Polyethyleneimine: Overview and Applications in Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment
Mar 8,2024
General Description
Polyethyleneimine, a cationic polymer characterized by its unique distribution of amino groups, plays a pivotal role in diverse industrial and biomedical applications due to its structural versatility and cost-effectiveness. In cancer treatment, Polyethyleneimine enhances chemotherapy efficacy by overcoming multidrug resistance through effective drug conjugation and targeted delivery, facilitated by its ability to form stable nanoparticles and ensure controlled drug release in tumor environments. Additionally, as a nonviral vector in gene therapy, Polyethyleneimine's efficiency is tempered by its cytotoxicity, prompting modifications like conjugation with biocompatible substances to improve safety and targeting. These adaptations underscore Polyethyleneimine's potential for advancing therapeutic strategies, particularly in cancer treatment and gene therapy, by leveraging its unique properties and addressing its limitations.

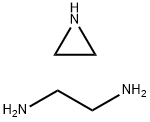
Figure 1. Polyethyleneimine
Overview
Polyethyleneimine is a versatile cationic polymer recognized for its unique composition of primary, secondary, and tertiary amino groups in a 1:2:1 ratio, exhibiting strong positive charges. This polymer is available in two structural forms: linear and branched, with molecular weights varying from 700 Da to 1000 kDa, depending on the degree of polymerization. The synthesis of Polyethyleneimine is straightforward, involving a simple one-step reaction using an AB-type monomer. Its cost-effectiveness compared to dendrimers of similar molecular weight makes Polyethyleneimine an attractive option for various applications. Polyethyleneimine's abundant amino groups contribute to its widespread usage across different sectors. Industrially, it serves as a flocculant for oil removal in water treatment, a wet strength agent in paper manufacturing, and an ingredient in shampoo production. In the biomedical field, Polyethyleneimine is instrumental in enzyme immobilization, virus immobilization on cellulose, cell adhesion, gene transfection, and the synthesis of nanoparticles (NPs) to improve stability and anticancer efficacy. Branched Polyethyleneimine, characterized by a hyperbranched structure synthesized through the monomer method, excels in gene transfection, drug delivery, and molecular imaging due to its ability to encapsulate NPs and stabilize metal ions through coordination interaction. Linear Polyethyleneimine, on the other hand, contains only secondary amines and is solid at room temperature, distinguishing itself with antibacterial properties and high efficiency as a nonviral gene vector. 1
Polyethyleneimine-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment
Chemotherapy
Polyethyleneimine has emerged as a significant player in enhancing chemotherapy's efficacy, particularly in overcoming multidrug resistance (MDR), a prevalent cause of treatment failure in cancer. Due to its unique structure, PEI can effectively coat or conjugate with anticancer drugs, such as Doxorubicin (DOX), facilitating improved drug delivery efficiency. The amino groups on Polyethyleneimine's surface allow for functionalization, enabling targeted drug delivery, which further enhances the therapeutic outcomes. Studies have demonstrated that PEI-based nanoparticles can stabilize drug molecules and ensure their controlled release under specific conditions, such as lower pH levels typical of tumor environments. This pH-sensitive release mechanism ensures that drugs are more effectively delivered to and retained within cancer cells, thereby increasing their cytotoxic impact while minimizing effects on healthy cells. For instance, by modifying Polyethyleneimine with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and linking DOX through a pH-sensitive bond, researchers have developed systems that show enhanced ability to circumvent MDR, allowing for more effective drug accumulation in both the cytoplasm and nucleus of cancer cells. This approach not only improves the direct antitumor activity of the drugs but also facilitates the co-delivery of nucleic acids, offering a dual therapeutic strategy that combines chemotherapy with gene therapy to more effectively target and destroy cancer cells. Through such innovations, Polyethyleneimine stands out as a promising tool in the development of more efficient and targeted chemotherapy treatments, offering hope for better outcomes in cancer therapy. 2
Gene Therapy
Polyethyleneimine is a key nonviral vector in gene therapy, known for its efficient delivery of genetic material via the proton sponge effect. However, its clinical application has been limited due to high cytotoxicity. To mitigate this issue, researchers have developed various strategies to modify Polyethyleneimine, enhancing its biocompatibility while maintaining gene delivery efficiency. Modifications include conjugation with lithocholic acid and hyaluronic acid to reduce toxicity, cysteamine-modified gold nanoparticles for targeted siRNA delivery, polyethylene glycol conjugation to improve biocompatibility, and sodium alginate modification to stabilize Polyethyleneimine/DNA complexes and enhance tumor targeting. These innovative approaches signify progress towards safer, more effective gene therapy applications, leveraging Polyethyleneimine's potential while addressing its limitations. 2
Reference
1. Fahira AI, Amalia R, Barliana MI, Gatera VA, Abdulah R. Polyethyleneimine (PEI) as a Polymer-Based Co-Delivery System for Breast Cancer Therapy. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2022;14:71-83.
2. Zhao C, Zhou B. Polyethyleneimine-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Theranostics. J Funct Biomater. 2022;14(1):12.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Non-viral vector polyethyleneimine in light anticancer therapeutic strategies Nov 27, 2023
Polyethyleneimine (PEI) is a synthetic, water-soluble, linear or branched polymer. Polyethyleneimine-based lipopolyplexes as carriers in anticancer gene therapies.
- What is branched polyethylenimine? Mar 10, 2023
Branched polyethylenimine acts as an auxiliary agent. It is used in paper-making, water treatment, detergents, adhesives and cosmetics.
Perfluorotributylamine, valued for stability in electronics and tumor treatment, poses environmental and health risks requiring regulatory control and alternative exploration.....
Nov 13,2024APINowadays, more than 40% of the total production of BDO is manufactured by the eppe process, and more than 30% of the total production of BDO is manufactured by the direct hydrogenation of maleic anhydride.....
Mar 8,2024Organic Chemistrypolyethyleneimine
25987-06-8You may like
polyethyleneimine manufacturers
- Polyethylenimine
-

- $0.00 / 200KG
- 2024-10-31
- CAS:25987-06-8
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg
- Polyethylenimine
-

- $30.00 / 1kg
- 2024-10-25
- CAS:25987-06-8
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 10 tons
- Polyethylenimine
-

- $15.00 / 1KG
- 2024-10-11
- CAS:25987-06-8
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000kg