| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Properties]
The Mr of mature eel VNP is 3940, and the pI is about
10. It is freely soluble in water, acid, and 67% acetone, but
insoluble in 99% acetone. VNP solution in water at
>10-4M is stable for more than a year at -20°C. | [Gene, mRNA, and precursor]
By linkage mapping, the rainbow trout VNP gene was
found to be localized in tandem with the atrial natriuretic
peptide (ANP) and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
genes on the same chromosome. The VNP gene is on
the same scaffold as those of ANP and BNP in the eel
genome database. However, the precise chromosomal
location of the VNP gene has not been determined yet
in the two species. The size of eel VNP mRNA is
1024 bp. Unlike BNP mRNA, there is no repetitive
AUUUA motif in the 30
-untranslated region of VNP
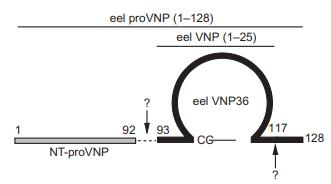
mRNA. Eel proVNP1–128 is cleaved into VNP-36
(VNP93–128) and N-terminal (NT)-proVNP1–92 by prohormone convertase. | [Synthesis and release]
In eels, a major stimulus for VNP release is osmotic
stimulus, particularly an acute increase in plasma osmolality. The plasma eel VNP level is transiently and rapidly
increased after seawater transfer, or injections of hypertonic NaCl or mannitol. Increased blood volume (vol�ume stimulus) also induces VNP release, although it is
less potent when compared to mammals. Increased
VNP is cleared from the circulation quickly due to the
high metabolic clearance rate (2.7±0.2mL/min: metabolic clearance rate of eel ANP is 1.7±0.1mL/min). Similarly to ANP in mammals, the chronic volume load, but
not the salt load, is a major stimulus for VNP secretion in
the trout. The promoter region and potential transcrip-tion factors have not been identified yet for the VNP gene. | [Receptors]
Eel VNP binds to the eel A-type NP receptor
(NPR-A: Kd=0.1nM), the C-type NP receptor (NPR-C:
Kd=0.15nM), and the D-type NP receptor (NPR-D:
Kd=1nM) when they are transiently expressed in COS-7
cells. Although the binding affinity to the eel B-type NP
receptor (NPR-B) has not been determined yet, eel VNP
stimulates the guanylyl cyclase activity of eel NPR-B
expressed in COS-7 cells at 10nM. Therefore, it is assumed
that VNP is a ligand not only for NPR-A but also for NPR-B
when its secretion is enhanced. Eel NPR-A, -B, and -C are
widely distributed while eel NPR-D is specifically
expressed in the brain and gills. A VNP-specific receptor
has not yet been found. | [Agonists and Antagonists]
C-ANF is a selective agonist for both NPR-C and -D.
Osteocrin containing the NP motif selectively binds to
the NPR-C, but not to the NPR-A or -B. HS-142-1 blocks the binding of VNP to eel NPR-A, -B,
and -D, but not NPR-C. | [Biological functions]
VNP is as potent as ANP, and more potent than BNP
for cardiovascular effects in eels and trout. The systemic
injection of eel VNP at doses of 0.1–1 nmol/kg decreases
blood pressure and increases hematocrit. The hypotensive action of eel VNP lasts longer than that of eel
ANP. In seawater-adapted eels, VNP decreases the
plasma Na+ concentration by inhibiting the drinking rate
and subsequent intestinal NaCl absorption. Thus, VNP
is thought to be an important hormone for seawater
acclimation in eels. Eel VNP potentiates the steroidogenic
action of ACTH. In rats, the natriuretic and hypotensive
effects of eel VNP are observed at 1–10 nmol/kg. |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
VNP was purified in 1991 from the eel ventricle. Deduced eel proVNP consists of 128 aa residues. Bioactive mature eel VNP (36 aa residues) is
located at the C-terminus. Eel VNP has 17 aa residues
of an intramolecular ring, from which a long
C-terminal tail sequence (14 aa residues) extends. The
C-terminally truncated form, VNP1–25, is also present in
eel plasma. An NP gene abundantly expressed in the
chicken kidney, named renal NP (RNP), may be an ortholog of VNP.
 | [Structure and conformation]
Deduced eel proVNP consists of 128 aa residues. Bioactive mature eel VNP (36 aa residues) is
located at the C-terminus. Eel VNP has 17 aa residues
of an intramolecular ring, from which a long
C-terminal tail sequence (14 aa residues) extends. The
C-terminally truncated form, VNP1–25, is also present in
eel plasma. An NP gene abundantly expressed in the
chicken kidney, named renal NP (RNP), may be an ortholog of VNP. The sequence identity is >75% in the mature sequences
of the eel, salmon, sturgeon, and bichir VNP. The VNP gene is absent in the genome database of several
advanced teleost species (e.g., the medaka and pufferfish)
and other advanced classes of vertebrates, except in
birds (the chicken). |
|
|