Maytansine: Unveiling the Potential of a Plant-Derived Compound in Targeted Cancer Therapy
Apr 19,2024
Introduction
Maytansine, a potent plant-derived compound, has intrigued the scientific community since its discovery in 1972 from the Ethiopian shrub Maytenus serrata. Characterized by its potent antimitotic activity, Maytansine has emerged as a focal point in the development of anticancer drugs. Despite its initial toxicity challenges in clinical settings, Maytansine has found new life in the realm of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), showcasing significant promise in targeted cancer therapy[1].
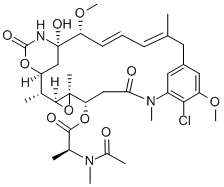
Figure 1molecular structure diagram of Maytansine
Production Methods
The journey of Maytansine production epitomizes the fusion of age-old botanical extraction methods with cutting-edge biotechnological innovations. Originating from the intricate biological matrices of certain African shrubs, such as Maytenus serrata, the initial extraction of Maytansine highlighted both its rarity and the complexity of sourcing sufficient quantities from natural habitats. These challenges underscored the necessity for scalable production solutions, leading researchers to explore and eventually harness the power of microbial fermentation as a viable production method.
Advancements in recombinant DNA technology have been pivotal in this transition. By inserting genes responsible for Maytansine synthesis into the DNA of microorganisms, scientists have been able to turn these living cells into efficient, bio-based factories for Maytansine production. This genetic engineering feat not only surmounted the hurdles of extracting the compound from its natural sources but also significantly improved the efficiency and sustainability of the production process. Microbial fermentation, facilitated by genetically modified microorganisms, now allows for the controlled and scalable production of Maytansine and its derivatives under laboratory conditions. This method offers numerous advantages, including consistency in product quality, scalability of production, and a reduced environmental footprint compared to traditional extraction techniques.
Furthermore, the synthetic production of Maytansine via microbial fermentation has opened new avenues for the development of its analogs. These analogs, designed to possess similar pharmacological properties with potentially reduced toxicity or enhanced efficacy, are synthesized through the manipulation of the microbial production pathways. By tweaking the genetic makeup of the microorganisms or altering fermentation conditions, researchers can now explore a wider array of Maytansine-like molecules, broadening the horizons for therapeutic applications.
Pharmacological Effects
At the molecular level, Maytansine exhibits a remarkable mechanism of action by targeting the microtubules essential for cell division, making it a powerful agent against rapidly proliferating cancer cells. Its binding affinity to tubulin disrupts microtubule dynamics, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in tumor cells. Despite its potency, the direct application of Maytansine as a therapeutic agent has been limited due to systemic toxicity. The breakthrough came with the development of Maytansine-loaded ADCs, where the compound is conjugated to antibodies specific to cancer cell antigens, allowing for targeted delivery. This section delves into the pharmacodynamics of Maytansine, highlighting its transformative impact on cancer therapy through ADC technology.
Storage and Handling Characteristics
The stability and storage of Maytansine are critical for its effectiveness and safety as a pharmaceutical compound. This segment covers the chemical stability of Maytansine under various conditions, including temperature, pH, and light exposure, providing guidelines for optimal storage to maintain its therapeutic integrity. Additionally, the handling precautions necessary to ensure the safe handling of this cytotoxic agent are discussed, including measures to prevent exposure and degradation during transport and use in clinical settings.
Conclusion
Maytansine's journey from a natural extract with cytotoxic challenges to a cornerstone of innovative cancer treatment strategies underscores its significance in the field of medicinal chemistry. The ongoing research and development of Maytansine-based ADCs represent a promising frontier in targeted cancer therapy, offering a glimpse into the future of oncological treatments. As the scientific community continues to unravel the potential of Maytansine and its derivatives, its story exemplifies the relentless pursuit of therapeutic excellence in the battle against cancer[2].
References
[1]Issell BF, Crooke S T. Maytansine[J]. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 1978, 5(4): 199-207.
[2]Remillard S, Rebhun L I, Howie G A, et al. The antimitotic activity of the potent tumor inhibitor maytansine[J]. Science, 1975, 189(4207): 1002-1005.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What is Maytansine? Sep 7, 2023
Maytansine is an important antineoplastic and antimicrobial compound with high cytotoxicity.
1,7-Dimethylxanthine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound that can enhance alertness and reduce drowsiness.....
Feb 27,2025API1-PHENYL-2-PROPANOL, a compound with a distinctive chemical structure, is not merely a molecule but a cornerstone in the realm of organic chemistry.....
Apr 19,2024APIMaytansine
35846-53-8You may like
Maytansine manufacturers
- Maytansine
-

- $59.00 / 5mg
- 2024-11-19
- CAS:35846-53-8
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.62%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Maytansine
-

- $10.00 / 1Kg/Bag
- 2021-08-31
- CAS:35846-53-8
- Min. Order: 1Kg/Bag
- Purity: 99%min
- Supply Ability: 2000
- maytansine
-

- $15.00 / 1KG
- 2021-07-13
- CAS:35846-53-8
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%+ HPLC
- Supply Ability: Monthly supply of 1 ton