Furaneol: Biosynthesis and Pharmacological Activities
May 10,2024
General Description
Furaneol, a key flavor compound in fermented soy sauce, is synthesized by yeast and bacteria through complex biological and chemical pathways. Yeast strain Zygosaccharomyces rouxii plays a vital role in its formation, influenced by factors like carbon sources and enzymatic processes. Bacterial synthesis, as seen in Pichia capsulata and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, highlights the diversity of organisms capable of producing Furaneol. Pharmacologically, Furaneol exhibits antimicrobial properties against pathogens and fungi, without harming human cells. Its ability to activate odor receptors, like OR5M3, sheds light on its sensory perception and potential applications in food science and medicine.Furaneol, a key flavor compound in fermented soy sauce, is synthesized by yeast and bacteria through complex biological and chemical pathways. Yeast strain Zygosaccharomyces rouxii plays a vital role in its formation, influenced by factors like carbon sources and enzymatic processes. Bacterial synthesis, as seen in Pichia capsulata and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, highlights the diversity of organisms capable of producing Furaneol. Pharmacologically, Furaneol exhibits antimicrobial properties against pathogens and fungi, without harming human cells. Its ability to activate odor receptors, like OR5M3, sheds light on its sensory perception and potential applications in food science and medicine.

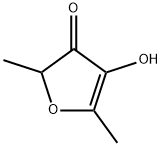
Figure 1. Furaneol
Biosynthesis
Yeast synthesis
Furaneol is a compound known for its contribution to the flavor profile of fermented soy sauce, particularly as one of the major components of the taste. Initially isolated from fermented soy sauce, it is formed through a process involving various biological and chemical reactions. In the process, a specific strain of yeast, Zygosaccharomyces rouxii, plays a crucial role. This yeast strain, when cultivated in a medium containing ribose and glycine-based amino carbonyl (Maillard) reaction products, facilitates the formation of 4-hydroxy-5-methyl-3(2H)-Furaneol (HEMF). HEMF's molecular structure, including its pentose ring and methyl side chain, originates from ribose and either D-glucose or acetaldehyde. Further experiments indicate that HEMF formation can also occur via enzymatic pathways, particularly involving the phosphorylated carbon compounds and LuxS enzyme. The involvement of LuxS enzyme, which catalyzes the formation of the extracellular signaling molecule AI-2, suggests a broader role of HEMF in intercellular communication among bacteria. Moreover, the formation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-Furaneol by Z. rouxii under different culture conditions has been studied. It was observed that HDMF formation correlates with the concentration of D-fructose-1,6-diphosphate, with external sources providing the carbon necessary for its synthesis. The process is influenced by factors such as pH, salt stress, and the presence of capturing agents for Maillard intermediates. Additionally, the chiral enrichment of HDMF, indicating stereoselective enzymatic processes, has been demonstrated through experiments with Z. rouxii and strawberry protein extracts under specific pH conditions. In summary, the synthesis of Furaneol involves a complex interplay of biological and chemical reactions, with its formation influenced by various environmental and enzymatic factors. 1
Bacterial synthesis
The synthesis of Furaneol by bacteria involves specific growth conditions and metabolic processes. For instance, in a case involving Pichia capsulata grown on a casein peptone medium containing L-arabinose, stable isotope analysis confirmed L-arabinose as the carbon source for 5-hydroxymethyl-2-Furaneol (HDMF) synthesis. Time-course experiments suggest that HDMF may be formed as an intermediate during the heat sterilization of the medium, similar to proposals for its formation by other yeasts. Furthermore, increased levels of HDMF were observed when Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris fermented in the same medium, indicating the potential for Furaneol production by various bacteria. 1
Pharmacological Activities
Furaneol exhibits significant pharmacological activities, particularly in its antimicrobial properties against human pathogens and fungi. This compound, commonly found in strawberries, pineapples, and processed foods, has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as fungi. Importantly, it shows no hemolytic effects on human red blood cells. In terms of its antifungal activity, Furaneol induces the accumulation of intracellular trehalose as a stress response marker, impacting the morphological transition of Candida albicans. By disrupting serum-induced hyphal formation, Furaneol demonstrates its efficacy against fungal infections. Furthermore, Furaneol, along with its structural analogue Sotolone, plays a crucial role in activating different odor receptors. While these compounds are important natural flavoring agents with caramel and savory notes, their activation of odor receptors is not solely determined by molecular shape but rather by specific receptor activation parameters. Recent research has identified OR5M3 as a receptor specifically activated by Furaneol and Homofuraneol, providing insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the perception of these aroma compounds. This discovery enhances our understanding of the sensory perception of Furaneol and its potential applications in various fields, including food science and medicine. 2
Reference
1. Schwab W. Natural 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (Furaneol®). Molecules. 2013; 18(6): 6936-6951.
2. Haag F, Hoffmann S, Krautwurst D. Key Food Furanones Furaneol and Sotolone Specifically Activate Distinct Odorant Receptors. J Agric Food Chem. 2021; 69(37): 10999-11005.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Unlocking the Flavor Potential of Furaneol: Applications and Toxicity Considerations in the Food Industry Dec 22, 2023
Furaneol, a widely used flavoring agent, has a sweet aroma but raises toxicity concerns due to adverse effects in animal studies, mutagenicity, and genetic damage.
- Furaneol:Activity, Application and Chemical Studies Feb 28, 2023
As the king of spices, furaneol exists in food, tobacco and beverages, and has an obvious aroma-modifying effect, so it is widely used as a flavoring agent for food, tobacco and beverages.
p-Coumaric acid's diverse bioactivities include antioxidant and antimicrobial effects. Despite limited permeability, it shows promise in melanin inhibition and transdermal delivery.....
May 10,2024APIUrolithin A's multifaceted benefits include anti-inflammatory properties, enhancing mitochondrial health and offering therapeutic potential in various health conditions.....
May 10,2024APIFuraneol
3658-77-3You may like
- Strawberry Flavor Furanone
-

- $120.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-16
- CAS:3658-77-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20ton
- Furaneol
-

- $18.00 / 10kg
- 2024-05-07
- CAS:3658-77-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99.9
- Supply Ability: 5000
- Furaneol
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-07
- CAS:3658-77-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000kg