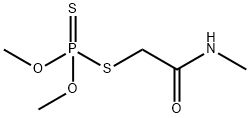
What is Dimethoate?
Oct 11,2021
Dimethoate is an organophosphorus insecticide–acaricide that is effective against a wide range of insect pests on agricultural crops and lawns, among other applications.
Uses
Dimethoate is a systemic and contact insecticide–acaricide used on a range of insects including mites, flies, aphids, and plant hoppers. All nonagricultural uses of dimethoate in the United States were canceled in 2000. Dimethoate is used very commonly in livestock for the control of botflies and mites. Formulations include aerosols, dusts, granules, and emulsifiable concentrates. Dimethoate continues to rank in the top 10 of pesticides used in the United States based on pounds active ingredient applied per year.

Mechanism of Toxicity
The acute toxicity of dimethoate is caused by inhibition of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Dimethoate is an indirect inhibitor of cholinesterases. The active oxidative metabolite (i.e., omethoate) is two to three times more potent in inhibiting acetylcholinesterase than the parent compound. The Ndemethylated omethoate may be the most potent metabolite. The enzyme in red blood cells may be more sensitive to inhibition than plasma enzyme following dimethoate exposure. The signs of toxicity associated with exposure to dimethoate are generally similar to those caused by other organophosphorus insecticides (see Cholinesterase Inhibition).
Environmental Fate
Dimethoate has low persistence in soil. It is primarily dissipated via microbial hydrolyses and oxidations in aerobic soils, with a half-life of about 2–4 days. O-desmethyl dimethoate and O,O-dimethyl thiophosphoric acid were noted under aerobic conditions. Under some field conditions, omethoate can be found in soils. This more toxic metabolite also shows persistence. Although less prominent, anaerobic soil dissipation is also possible. Dimethoate does not exhibit significant photodegradation in soils. It is highly soluble in water and shows only weak adsorption to soil particulates, which suggests the possibility of leaching. Dimethoate hydrolyzes rapidly under alkaline conditions (half-life at pH 9 at 25℃ is about 4 days) leading to O-desmethyl dimethoate and O,O-dimethyl thiophosphoric acid. In neutral to acidic conditions, greater persistence is noted. Dimethoate also shows little photodegradation in water. In surface waters, dimethoate and O-desmethyl dimethoate are detected. Dimethoate is not expected to persist in air or be substantially transported via the atmosphere. Dimethoate is metabolized in certain crop plants, with the potential for generating the more reactive metabolite, omethoate.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Toxicity of Dimethoate Jan 19, 2022
Dimethoate is an organophosphorus insecticide–acaricide that is effective against a wide range of insect pests on agricultural crops and lawns, among other applications.
Isotretinoin is the 9-cis isomer of retinoic acid, a close relative of retinol, or vitamin A. First shown to be an effective treatment for acne in 1982, its development stemmed from advances in knowledge of the effects of vitamin A to reduc....
Oct 11,2021APIDimethyl ether(DME), also known as methyl ether and methoxymethane, is the simplest fatty ether. It is a derivative of the dehydration condensation of two molecules of methanol.....
Oct 12,2021Organic ChemistryDimethoate
60-51-5You may like
- Dimethoate
-

- $0.00 / 25kg
- 2025-04-11
- CAS:60-51-5
- Min. Order: 100kg
- Purity: 98
- Supply Ability: 10000
- Dimethoate
-

- $29.00 / 50mg
- 2024-11-19
- CAS:60-51-5
- Min. Order:
- Purity: ≥98%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Dimethoate
-
- $8.00 / 1kg
- 2024-04-05
- CAS:60-51-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: g-kg-tons, free sample is available