| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
AR-13324 (hydrochloride) | [CAS]
1253952-02-1 | [Synonyms]
AR-13324
Netarsudil
AR13324 HCl
AR-13324 HCl
Netarsudil (AR-13324)
AR-13324 dihydrochloride
AR-13324 (hydrochloride)
Netarsudil hydrochloride
Netarsudil dihydrochloride
Netarsudil (AR-13324) 2HCl
AR-13324 hydrochloride:AR13324 hydrochloride
NETARSUDIL; NETARSUDIL HYDROCHLORIDE; AR-13324 HCL; AR-13324 HCL; AR13324 HCL; AR13324 HCL; RHOPRESSA;
2,4-Dimethylbenzoic acid [4-[(1S)-1-(aminomethyl)-2-(6-isoquinolinylamino)-2-oxoethyl]phenyl]methyl ester hydrochloride (1:2) | [Molecular Formula]
C28H29Cl2N3O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD29472289 | [MOL File]
1253952-02-1.mol | [Molecular Weight]
526.454 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [solubility ]
≥26.3 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming and ultrasonic; insoluble in EtOH; ≥7.783 mg/mL in DMSO | [form ]
solid | [color ]
White to off-white |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
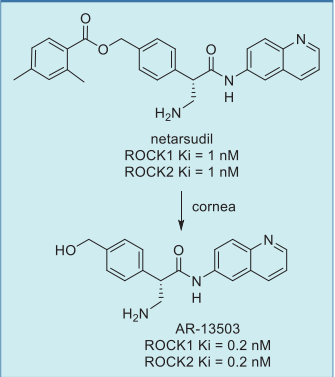
Netarsudil is a member of the aminoisoquinoline amide class of Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) inhibitors, binding reversibly to the ATP-binding sites of both ROCK1 and ROCK2 isoforms with low nanomolar affinity. As a 2,4-dimethylbenzoate ester prodrug of AR-13503, netarsudil offers enhanced permeability through the eye compared to the active drug. Upon ocular administration, it is absorbed through the cornea and metabolized by corneal esterases to release the more potent metabolite AR-13503, which has five times greater ROCK inhibitory activity than netarsudil itself.
 | [Uses]
Netarsudil is the first trabecular outflow drug approved in 2017 for lowering elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma (OAG) or ocular hypertension. | [Brand name]
Rhopressa | [General Description]
Class: serine/threonine kinase;
Treatment: glaucoma;
Other name: AR-13324;
Protein binding = >97% | [Biological Activity]
ki: 0.2-10.3 nmnetarsudil (ar-13324) is a rock inhibitor.the rho kinases are serine/threonine protein kinases existing as 2 isoforms, rock1 and rock2, which are widely expressed in various tissues, such as the trabecular meshwork. rock can promote the assembly of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions and can also regulate cell contraction and motility. | [in vitro]
previous study showed that at the cellular level, netarsudil had been shown to be able to induce loss of actin stress fibers, cell shape changes, loss of focal adhesions, as well as changes in extracellular matrix composition of tm cells [1]. | [in vivo]
animal efficacy study found that the topical treatment of netarsudil was able to affect both proximal (trabecular meshwork and schlemm's canal) and distal portions (intrascleral vessels) of the mouse conventional outflow tract [2]. | [target]
Primary targets: ROCK1/2, NET | [References]
[1] sturdivant jm et al. discovery of the rock inhibitor netarsudil for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma. bioorg med chem lett. 2016 may 15;26(10):2475-80.
[2] li g et al. visualization of conventional outflow tissue responses to netarsudil in living mouse eyes. eur j pharmacol. 2016 sep 15;787:20-31. |
|
|