Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt: Antifungal Activity and Applications in Cellular Imaging
May 28,2024
General Description
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt shows promising antifungal activity against Fusarium graminearum, reducing mycotoxin production and inhibiting fungal cell wall synthesis through chelation of essential ions. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt offers a new approach to combat resistance in fungi, making it effective in managing infections and reducing health risks in crops. Additionally, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt plays a critical role in synthesizing silicon nanoparticles with high fluorescence quantum yield, enhancing bioimaging applications. Its use as a reductant leads to the production of biocompatible nanoparticles suitable for cellular imaging, contributing to advancements in biological research and medical diagnostics.

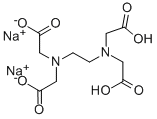
Figure 1. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt
Antifungal Activity
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt is emerging as a promising antifungal agent against Fusarium graminearum, a fungus notorious for causing significant agricultural losses and producing harmful mycotoxins like deoxynivalenol (DON). This compound acts through mechanisms distinct from traditional fungicides, which is crucial given the rising resistance of Fusarium species to common fungicidal chemicals. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt's effectiveness was demonstrated in several studies, including laboratory tests and field trials. Laboratory results showed that applying Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt at a concentration of 4 mM could suppress the infection of wheat seedlings by over 90%, a similar efficacy observed in field conditions. This highlights its potential practical applicability in managing Fusarium infections in agricultural settings. One of the key mechanisms by which Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt exerts its antifungal effects is through the inhibition of DON biosynthesis. Mycotoxin production assays indicated that even at a lower concentration of 0.4 mM, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt could reduce DON production by 47% compared to untreated controls. This significant decrease in toxin production could potentially reduce the health risks associated with the consumption of Fusarium-contaminated grains. Furthermore, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt disrupts the fungal cell structure by targeting chitin synthase activity, an essential enzyme for fungal cell wall synthesis. Chitin synthases in Fusarium are dependent on manganese (Mn2+) ions for their activity. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt acts by chelating Mn2+ ions, leading to a deficiency of this critical cofactor within the fungal cells, thereby inhibiting chitin synthase activity. This action not only impedes the growth and proliferation of the fungus but also compromises the integrity of the fungal cell wall and cytomembrane. The inhibition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production and the downregulation of several TRI genes involved in trichothecene biosynthesis are additional pathways through which Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt demonstrates its antifungal activities. These findings underscore the multifaceted mechanisms of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt and support its potential as an effective fungicide candidate for controlling Fusarium head blight (FHB) and reducing DON levels in crops. This compound offers a promising alternative to combat fungal resistance and ensure crop safety and yield. 1
Applications in Cellular Imaging
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt plays a crucial role in the synthesis of silicon nanoparticles (Si NPs) used in cellular imaging. Due to their excellent photoluminescence, robust chemical inertness, and low cytotoxicity, Si NPs are ideal candidates for bioimaging applications. However, producing Si NPs with high fluorescence quantum yield (QY) has been a challenge, limiting their broader use. In recent advancements, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt has been utilized as an effective reductant in a mild, simple, and green one-pot synthesis method to create N-doped fluorescent Si NPs. This innovative approach has led to the production of Si NPs with an ultrahigh QY of up to 62%. The use of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt in this process is pivotal, as it not only acts as a reducing agent but also enhances the luminescence properties of the nanoparticles. The Si NPs produced using ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt exhibit several desirable features, including small size (approximately 2 nm), water dispersibility, robust stability, and biocompatibility. These properties make them exceptionally suitable for cellular imaging. The effectiveness of these nanoparticles was demonstrated in practical applications, where they were used for cellular imaging with satisfactory results. This highlights the potential of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt-synthesized Si NPs in various bioimaging applications. Overall, the use of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt in the synthesis of fluorescent Si NPs represents a significant advancement in the field of cellular imaging. By facilitating the production of high-quality Si NPs, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt contributes to the broader applicability and effectiveness of nanoparticle-based imaging techniques in biological research and medical diagnostics. 2
Reference
1. Song XS, Gu KX, Gao J, Wang JX, Ding SC, Zhou M. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt Acts as an Antifungal Candidate Molecule against Fusariumgraminearum by Inhibiting DON Biosynthesis and Chitin Synthase Activity. Toxins (Basel). 2020; 13(1): 17.
2. Geng X, Li Z, Hu Y, et al. One-Pot Green Synthesis of Ultrabright N-Doped Fluorescent Silicon Nanoparticles for Cellular Imaging by Using Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt as an Effective Reductant. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10(33): 27979-27986.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Mechanism of EDTA Mar 21, 2022
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt also known as disodium ethylenediamine tetraacetate, commonly known as disodium ethylenedicarboxylate
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt Nov 10, 2021
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA) (CAS: 139-33-3) is a good compounding agent. It has six coordination atoms, and the complex formed is called a chelate. EDTA is often used in coord
Butyl Isocyanate is a colourless liquid, it may polymerize due to heating. Decomposes on burning.....
Jan 26,2025Organic Chemistry4-Chlorobenzaldehyde plays a vital role in medicinal chemistry, enabling the creation of diverse pharmacological agents, though its handling necessitates caution due to associated health hazards.....
May 28,2024APIYou may like
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt manufacturers
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt
-

- $5.00 / 25kg
- 2025-01-24
- CAS:139-33-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: ≥99%
- Supply Ability: 2000mt/year
- EDTA-2NA
-

- $99.00 / 1kg
- 2025-01-24
- CAS:139-33-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5000 ton
- Disodium EDTA
-

- $60.00 / 1kg
- 2025-01-24
- CAS:139-33-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99
- Supply Ability: 5000