Inorganic chemicals is the shortened form of inorganic chemical industry and is an important branch of the chemical industry with natural resources and industrial by-products as raw materials for the production of sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid, soda ash, caustic soda, synthetic ammonia, fertilizer and inorganic salts, etc. This includes sulfuric acid industry, soda industry, the chloro-alkali industry, synthetic ammonia industry, fertilizer industry and mineral industry. Its broad definition also includes the production of inorganic non-metallic materials and fine inorganic product such as ceramics and inorganic pigment. The main raw material of inorganic chemical products are mineral product including sulfur, sodium, phosphorus, potassium and calcium and coal, oil, gas, and air, water and so on. Inorganic chemicals can be traced back to the ancient process of ceramics, alchemy, brewing, dyeing at thousands of years ago. Although with small scale, backward technology and pure manual manipulation, but it is the prototype of inorganic chemicals. For thousands of years, due to the low productivity, it gets slow development. Until the 18th century, it had developed rapidly. In the middle of 18th century, Britain had first applied lead chamber method using saltpeter and sulfur as raw materials to produce sulfuric acid. In 1783, Lu Bulan (France) proposed the soda method using sodium chloride, sulfuric acid, coal as raw materials. In the latter half of the 18th century, the modern chemical industry taking inorganic chemical industry as the main content had began to emerge. In 1841, people began the production of phosphate fertilizer; In 1965 Belgian Solvay realized the industrialization of ammonia soda for production of soda; with the rise of preparing potassium industry in 1870; In 1890, people began to use electrolytic approach for making Cl2 and caustic soda; In 1913, people had achieved the catalytic synthesis
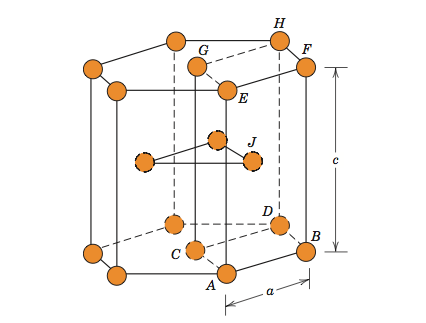
Structure and Properties of Tantalum Pentoxide
Tantalum pentoxide is disordered, being either amorphous or polycrystalline. It has at least 2 polymorphs exist. A low temperature form, known as L- or β-Ta2O5, and the high temperature form known as
Mar 29,2024 Inorganic chemistryUranium(IV) oxide:Crystal structure,Application,Preparation
Uranium(IV) oxide is characterized by high melting point, good high-temperature stability, strong radiation resistance, good corrosion resistance, and good compatibility with zirconium or stainless st
Mar 29,2024 Inorganic chemistryYtterbium oxide nanofibers
Ytterbium Oxide (Yb2O3) is a white Powder, water-insoluble powder with a cubic crystal structure. It is used as a colorant for glasses and enamels and as a dopant for garnet crystals in lasers.
Mar 29,2024 Inorganic chemistryCrystal Structure of Aluminum Nitride(AlN)
Aluminum nitride has recently attracted considerable attention because of its electric ability, the most critical design aspect of a piezoelectric device is its crystal quality, this article will intr
Mar 29,2024 Inorganic chemistryNiobium silicide:Crystal Structure,Properties,Uses,Synthesis
Niobium silicide is a compound of niobium and silicon with the chemical formula NbSi2. It is used for niobium silicide-based turbine components, high-temperature structural materials, etc.
Mar 28,2024 Inorganic chemistryCrystal structure and Uses of ?Tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide has the chemical symbol WC. In its natural state, it is a fine grey powder, which can either be sintered (compacted using heat or pressure) onto a surface, or cemented (bound with a m
Mar 28,2024 Inorganic chemistryThermal Stabilities, Electronic Structures, Magnetic Properties and the Charge Transfers of Cerium Boride
The group of Professor Guanglei Zhang investigated the thermal stabilities, electronic structures, magnetic properties and the charge transfers of the rare earth Cerium hexaborides CeB6.
Mar 28,2024 Inorganic chemistryWhat is the Crystal Structure of Molybdenum Carbide?
In the transition metal carbides series, molybdenum carbide has proven as an effective catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). This article will introduce the performance of molybdenum car
Mar 28,2024 Inorganic chemistryUranium diboride:Crystal structure,Uses,Synthesis
Uranium diboride (UB2) is a refractory ceramic with physical properties that make it a promising candidate for the development of high-performance nuclear materials, including fuel.
Mar 27,2024 Inorganic chemistryUses and Features of Chromium nitride
Chromium nitride is very hard and is extremely resistant to corrosion. It is an interstitial compound, with nitrogen atoms occupying the octahedral holes in the chromium lattice.
Mar 27,2024 Inorganic chemistry