Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
Is 4-Butylresorcinol safe in the treatment of melasma?
4-Butylresorcinol 0.1% Cream has shown rapid efficacy and good tolerability when used in the treatment of melasma.
Jan 3,2024 APIGlycerol: Uses; Side Effects and Precautions
Glycerin is FDA-approved for the treatment of constipation. The use of glycerin as a suppository or rectal enema may reduce constipation in adults and children at least 2 years of age.
Jan 3,2024 APIPolarity of Aluminium oxide
Aluminium oxide is a polar column chromatography adsorbent that can be separated by polar interactions.
Jan 3,2024 APIN,N-Dimethylformamide: Polarity and Application
N,N-Dimethylformamide is a colourless, odourless liquid solvent. It is miscible with water and many organic liquids. It has a polarity index of 6.4, a dipole moment of 3.86, and a dielectric constant
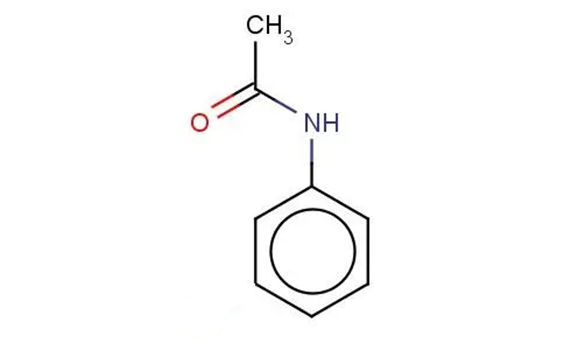
Jan 3,2024 APIPolarity of Acetanilide
Acetanilide has several polar bonds, therefore, acetanilide is a polar molecule. Water is also a polar molecule, so acetanilide is moderately soluble in boiling water, but much less soluble in room te
Jan 3,2024 APIUnderstanding the Diverse Applications and Potential Hazards of Sodium Thiocyanate
Sodium thiocyanate is a white crystalline powder and highly soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone. It has various industrial applications but poses health risks and environmental hazards.
Jan 3,2024 APIPyromellitic Dianhydride: A Promising Candidate for Creating Functional Carriersbility and Safety
Pyromellitic dianhydride is a white powder with moderate lipophilicity, used to synthesize cyclodextrin polymers for drug delivery, but poses safety hazards.
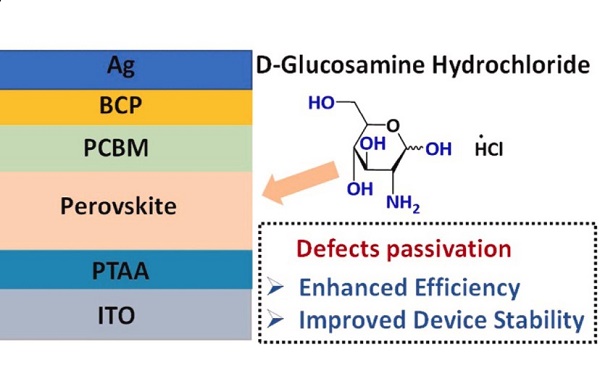
Jan 3,2024 APIThe uses of D-Glucosamine hydrochloride.
D-glucosamine hydrochloride is an endogenous amino monosaccharide synthesized from glucose that is useful in the treatment of joint diseases in both humans and animals.
Jan 3,2024 APISalcaprozate Sodium Facilitates Oral Delivery of Low-Permeability Drugs
Salcaprozate sodium enhances API absorption, potentially improving drug efficacy and bioavailability. Extensively studied in oral formulations, it is deemed safe by the FDA.
Jan 3,2024 APIUnderstanding the Applications and Safety Considerations of (2-Bromoethyl)benzene
(2-Bromoethyl)benzene is a moderately lipophilic compound used in pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals. It has limited solubility in water, acute toxicity, and can pose occupational exposure risks.
Jan 3,2024 API