7080-50-4
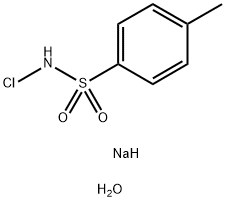 7080-50-4 结构式
7080-50-4 结构式
基本信息
氯胺T三水合物
三水合氯铵-T
氯胺T钠
对甲苯磺酰氯胺钠三水合物
氯亚明 T
氯胺T三水合物, ACS, 98.0-103.0%
CHLORAMINE T SODIUM SALT TRIHYDRATE
CHLORAMINE T TRIHYDRATE
CHLOROAMINUM
CHLOROMINE-T SOLUTION
N-CHLORO-4-TOLUENESULFONAMIDE SODIUM SALT TRIHYDRATE
N-CHLORO-P-TOLUENESULFONAMIDE, SODIUM SALT
N-CHLORO-P-TOLUENESULFONAMIDE, SODIUM SALT TRIHYDRATE
N-CHLORO-P-TOULENESULFONAMIDE, SODIUM SALT TRIHYDRATE
P-TOLUENESULFONCHLORAMIDE SODIUM SALT TRIHYDRATE
SODIUM P-TOLUENESULFONCHLORAMIDE TRIHYDRATE
SODIUM P-TOLUENESULFONCHLORAMID TRIHYDRATE
SODIUM P-TOLUENESULFONCHLOROAMIDE TRIHYDRATE
TOSYLCHLORAMIDE SODIUM TRIHYDRATE
Chloramine-T, Sodium salt
N-Chloro-p-toluenesulphonamide sodium salt trihydrate
N-Chloro p-Toluene sulfonamide
CHLORAMINE T TRIHYDRATE, PH EUR
CHLORAMINE-T TRIHYDRATE, 98%, A.C.S. REA GENT
CHLORAMINE-T TRIHYDRATE 98% &
物理化学性质
安全数据
知名试剂公司产品信息
Chloramine-T trihydrate, 98%(7080-50-4)
| 报价日期 | 产品编号 | 产品名称 | CAS号 | 包装 | 价格 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-U00087 | 氯胺-T 三水合物 Tosylchloramide sodium trihydrate | 7080-50-4 | 5 g | 100元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-U00087 | 氯胺-T 三水合物 Tosylchloramide sodium trihydrate | 7080-50-4 | 10 mM * 1 mLin DMSO | 110元 |
| 2025/02/08 | 30037618 | 氯胺T,三水 chloramine t trihydrate;n-chloro-p-toluenesulfonamide sodium salt;tosylchloramide sodium | 7080-50-4 | 500G | 108元 |
常见问题列表
Gram-positive growth is reduced by 95% to 100% after tosylchloramide treatment, regardless of dose, with or without serum. E coli (gram-negative; with/without serum) is reduced 94% to 100% at antiseptic concentrations of 300 and 400 ppm. At 200 ppm, E coli growth is fully inhibited without serum present and by 50% with serum. At 100 and 200 ppm, cell viability remains greater than 90% under all experimental conditions. A 300-ppm, 3-minute exposure to tosylchloramide results in cell viability of up to 70%, with longer exposures producing lower viabilities. Serum does not affect cell viability in any condition.
A dose-dependently significant DNA damage in the rat tissues and inflammation is histopathologically noted around the terminal airways of the lung in both male and female rats. The 24-h exposure to 50 mg/L of chloramine-T is toxic for crayfish and leads to substantial loss of energy that became apparent during subsequently conducted physical stress. Tosylchloramide may potentiate the toxicity of many xenobiotics via metabolic activation and/or accumulation of reactive metabolites. The activities of CYP2E1, CYP1A1/2 CYP2B1/2, CYP3A4 and CYP4A1/2 enzymes significantly increase after treatment with 2.50, 5 and 10 mg/kg bw/day tosylchloramide, in a dose-dependent manner. This effect is not observed after tosylchloramide treatment at dose of 1.25 mg/kg bw/day.


