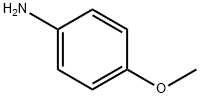
p-Anisidine synthesis
- Product Name:p-Anisidine
- CAS Number:104-94-9
- Molecular formula:C7H9NO
- Molecular Weight:123.15
Synthesis of p-Anisidine by Hydrogenation with Raney-RuNiC as Catalyst
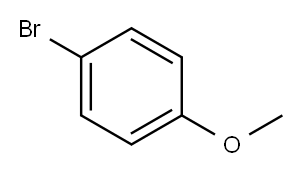
104-92-7
423 suppliers
$10.00/10g

104-94-9
472 suppliers
$9.00/1g
Yield:104-94-9 99%
Reaction Conditions:
with ammonium hydroxide;copper(l) iodide;N,N-dimethylethylenediamine in dimethyl sulfoxide at 130; for 24 h;Sealed tube;Inert atmosphere;Reagent/catalyst;
Steps:
4.2 General procedure for the synthesis of primary arylamines using CuI/DMEDA in NH4OH/DMSO (Method A)
General procedure: A 10mL-sealed tube was charged with aryl iodides or bromides (1mmol), CuI (19mg, 0.1mmol), and DMEDA (13mg/16μL, 0.15mmol) in NH4OH (1.5mL, 27% NH3 in H2O) and DMSO (0.5mL). The tube was flushed with Ar gas before being capped. The solution was stirred for the given times at 130°C or 110°C. The resulting suspension was cooled to room temperature and saturated aqueous Na2SO4 solution (5mL) was added. The resulting solution was extracted with EtOAc (20mL×3). The organic layer was separated, dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography (hexanes/EtOAc=5/1→1/2 or EtOAc) to give the desired primary arylamines.
References:
Jung, Hee Seon;Yun, Taeil;Cho, Yungyeong;Jeon, Heung Bae [Tetrahedron,2016,vol. 72,# 40,p. 5988 - 5993]
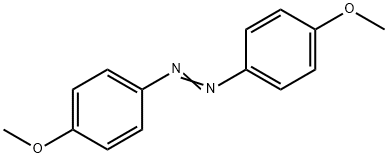
501-58-6
12 suppliers
inquiry

104-94-9
472 suppliers
$9.00/1g
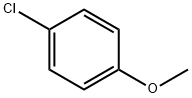
623-12-1
273 suppliers
$10.00/25g

104-94-9
472 suppliers
$9.00/1g
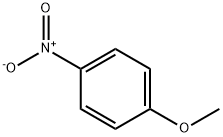
100-17-4
5 suppliers
$24.00/25g

104-94-9
472 suppliers
$9.00/1g
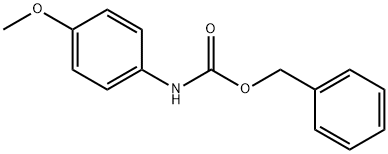
92851-13-3
18 suppliers
$175.00/500mg

104-94-9
472 suppliers
$9.00/1g