Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
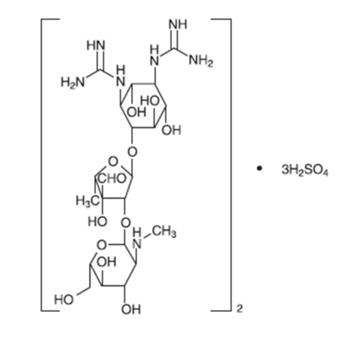
Introduction and Preparation of Streptomycin Sulfate
Streptomycin sulfate is the sulfate salt form of?streptomycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseus with antibacterial property.
Nov 18,2022 APIEthylene Glycol Poisoning
Ethylene glycol poisoning is poisoning caused by drinking ethylene glycol. Early symptoms include intoxication, vomiting and abdominal pain.
Nov 17,2022 APIThe Side Effects of Acetaminophen
The passage describes the side effects of Acetaminophen.
Nov 17,2022 APIAluminum Chloride: Uses and Solubility
Aluminum chloride is used widely in different fields and freely soluble in numerous organic.
Nov 16,2022 APISodium sulfate: Physical Properties and Uses
Sodium sulfate has unusual solubility characteristics in water and has different uses.
Nov 16,2022 APISynthesis, Toxicology and Application of Lead acetate trihydrate
Lead acetate trihydrate is used as pigment, stabilizer and catalyst.
Nov 14,2022 API