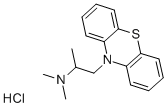
Promethazine Hydrochloride: Overview
Oct 22,2024
Promethazine hydrochloride salt form of promethazine, a phenothiazine derivative with antihistaminic, sedative and antiemetic properties. Promethazine hydrochloride selectively blocks peripheral H1 receptors thereby diminishing the effects of histamine on effector cells. Promethazine hydrochloride also blocks the central histaminergic receptors, thereby depressing the reticular system causing sedative and hypnotic effects.

FDA approved-indications
Promethazine hydrochloride is used to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting related to certain conditions (such as before/after surgery, motion sickness). It is also used to treat allergy symptoms such as rash, itching, and runny nose. It may be used to help you feel sleepy/relaxed before and after surgery or to help certain opioid pain relievers (such as meperidine) work better. It may also be used for a short time to treat a runny nose due to the common cold.
Promethazine is an antihistamine and works by blocking a certain natural substance (histamine) that your body makes during an allergic reaction. Its other effects (such as anti-nausea, calming, pain relief) may work by affecting other natural substances (such as acetylcholine) and by acting directly on certain parts of the brain.
References:
[1] Promethazine[J]. Reactions Weekly, 2022, 1935 1: 367-367. DOI:10.1007/s40278-022-29162-0.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringHafnium tetrachloride (HfCl4) is a metal inorganic salt compound commonly used as a precursor for the production of hafnium metal and various hafnium compounds.....
Oct 23,2024APIPromethazine hydrochloride
58-33-3You may like
Promethazine hydrochloride manufacturers
- Promethazine hydrochloride
-

- $29.00 / 1g
- 2025-12-18
- CAS:58-33-3
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 95.36%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Promethazine hydrochloride
-

- $29.00 / 1g
- 2025-12-18
- CAS:58-33-3
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 95.36%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Promethazine hydrochloride
-

- $10.00 / 1ASSAYS
- 2025-12-18
- CAS:58-33-3
- Min. Order: 1ASSAYS
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1 ton