure after having a slimming regimen including powdered extracts of Chinese herbal preparations. This outbreak of renal failure eventually resulted in about 100 cases in 1998, 70% of them being in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) . Recent research has confirmed that the main reason leading to renal injury is aristolochic acid found in many Chinese herbs . Aristolochic acid, a potent human carcinogen from
Aristolochia plants, is associated with the incidence of urothelial carcinoma in the
upper urinary tract (UUC). After the metabolic activation, aristolochic acid reacted
with DNA to form aristolactam (AL)-DNA adducts. Mainly pathological changes
are in renal cortex, where they serve as a specific biomarker, and are also found in
urothelium, where they lead to a unique mutational signature in the TP53 tumorsuppressor gene. The conclusion is that exposure to aristolochic acid gives rise to
the incidence of UUC, a finding with significant implications for the global public
health .
Clinical Use
Aristolochia species are nephrotoxic and carcinogenic, and FDA has issued warnings regarding consumption of AA-containing supplements.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen.
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and
intravenous routes. Mutation data reported.
When heated to decomposition it emits
toxic fumes of NO,.
Potentially Toxic Chemicals: April 1982."
Vol. 5 No. 1: The Ministry of Health of the
Federal Republic of Germany has
withdrawn from the national market drugs
containing aristolochic acid. The decision
resulted from the demonstration of a
carcinogenic potential in a three-month
ingestion toxicity study undertaken in rats.
Aristolochic acid is claimed to promote
phagocytosis and to have immunostimulant
activity. A growth-inhibiting effect on
experimentally induced tumors has been
described, but this effect has not been
shown to have any clinical relevance.
Extracts of species of Aristolochiacea have
tradtionally been used as a bitter, and a
broad range of therapeutic effects has been
claimed.
잠재적 노출
Aristolochic acids are alkaloids used
primarily as a chemical intermediate for pharmaceuticals,
lab chemicals, herbal extract, drug.
운송 방법
UN1544 Alkaloids, solid, n.o.s. or Alkaloid salts,
solid, n.o.s. poisonous, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-
Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. PG III.
비 호환성
Compounds of the carboxyl group react
with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines)
releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be
harmful. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates,
peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine,
fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep
away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids,
oxoacids, epoxides.
폐기물 처리
It is inappropriate and possibly
dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or
waste drugs and pharmaceuticals by flushing them down
the toilet or discarding them to the trash. Household quantities
of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed
with wet cat litter or coffee grounds, double-bagged in
plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully
take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA
regulations. If possible return the pharmaceutical to the
manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properly
label and securely package the material. Alternatively, the
waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged
and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor
to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste
landfill or incinerator. All federal, state, and local environmental
regulations must be observed.
아리스토로크산 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품