Antineoplastic is a class of medicine to restrain or kill tumor cells in the body. It plays an important role in comprehensive cancer treatment, particularly for disseminated tumor and leukemia that cannot be treated with surgery. Most current antineoplastics work by inhibiting DNA or RNA synthesis, or even damaging the structure of DNA. Antineoplastics can be divided into CCNSA (Cell cycle nonspecific drug) and CCSA (Cell Cycle Specific agents) according to their different effect on tumor cells in different stages of generation cycles. Both of them have a killing effect on bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells and other cells with a short growth cycle, as well as an inhibiting effect on the body's immune response. Antineoplastic has a wide variety of drugs, which can be divided into following categories: alkylating agents, such as cyclophosphamide, Glyciphosphoramide, thiotepa, etc.; antimetabolites, such as methotrexate, mercaptopurine, fluorouracil, hydroxyurea, etc.; antibiotics, such as dactinomycin, mitomycin C, bleomycin, etc.; hormones, such as prednisone, testosterone propionate, diethylstilbestrol, etc.; some botanical drugs, such as Vinblastine, camptothecin, colchicine, etc.; and other classes, such as procarbazine, propylene imine, Yishuangmalin, etc. With their enormous diversity and different mechanisms, antineoplastics must be carefully selected for clinical application.
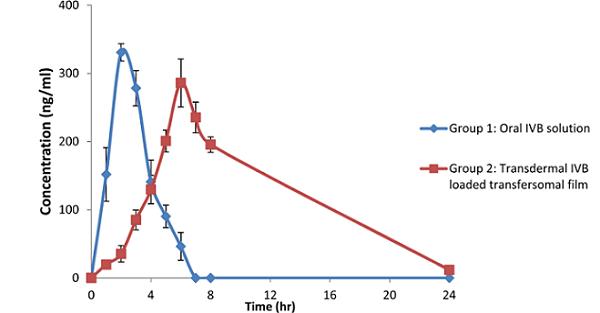
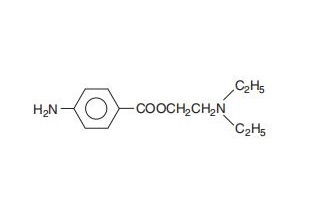
Ivabradine Hydrochloride in Angina and Cardiac Therapy
Ivabradine hydrochloride is a selective heart rate–reducing agent used in angina, with novel transdermal delivery formulations under study.
Aug 28,2025 Antineoplastic agentsSaponin: A Multifunctional Compound with Expanding Applications
Saponins have garnered significant interest in recent years for their unique properties and diverse applications across industries.
Nov 25,2024 Antineoplastic agentsTianeptine Sodium Salt: A Unique Compound with Diverse Applications
Tianeptine sodium salt is a remarkable compound with distinct pharmacological properties, particularly in mental health and neuroprotective research.
Nov 25,2024 Antineoplastic agentsUses and characteristics of HEPES buffer
HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid) is a zwitterionic sulfonic acid buffering agent; one of the twenty Good's buffers.
Apr 13,2022 Antineoplastic agentsHexylresorcinol: Providing Skin Benefits by Modulating Multiple Molecular Targets
Hexylresorcinol (HR) is an alkylresorcinol (AR), a type of phenolic lipid, having an n-hexyl chain attached to the 4 position of the 1,3-dihydroxybenzene ring. It can be synthesized by reacting resorc
Mar 3,2022 Antineoplastic agentsWhat is Dasatinib?
Dasatinib Anhydrous is an orally bioavailable synthetic small molecule-inhibitor of SRC-family protein-tyrosine kinases. Dasatinib binds to and inhibits the growth-promoting activities of these kinase
Aug 27,2021 Antineoplastic agentsWhat is Tetracaine Hydrochloride used for?
Tetracaine hydrochloride is also known as ropivacaine hydrochloride, pantocaine, pantocaine and four ropivacaine hydrochloride. It is easily soluble in water and ethanol, but insoluble in ether, benze
Sep 28,2020 Antineoplastic agentsWhat is Procaine hydrochloride?
Procaine hydrochloride is used as the sole local anesthetic agent for pain control in dentistry, as it was from its introduction in 1904 until the introduction of the amide local anesthetic lidocain
Sep 27,2020 Antineoplastic agentsBenzocaine-----Uses as a Local anaesthetic
Benzocaine is one of the more common and widely used topical anesthetics. It is available in gel, cream, ointment, lozenge, liquid solution, spray, and patch.
Sep 25,2020 Antineoplastic agents