| Identification | More | [Name]
N-(3-Chloro-ortho-tolyl) anthranilic acid | [CAS]
13710-19-5 | [Synonyms]
2 (3-CHLORO-2-METHYLANILINO)BENZOIC ACID
2-[(3-CHLORO-2-METHYLPHENYL)AMINO]BENZOIC ACID
2-(3-CHLORO-O-TOLUIDINO)BENZOIC ACID
CLOTAM
LABOTEST-BB LT00772313
N-(3-CHLORO-2-METHYLPHENYL)ANTHRANILIC ACID
n-(3-chloro-ortho-tolyl) anthranilic acid
TOLFENAMIC ACID
2-((3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino)-benzoicaci
gea6414
n-(2-methyl-3-chlorophenyl)anthranilicacid
n-(3-chloro-o-tolyl)-anthranilicaci
n-(3-chloro-o-tolyl)-anthranilicacid
Tolfenamic
Benzoic acid, 2-(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino-
2 (3-Chloro-2-methylanilino)benzoic acid, 2-([3-Chloro-2-methylphenyl]amino)benzoic acid
2-[(4-Chloro-3-methylphenyl)amino]benzoic acid
Tolfedine
2-[(3-Chloro-o-tolyl)amino]benzoic acid | [EINECS(EC#)]
237-264-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C14H12ClNO2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00133865 | [Molecular Weight]
261.7 | [MOL File]
13710-19-5.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
210-214°C | [Boiling point ]
405.4±40.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.2037 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.5270 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C | [solubility ]
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in dimethylformamide, sparingly soluble in ethanol and in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides. | [form ]
neat | [pka]
3.66±0.36(Predicted) | [color ]
White to Off-White | [Water Solubility ]
Soluble in water (slightly), acetone (~10 mg/ml), DMSO (52 mg/ml at 25°C), methanol (~10 mg/ml) and ethanol (50 mg/ml). | [Merck ]
9513 | [InChIKey]
YEZNLOUZAIOMLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
13710-19-5(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Benzoic acid, 2-[(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino]- (13710-19-5) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R22:Harmful if swallowed. | [RIDADR ]
UN 2811 6.1/PG 3
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
CB2687500
| [HazardClass ]
6.1 | [PackingGroup ]
III | [HS Code ]
29224919 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
White Solid | [Uses]
A non steroidal anti-inflammatory agent found to inhibit COX-2 isoenzymes | [Uses]
Amidated GRF fragment equipotent to GRF in release of somatotropin from anterior pituitary | [Uses]
antiinflammatory, analgesia | [Uses]
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). | [Definition]
ChEBI: An aminobenzoic acid that is anthranilic acid in which one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a 3-chloro-2-methylphenyl group. Tolfenamic acid is used specifically for relieving the pain of migraine. It also shows anticancer activity. | [General Description]
Tolfenamic Acid is an anthranilic acid derivative and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Its applications in treating pancreatic, esophageal, colorectal and lung cancer is being investigated. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent. Interferes with synthesis of β-amyloid precursor protein, and thus Aβ peptides, by promoting degradation of an essential transcription factor. | [Clinical Use]
NSAID:
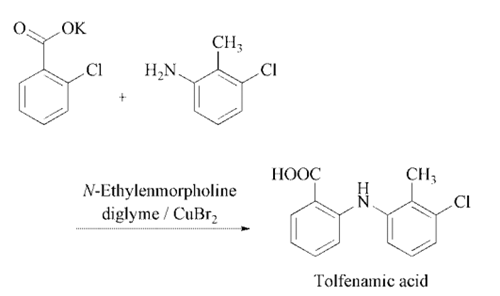
Treatment of migraine | [Synthesis]
Tolfenamic acid is obtained by
condensation of 2-chlorobenzoic acid with 3-
chloro-2-methyl-phenylamine using CuBr2 in
diethylenglycol dimethyl ether .
 | [Veterinary Drugs and Treatments]
Tolfenamic acid may be useful for the treatment of acute or chronic
pain and/or inflammation in dogs and acute pain/inflammation in
cats. In Europe, it is also approved for use in cattle. | [Drug interactions]
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
antagonism of hypotensive effect; increased risk of
nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemia.
Analgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more
NSAIDs, including aspirin (increased side effects);
avoid with ketorolac (increased risk of side effects
and haemorrhage).
Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of convulsions
with quinolones.
Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and
phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of
bleeding with heparins, dabigatran and edoxaban.
Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with
SSRIs and venlafaxine.
Antidiabetic agents: effects of sulphonylureas enhanced.
Antiepileptics: possibly increased phenytoin
concentration.
Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity
with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: reduced excretion of methotrexate;
increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib.
Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
antagonism of diuretic effect; hyperkalaemia with
potassium-sparing diuretics.
Lithium: excretion decreased.
Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleeding.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity | [Metabolism]
Tolfenamic acid is metabolised in the liver; the metabolites and unchanged drug are conjugated with glucuronic acid. About 90
% of an ingested dose is excreted in the urine and the remainder in the faeces. |
|
|