Food Additives refers to a kind of natural or artificially synthetic chemicals which can improve the sensory properties (color, smell, taste) of food and food quality. To the adult foods, we can add some additives according to the China's health standards. However, the food additives should be strictly controlled to be applied to infant foods. Infant body has a relative weak detoxification mechanisms or protection mechanisms, being likely to cause the accumulation of large quantities of chemical substances. The World Health Organization and many countries have specified that food additives are not allowed to be supplemented to the infant food. Children's food should also be limited from using of food additives such as saccharin, colorings and flavors. Especially, for the food of baby of less than 12-week-old such as infant formula and cereal products, they should be completely free of food additives. Classification of the food additives: Food additives can be divided into two categories including natural food additives and synthetic food additives. Natural food additive is obtained through using animal and plant or microbial metabolites as raw materials and further extraction. Chemical synthetic additives are obtained through de novo synthesis using chemical substances as raw materials. According to the usage purpose and the nature of chemicals, food additives can be divided into various categories, namely: (1) acid, alkali, salt; (2) bulking agent; (3) antioxidant and synergist; (4) the carrier solvent ; (5) edible pigment; (6) emulsifier, stabilizer and thickener; (7) enzyme preparation for food processing; (8) antifoaming agent; (9) the flavorant (10) bleaching agent; (11) color former; (12) quality improver; (13) sweetener; (14) preservative; (15) sour agent; (16) anti-caking agent; (17) coagulant and
What is Pectinase?
Pectinase is a collective term for enzymes that break down pectin and are as pectic enzymes. Polygalacturonase is one of the most well-known pectinase, and other common examples of this enzyme class i
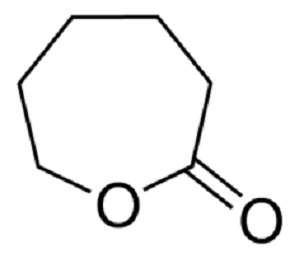
Oct 28,2020 Food AdditivesWhat is ε-Caprolactone?Uses_Chemical reaction_Safety
ε-Caprolactone or simply caprolactone is a lactone (a cyclic ester) possessing a seven-membered ring. Its name is derived from caproic acid. This colorless liquid is miscible with most organic solvent
Sep 30,2020 Food AdditivesUses of Lanolin
Lanolin has been used for thousands of years for its ability to soften and relieve dry, painful, and cracked skin. Its popularity peaked in the mid-1900s but is now declining due to its potential to c
Aug 27,2020 Food AdditivesEthoxylated hydrogenated castor oil-Properties & Uses
Ethoxylated hydrogenated castor oil(EHCO) is preferred over ethoxylated castor oil when higher oxidation stability, lighter color, less odor or higher melting point is required.
Dec 4,2019 Food AdditivesThe uses of Guaiacol
Guaiacol is present in wood smoke, resulting from the pyrolysis of lignin. The compound contributes to the flavor of many substances such as whisky and roasted coffee.
Nov 14,2019 Food AdditivesApplications of Polydextrose
Polydextrose (CAS no.68424-04-4) is a water-soluble polymer of glucose which provides to foods the bulk and texture of sucrose, but at only one-quarter the caloric value.
Oct 24,2019 Food AdditivesP-cresyl acetate: Chemical properties; Content analysis; Uses
P-cresyl acetate is suitable for narcissus, daffodil and large flower jasmine. It is also suitable for use in white orchid, lilac, lily of the valley, hyacinth, fragrant roy, and ylang-ylang type.
Oct 23,2019 Food AdditivesUses and Correlational research of Gelatin
Gelatin is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. Brittle when dry and gummy when moist. Gelatin is made from collagen. Collagen is o
Oct 21,2019 Food AdditivesAgar Gel - Natural Occurrence and Discovery
Agar, is also called Kanten, Japenese gelatine, or China grass, is a jelly-like substance derived from seaweed species of the genera Gelidium.
Oct 16,2019 Food AdditivesUses and Toxicity of Poly(vinyl acetate)
Poly(vinyl acetate) is used as a gum chew and does not enter the human body and is non-toxic. It cannot be absorbed by the body as it is a polymer substance that is insoluble in water and oil.
Oct 14,2019 Food Additives