Food Additives refers to a kind of natural or artificially synthetic chemicals which can improve the sensory properties (color, smell, taste) of food and food quality. To the adult foods, we can add some additives according to the China's health standards. However, the food additives should be strictly controlled to be applied to infant foods. Infant body has a relative weak detoxification mechanisms or protection mechanisms, being likely to cause the accumulation of large quantities of chemical substances. The World Health Organization and many countries have specified that food additives are not allowed to be supplemented to the infant food. Children's food should also be limited from using of food additives such as saccharin, colorings and flavors. Especially, for the food of baby of less than 12-week-old such as infant formula and cereal products, they should be completely free of food additives. Classification of the food additives: Food additives can be divided into two categories including natural food additives and synthetic food additives. Natural food additive is obtained through using animal and plant or microbial metabolites as raw materials and further extraction. Chemical synthetic additives are obtained through de novo synthesis using chemical substances as raw materials. According to the usage purpose and the nature of chemicals, food additives can be divided into various categories, namely: (1) acid, alkali, salt; (2) bulking agent; (3) antioxidant and synergist; (4) the carrier solvent ; (5) edible pigment; (6) emulsifier, stabilizer and thickener; (7) enzyme preparation for food processing; (8) antifoaming agent; (9) the flavorant (10) bleaching agent; (11) color former; (12) quality improver; (13) sweetener; (14) preservative; (15) sour agent; (16) anti-caking agent; (17) coagulant and
Ferrous bisglycinate:Efficacy, Benefits and Side effects
Ferrous bisglycinate is a chelate that is used as a source of dietary iron, it has been shown to have higher bioavailability and absorption compared to iron salts.
Dec 23,2025 Food AdditivesDetection of Sodium Formaldehyde Sulfoxylate
Sodium formaldehyde sulfoxylate,a powerful carcinogen, has been illegally used to whiten wheat foods. Its detection method was reported here.
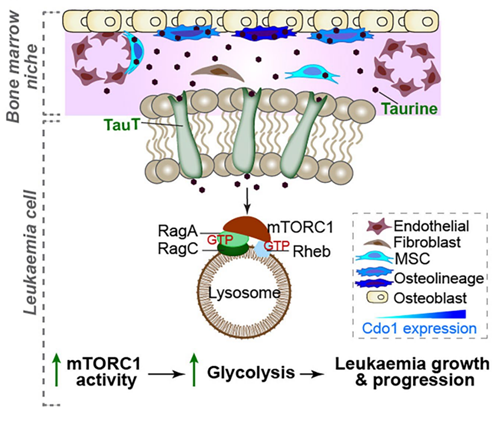
Sep 25,2025 Food AdditivesNature's blockbuster discovery: Taurine can help cancer cell metabolism and promote leukemia
Taurine is a conditionally essential micronutrient and rich aminosulfonic acid, widely distributed in various tissues and organs in the body.
Jul 15,2025 Food AdditivesDetermination methods of the Sodium Methylparaben
Sodium methylparaben as one kind of preservatives is widely used in our life, but it will do harm to health if it is eaten too much.
Apr 7,2025 Food AdditivesMonocaprylin: an alternative food preservative
Monocaprylin, a monoglyceride of caprylic acid, has a similar safety status and is used as an alternative food preservative.
Mar 21,2025 Food AdditivesCasein: An Essential Protein with Versatile Applications in the Chemical Industry
Casein consists of four major phosphoproteins with their homologous primary amino acid sequences into the following families αs1, αs2, β, and κ-casein.
Jan 26,2025 Food AdditivesWhat foods contain Coenzyme Q10?
Primary dietary sources of CoQ10 include oily fish (such as salmon and tuna), organ meats (such as liver), and whole grains.
Jan 20,2025 Food AdditivesMethyl cyclopentenolone:Introduction,Synthesis methods and Main applications
Due to its unique characteristics, methyl cyclopentenolone has a wide range of applications, significant economic benefits, and good development prospects.
Jan 20,2025 Food AdditivesMyristic acid: Description, Preparation method and Main application
Myristic acid is a 14-carbon, straight-chain saturated fatty acid found widely distributed in fats throughout the plant and animal kingdom.
Jan 13,2025 Food Additives