Tert-Butylhydroquinone: Effects on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Oct 23,2024
General Description
Tert-Butylhydroquinone, a potent synthetic antioxidant, demonstrates remarkable efficacy in combating oxidative stress and inflammation-related disorders. By activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway, it regulates inflammation and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines. Its actions on NF-κB pathway alleviate intestinal inflammation and improve cardiac health during myocardial ischemia. Additionally, Tert-Butylhydroquinone mitigates oxidative stress by enhancing antioxidant enzymes and modulating the Nrf2-Keap1-ARE pathway. Due to its antioxidant activity, researchers explored its effect against Cis-induced testicular toxicity.1

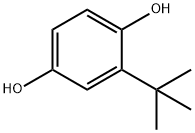
Figure 1. Tert-Butylhydroquinone
Background
Cisplatin (Cis) is a widely known anti-neoplastic drug which is effective in the treatment of different kinds of cancers, like; head, neck, lung, cervical, bladder and testicular cancer. Cis possesses DNA-alkylation effect since it can form both inter and intra-strand DNA adducts, which inhibits DNA synthesis/repair, leading to cancer cell cycle arrest. Due to the unspecific nature of most anti-neoplastic agents, administration of the therapeutic dose can cause some negative effects, which may be influenced by the patient’s age, presence of other underlying medical conditions, etc. However, the toxic effects that may require hospitalization are mostly dose and duration dependent.
Following prolonged use, cancer cells develop Cis resistance, requiring dose scaling for effectiveness. Unfortunately, this high dose is reported to be responsible for the multi-organ toxicities associated with Cis chemotherapy. Furthermore, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis are the major reported mechanisms that are responsible for Cis toxicity in non-target tissues.
Since Tert-Butylhydroquinone(tBHQ) demonstrates considerable antioxidant activity, the present study explored its effect against Cis-induced testicular toxicity. Particularly, we investigated the protective effects of Tert-Butylhydroquinone on Cis-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis, in addition to two important testicular processes; steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis.
Experiment
Twenty-four male Wistar rats were randomly assigned into four groups (n = 6) as follows; (1) normal control (NC) group which received 1 % DMSO (vehicle for Tert-Butylhydroquinone) orally for 14 days and intraperitoneal (i.p) injection of normal saline on Day 8; (2) Tert-Butylhydroquinone group which received 50 mg/kg b.w. of tBHQ in 1 % DMSO orally for 14 days and normal saline i.p on Day 8; (3) Cisplatin (Cis) group which received 1 % DMSO orally for 14 days, and Cis (7 mg/kg b.w., i.p.) on Day 8; (4) tBHQ+Cis group which received Tert-Butylhydroquinone as in group 2 and Cis on Day 8 as in group 3. The dose for Cis used in the present study was earlier reported to trigger significant testicular oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. The dose for tBHQ was selected after a preliminary experiment which employed tBHQ at 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg b.w. for 7 days. The dose of 50 mg/kg b.w. had no negative effects on liver enzymes and sperm parameters, hence, this dose was selected for the present study. Furthermore, this dose has been previously reported to activate Nrf2/ARE pathway and reduce apoptosis. The oral route of administration was selected to better represent the route through which this food additive enters the body.
Result
Cis significantly upregulated the pro-inflammatory NF-κB, iNOS and TNF-α genes, and downregulated the anti-inflammatory IL-10 gene relative to NC group. Intervention with tBHQ significantly downregulated NF-κB, iNOS and TNF-α genes, and upregulated IL-10 gene relative to Cis group.
Similarly, the pro-apoptotic Bax, Bax/Bcl2 ratio and caspase-3 genes where significantly upregulated, while the anti-apoptotic Bcl2 gene was significantly downregulated in Cis group relative to the NC group. However, Tert-Butylhydroquinone significantly downregulated the pro-apoptotic genes expression (Bax, Bax/Bcl2 ratio and caspase-3) and upregulated the anti-apoptotic Bcl2 gene expression relative to Cis group. To confirm these findings on apoptotic genes, authors assessed the immunoexpression of cleaved caspase-3 in the testis and found that the expression was highest in Cis group, which was significantly increased relative to NC group, but significantly decreased in tBHQ+Cis group relative to the Cis group.
Cis significantly decreased the number of viable testicular germ cells as evident in the significant decrease in the immunoexpression of PCNA in the testis relative to the NC group. Intervention with Tert-Butylhydroquinone significantly increased the immunoexpression of PCNA relative to Cis group.
References:
[1] VICTOR UDO NNA . Tert-butylhydroquinone preserve testicular steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in cisplatin-intoxicated rats by targeting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis[J]. Toxicology, 2020, 441. DOI:10.1016/j.tox.2020.152528.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
1,7-Dimethylxanthine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound that can enhance alertness and reduce drowsiness.....
Feb 27,2025APITestosterone propionate enhances BM-MSCs' proliferation and viability, while also reducing leukemia cell viability, through inflammatory signaling modulation, promising in cancer therapy.....
Nov 4,2024APItert-Butylhydroquinone
1948-33-0You may like
tert-Butylhydroquinone manufacturers
- tert-Butylhydroquinone
-
- $20.00 / 1KG
- 2025-04-23
- CAS:1948-33-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt
- tert-Butylhydroquinone
-

- $900.00/ ton
- 2025-04-23
- CAS:1948-33-0
- Min. Order: 1ton
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5000
- tert-Butylhydroquinone
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-21
- CAS:1948-33-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month