- p,p'-DDE
-

- $76.00 / 500mg
-
2024-11-08
- CAS:72-55-9
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.68%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- 4,4'-DDE
-

- $0.10 / 1KG
-
2024-08-05
- CAS:72-55-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 98.0%
- Supply Ability: 10
- 4,4'-DDE
-

- $8.00 / 1KG
-
2020-02-21
- CAS:72-55-9
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: >98% HPLC
- Supply Ability: kg--ton
|
| | 4,4'-DDE Basic information |
| Product Name: | 4,4'-DDE | | Synonyms: | 1,1’-(dichloroethylidene)bis(4-chlorobenzene);1,1’-dichloroethenylidene)bis(4-chlorobenzene);1,1-Bis(p-chlorophenyl)-2,2-dichloroethylene;1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethene;1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(para-chlorophenyl)ethylene;1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethene;dde(1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethylene);DDE(p,p') | | CAS: | 72-55-9 | | MF: | C14H8Cl4 | | MW: | 318.03 | | EINECS: | 200-784-6 | | Product Categories: | Analytical Chemistry;Chlorinated Compounds (Environmental Endocrine Disruptors);Environmental Endocrine Disruptors;Alphabetic;D;DA - DHMethod Specific;Oeko-Tex Standard 100;Pesticides | | Mol File: | 72-55-9.mol | 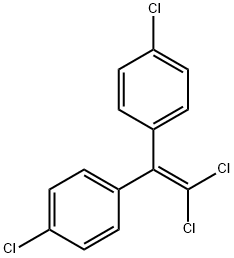 |
| | 4,4'-DDE Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 88-90 °C(lit.) | | Boiling point | 403.45°C (rough estimate) | | density | 1.3406 (rough estimate) | | vapor pressure | 13 at 30 °C (Wescott et al., 1981) | | refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) | | Fp | 11 °C | | storage temp. | 2-8°C | | solubility | ethanol: soluble | | form | Solid | | color | White, crystalline, odorless powder | | Water Solubility | 292mg/L(25 ºC) | | BRN | 1913355 | | Henry's Law Constant | 0.33 at 25 °C (gas stripping-GC, Jantunen and Bidleman, 2006) | | Stability: | Stable, but light-sensitive. Incompatible with strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. | | EPA Substance Registry System | p,p'-DDE (72-55-9) |
| | 4,4'-DDE Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | white crystalline powder | | Uses | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane(DDE) has been used to study the ability of Pseudomonas acidovorans M3GY to transform DDE and its unchlorinated analog, 1,1-diphenylethylene (DPE).It has been used to investigate the role of incubation time, solvent type, yeast inoculum growth stage and concentration on the results of yeast assay for estrogenic compounds. | | Uses | Military product; chemical research. Degradation product of p,p′-DDT. | | Definition | ChEBI: A chlorophenylethylene that is ethylene substituted by two 4-chlorophenyl groups at position 1 and two chlorine atoms at position 2. | | General Description | White crystalline solid or white powder. | | Air & Water Reactions | Insoluble in water. | | Reactivity Profile | 4,4'-DDE is sensitive to exposure to light. 4,4'-DDE is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong bases. Oxidation is catalyzed by UV radiation. | | Health Hazard | A derivative of DDT; structurally and toxicproperties are similar to those of DDT;however, the acute effects are somewhatmilder; moderately toxic by ingestion; ateratogenic substance; adequate evidence ofcarcinogenicity in experimental animals
LD50 oral (rat): 880 mg/kg
LD50 oral (mouse): 700 mg/kg. | | Fire Hazard | Flash point data for 4,4'-DDE are not available. 4,4'-DDE is probably combustible. | | Safety Profile | Suspected carcinogen withexperimental carcinogenic and neoplastigenic data. Poisonby ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutationdata reported. An insecticide. When heated todecomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cl-. | | Source | Agricultural runoff degradation of p,p′-DDT (quoted, Verschueren, 1983). | | Environmental Fate | Biological. In four successive 7-day incubation periods, p,p′-DDE (5 and 10 mg/L) was recalcitrant to degradation in a settled domestic wastewater inoculum (Tabak et al.,1981).
Photolytic. When an aqueous solution of p,p′-DDE (0.004uM) in natural water samples
collected from California and Hawaii was irradiated (maximum λ= 240 nm) for 120
hours, 62% was photooxidized to p,p′-dichlorobenzophenone (Ross and Crosby, 1985).
When p,p′-DDE in water was irradiated at 313 nm, a quantum yield of 0.3 was
achieved. A photolysis half-life of 0.9 days in summer and 6.1 days in winter by direct
sunlight at 40° latitude was observed. Photolysis products included DDMU (yield 20%),
o-chl
When p,p′-DDE in a methanol solvent was photolyzed at 260 nm, a dichloro-benzophenone,
a dichlorobiphenyl, DDMU and 3,6-dichlorofluorenone (yield 10%) formed
as the major products (Plimmer et al., 1970).
Chemical/Physical. May degrade to bis(chlorophenyl)acetic acid (DDA) and hydrochloric
acid in water (Verschueren, 1983) or oxidize to p,p′-dichlorobenzophenone using
UV light as a catalyst (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1989). | | Purification Methods | Crystallise DDE from MeOH or EtOH and dry it in vacuo. The purity is checked by TLC. [G.tzi & Stammbach Helv Chim Acta 28 569 1946, Beilstein 5 H 639, 5 III1891.] POSSIBLE CARCINOGEN. |
| | 4,4'-DDE Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|