Inorganic chemicals is the shortened form of inorganic chemical industry and is an important branch of the chemical industry with natural resources and industrial by-products as raw materials for the production of sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid, soda ash, caustic soda, synthetic ammonia, fertilizer and inorganic salts, etc. This includes sulfuric acid industry, soda industry, the chloro-alkali industry, synthetic ammonia industry, fertilizer industry and mineral industry. Its broad definition also includes the production of inorganic non-metallic materials and fine inorganic product such as ceramics and inorganic pigment. The main raw material of inorganic chemical products are mineral product including sulfur, sodium, phosphorus, potassium and calcium and coal, oil, gas, and air, water and so on. Inorganic chemicals can be traced back to the ancient process of ceramics, alchemy, brewing, dyeing at thousands of years ago. Although with small scale, backward technology and pure manual manipulation, but it is the prototype of inorganic chemicals. For thousands of years, due to the low productivity, it gets slow development. Until the 18th century, it had developed rapidly. In the middle of 18th century, Britain had first applied lead chamber method using saltpeter and sulfur as raw materials to produce sulfuric acid. In 1783, Lu Bulan (France) proposed the soda method using sodium chloride, sulfuric acid, coal as raw materials. In the latter half of the 18th century, the modern chemical industry taking inorganic chemical industry as the main content had began to emerge. In 1841, people began the production of phosphate fertilizer; In 1965 Belgian Solvay realized the industrialization of ammonia soda for production of soda; with the rise of preparing potassium industry in 1870; In 1890, people began to use electrolytic approach for making Cl2 and caustic soda; In 1913, people had achieved the catalytic synthesis
Difluoroacetic Acid: Environmental Behavior & C-H Difluoromethylation
Difluoroacetic acid exists in CFC-contaminated groundwater and acts as a novel radical source for controllable heteroaromatic C-H difluoromethylation.
Feb 9,2026 Inorganic chemistryApplication Research of Cerium(iii) nitrate hexahydrate
Cerium(iii) nitrate hexahydrate is a chemical compound with extensive applications.This paper mainly enumerates the relevant application research thereof.
Dec 26,2025 Inorganic chemistryZirconium Hydroxide: Advanced Material Applications
Zirconium hydroxide exhibits acid-base/redox activity, degrades CWAs and pollutants, and enables self-decontaminating air filter paper development.
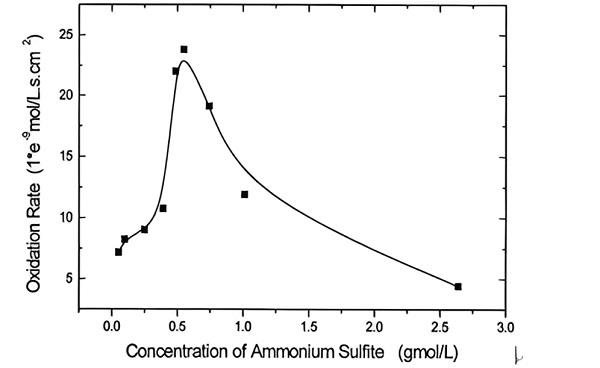
Dec 10,2025 Inorganic chemistryAmmoniacal Leaching and Oxidation of Ammonium Sulfite
Investigation about ammoniacal leaching of LIB metals and the kinetic behavior of ammonium sulfite oxidation.
Nov 24,2025 Inorganic chemistryTrifluoromethanesulfonimide: Proton Exchange Membranes and Allylsilane Annulations
Trifluoromethanesulfonimide enhances PEM proton conductivity and catalyzes allylsilane annulations to synthesize indanes/tetralins.
Oct 21,2025 Inorganic chemistryBentonite: Properties and Applications
Bentonite is a special type of hydrous aluminum silicate clay mineral, primarily composed of montmorillonite.
Sep 12,2025 Inorganic chemistrySynthesis and Toxicological Profile of Chromium(III) Chloride Anhydrous
Overview of chromium(III) chloride anhydrous synthesis, coordination complex formation, structural features, and potential genotoxic risks.
Sep 9,2025 Inorganic chemistryExploration of the Properties and Applications of Dysprosium Oxide
Dysprosium oxide, an important colourant in glasses and porcelain enamel glazes. It is widely applied as dopant in making optical fibre and amplifier.
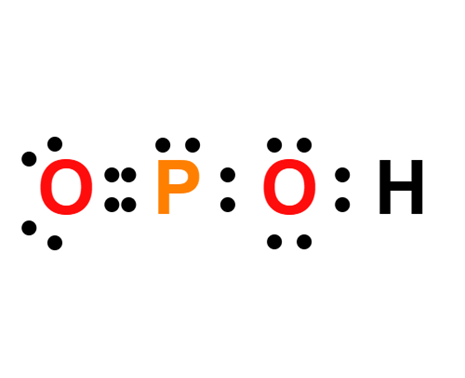
Apr 21,2025 Inorganic chemistryHypophosphorous acid:Lewis structure,Uses and Hazard
Pure hypophosphorous acid forms white crystals that melt at 26.5 °C (79.7 °F). The electronic structure of hypophosphorous acid is such that it has only one hydrogen atom bound to oxygen.
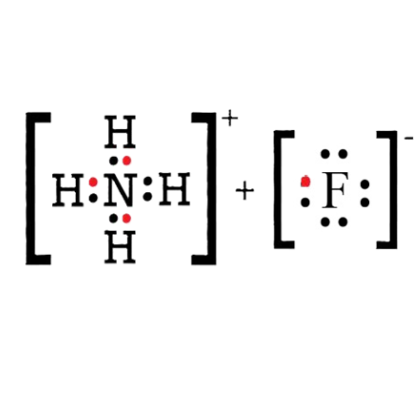
Apr 15,2025 Inorganic chemistryAmmonium fluoride:Lewis structure,Preparation,Uses and Hazards
Ammonium fluoride (NH4F) is a white, hydroscopic, crystal. It is used primarily for oil well acidification and metal processing.
Apr 1,2025 Inorganic chemistry