Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
Bromodiphenylmethane: Overview, Applications in Synthesis of N-Substituted Benzamides and Preparation
Bromodiphenylmethane enables N-substituted benzamide synthesis for pain treatment, showcasing its value and potential in pharmaceutical research and industrial applications.
Apr 2,2024 APIThe brief introduction of Sorafenib
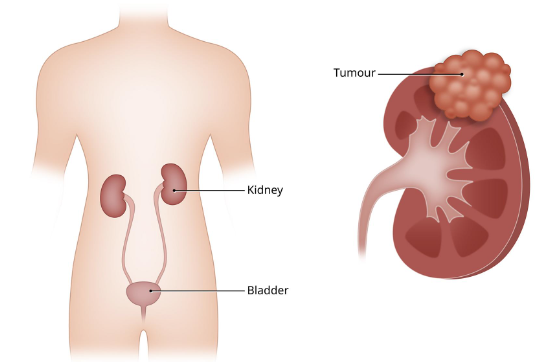
Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor that has recently obtained Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Apr 1,2024 APICinacalcet hydrochloride: A novel calcimimetic
Oral cinacalcet hydrochloride (HCl) is the first in a new class of therapeutic agents, calcimimetics, and has a novel mechanism of action. Cinacalcet hydrochloride classifies as a "calcimimetic."
Apr 1,2024 APIZineb: Overview, Preparation and Toxicological Effects
Zineb effectively fights fungal diseases but may pose toxicological risks, requiring responsible usage for crop management.
Apr 1,2024 APIAvatrombopag: Pharmacodynamic Properties, Therapeutic Efficacy, Dosage and Administration
Avatrombopag, a thrombopoietin receptor agonist, boosts platelet production without affecting function, offering potential treatment for ITP and CLD-associated thrombocytopenia.
Apr 1,2024 APIButyl Lactate: Natural Occurrence, Versatile applications and Safety Assessment
Butyl lactate, a natural flavor compound in foods and beverages, serves as a versatile solvent in various industries, with low risk in safety assessments.
Apr 1,2024 APIWhat is the difference between imatinib and nilotinib?
Nilotinib, an orally bioavailable, selective Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is 30-fold more potent than imatinib in pre-clinical models, and overcomes most imatinib resistant BCR-ABL mutations.
Mar 29,2024 APIDasatinib: Mechanism of action and Safety
Dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, primarily treats chronic myeloid leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Mar 29,2024 APILemborexant: A Dual Orexin Receptor Antagonist with Favorable Safety and Pharmacokinetic Profiles
Lemborexant promotes sleep by targeting orexin receptors, with good tolerability in adults. Caution advised for respiratory issues and potential drug interactions require careful management.
Mar 29,2024 APIThe Origin, Mechanism, Potential Benefits, and Disputes of YK11
YK11 was first studied in 2011 and was found to be a partial agonist of androgen receptor (AR) with genetic selectivity.
Mar 29,2024 API