Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
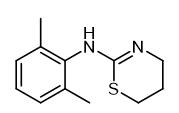
Synthesis and application of s-tert-butyl sulfonamide
S-tert-butyl sulfonamide is a chiral ligand used in pharmaceutical compositions.
Aug 31,2022 APISynthesis and Biochemical Effects of Xylazine
Xylazine has sedative, analgesic and central muscle relaxant effects.
Aug 31,2022 APIUses and effect of Mertansine
Mertansine, also called DM1, is a thiol-containing maytansinoid that for therapeutic purposes is attached to a monoclonal antibody through reaction of the thiol group with a linker structure to create
Aug 29,2022 APISynthesis and Application of Toltrazuril
Toltrazuril is an antiprotozoal drug that acts against coccidia parasites.
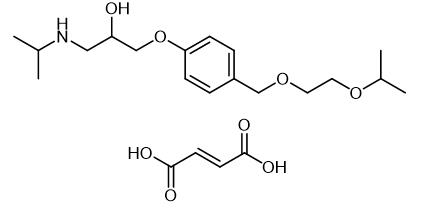
Aug 29,2022 APISynthesis and Detection method of Bisoprolol fumarate
Bisoprolol fumarate is used to treat conditions such as hypertension and angina pectoris.
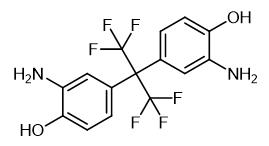
Aug 29,2022 APISynthesis and Application of 2,2-bis(3-amino-4-hydroxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane
2,2-Bis(3-amino-4-hydroxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane is an important synthetic intermediate.
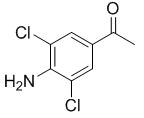
Aug 26,2022 APISynthesis and application of 3,5-dichloro-4-aminoacetophenone
3, 5-dichloro-4-aminoacetophenone is an intermediate in the synthesis of the antitussive and antiasthmatic drug gramtin.
Aug 26,2022 APISynthesis and application of hexafluoro dianhydride (6FDA)
Hexafluoric anhydride (6FDA) is an organic synthesis intermediate and pharmaceutical intermediate, which can be used in laboratory research and development processes.
Aug 26,2022 APIThe application of vinylene carbonate in Li-ion batteries
The vinylene carbonate (VC) is a cyclic, reactive, unsaturated carbonate ester.
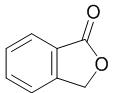
Aug 26,2022 APISynthesis of phthalide and its biological information
Phthalide is a natural product found in Ligusticum sinense and Ligusticum chuanxiong with data available.
Aug 25,2022 API