2-Methylbutyric Acid: An Overview of Its Properties, Composition, Applications, and Storage
Sep 11,2024
Introduction
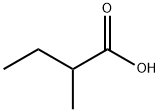
2-Methylbutyric acid, also known as isopentanoic acid, is a branched-chain fatty acid with the chemical formula C₅H₁₀O₂. As an organic compound, it is recognized for its distinctive smell, which is often described as cheesy or sweat-like, and plays a significant role in various industrial and biochemical applications. Its unique chemical structure and properties make it an essential substance in the field of chemistry, particularly in the synthesis of esters and as a flavoring agent in the food industry. This article provides an in-depth look at 2-methylbutyric acid, focusing on its properties, composition, applications, and proper storage methods.

Figure 1 Characteristics of 2-Methylbutyric Acid
Properties of 2-methyl-butyric Acid
2-Methylbutyric acid is a colorless liquid at room temperature with a sharp, penetrating odor. Its molecular structure consists of a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a four-carbon branched chain, making it an aliphatic carboxylic acid. The acid's physical and chemical properties are as follows:
Molecular Formula: C₅H₁₀O₂
Molecular Weight: 102.13 g/mol
Boiling Point: Approximately 176°C (349°F)
Melting Point: -29°C (-20°F)
Density: 0.944 g/cm³
Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, but highly soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and chloroform.
The slightly polar nature of 2-methylbutyric acid due to its carboxyl group allows it to engage in hydrogen bonding, which influences its solubility and boiling point. These properties are crucial in determining its behavior in various chemical reactions and applications.
Main Components and Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of 2-methylbutyric acid is relatively simple, with its primary components being carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms arranged in a specific molecular structure. The acid is one of the isomers of valeric acid (pentanoic acid) and differs from its structural isomer, 3-methylbutyric acid (isovaleric acid), in the position of the methyl group attached to the carbon chain.
The chemical structure of 2-methyl butyric acid is as follows:
Carbon Skeleton: Four carbon atoms form the backbone of the molecule, with one of these carbons also bonded to a methyl group (-CH₃).
Carboxyl Group: The terminal carbon in the chain is bonded to a carboxyl group (-COOH), which is responsible for the compound's acidic properties.
This structure results in a branched-chain acid with a slightly lower boiling point compared to its straight-chain counterparts, due to the presence of the methyl group, which reduces the intermolecular forces between molecules.
Applications of 2-methyl butyric Acid
2-Methylbutyric acid finds diverse applications across various industries, thanks to its unique properties. Some of its primary uses include:
Flavoring and Fragrance Industry: One of the most notable applications of 2-methylbutyric acid is in the flavor and fragrance industry. Due to its pungent odor, it is often used as a flavoring agent in food products, particularly in the formulation of cheese, butter, and fruit flavors. It is also utilized in the creation of artificial fragrances, where its sharp, sour scent contributes to the overall aroma profile of products like perfumes and scented candles.
Chemical Synthesis: In organic chemistry, 2-methylbutyric acid serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of various esters and other organic compounds. The acid's ability to form esters with alcohols makes it valuable in the production of flavorings, plasticizers, and pharmaceuticals. Its reactivity with alcohols to produce esters like 2-methylbutyl acetate is particularly important in the flavoring industry.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Although not as common as in other applications, 2-methylbutyric acid is sometimes used in the pharmaceutical industry as a precursor in the synthesis of certain drugs. Its derivatives are studied for potential therapeutic properties, although this area of application is still under exploration.
Agriculture: In agriculture, 2-methylbutyric acid has been researched for its potential as a pheromone in pest control. Certain insects are attracted or repelled by specific odors, and 2-methylbutyric acid can be utilized in developing environmentally friendly pest management strategies.
Storage and Handling of 2-Methylbutyric Acid
Proper storage and handling of 2-methylbutyric acid are essential to maintain its stability and prevent hazardous situations. The acid should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area, away from sources of ignition and incompatible substances such as strong oxidizing agents. It is typically kept in tightly sealed containers made of materials resistant to organic acids, such as glass or certain plastics.
Temperature: To ensure stability, 2-methylbutyric acid should be stored at a temperature below its boiling point, ideally in a controlled environment between 15°C and 25°C. Freezing should be avoided as it may lead to changes in the acid’s physical properties upon thawing.
Ventilation: Good ventilation is crucial when handling 2-methylbutyric acid due to its strong odor and potential for irritating the respiratory system. In industrial settings, appropriate ventilation systems should be in place to prevent the accumulation of vapors.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When handling 2-methylbutyric acid, proper personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and lab coats, should be worn to avoid skin and eye contact. In case of spills, appropriate neutralization and cleaning protocols should be followed.
Compatibility: Care should be taken to store 2-methylbutyric acid away from incompatible materials, particularly strong bases and oxidizing agents, as reactions with these substances could result in hazardous conditions.
Conclusion
2-Methylbutyric acid is a versatile compound with a range of applications across various industries, from food flavoring and fragrance production to chemical synthesis and potential agricultural uses. Its unique chemical structure and properties make it an important substance in organic chemistry. However, due to its strong odor and potential hazards, proper handling and storage are crucial to ensure safety and maintain the compound's efficacy. As research continues, 2-methylbutyric acid may find even more diverse applications, further solidifying its role in the chemical industry.
![]() Reference
Reference
[1] Lee Y S, Cho J Y, Moon J H, et al. Identification of 2-methylbutyric Acid as a Nematicidal Metabolite, and Biocontrol and Biofertilization Potentials of Bacillus pumilus L1[J]. Korean Journal of Soil Science and Fertilizer, 2016, 49(4): 401-408.
[2] Attygalle A B, Wu X, Will K W. Biosynthesis of tiglic, ethacrylic, and 2-methylbutyric acids in a carabid beetle, Pterostichus (Hypherpes) californicus[J]. Journal of chemical ecology, 2007, 33: 963-970.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
L-Hydroxyproline (Hydroxyproline, Hyp) is an important amino acid, accounting for about 13% of the collagen content of amino acids.....
Sep 10,2024Amino Acids and DerivativesLithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF?) has emerged as a cornerstone in the field of electrochemistry, particularly within the context of lithium-ion batteries.....
Sep 11,2024API2-Methyl butyric acid
116-53-0You may like
2-Methyl butyric acid manufacturers
- 2-Methyl butyric acid
-

- $50.00 / 1KG
- 2024-10-11
- CAS:116-53-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000kg
- 2-Methyl butyric acid
-

- $0.00 / 25kg
- 2024-10-11
- CAS:116-53-0
- Min. Order: 25kg
- Purity: 98%min
- Supply Ability: 1000kg
- 2-Methyl butyric acid
-

- $3.50 / 1kg
- 2024-10-11
- CAS:116-53-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: ≥99%
- Supply Ability: 3000tons/month