Titandioxid Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
FARBLOSES BIS WEISSES KRISTALLINES PULVER.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: (als TWA) 10 mg/m?Krebskategorie A4 (nicht klassifizierbar als krebserzeugend für den Menschen); (ACGIH 2005).
MAK: 1,5 mg/m?(Alveolengängige Fraktion); Schwangerschaft: Gruppe C; (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den Körper durch Inhalation des Aerosols.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Eine belästigende Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann beim Dispergieren schnell erreicht werden.
LECKAGE
Verschüttetes Material in Behältern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Persönliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzgerät, P1-Filter für inerte Partikel.
R-Sätze Betriebsanweisung:
R20:Gesundheitsschädlich beim Einatmen.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R20/21/22:Gesundheitsschädlich beim Einatmen,Verschlucken und Berührung mit der Haut.
R38:Reizt die Haut.
R20/21:Gesundheitsschädlich beim Einatmen und bei Berührung mit der Haut.
R10:Entzündlich.
R36/38:Reizt die Augen und die Haut.
R22:Gesundheitsschädlich beim Verschlucken.
S-Sätze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
S25:Berührung mit den Augen vermeiden.
S2:Darf nicht in die Hände von Kindern gelangen.
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
Beschreibung
Titanium dioxide, TiO2, is a white powder and has the greatest hiding power of all white pigments. It is noncombustible; however, it is a powder and, when suspended in air, may cause a dust explosion if an ignition source is present. It is not listed in the DOT Hazardous Materials Table, and the DOT does not consider it hazardous in transportation. The primary uses are as a white pigment in paints, paper, rubber, and plastics; in cosmetics; in welding rods; and in radioactive decontamination of the skin.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Ttitanium dioxide is an odorless white powder.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
Metastable over long periods of
time despite being less
thermodynamically stable than
rutile. However, above 700°C,
the irreversible and rapid
monotropic conversion of
anatase to rutile occurs. It
exhibits a greater transparency
in the near-UV than rutile. With
an absorption edge at 385 nm,
anatase absorbs less light at the
blue end of the visible spectrum
and has a blue tone.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
The naturally occurring dioxide exists in three crystal forms: anatase, rutile and brookite. While rutile, the most common form, has an octahedral structure. Anatase and brookite have very distorted octahedra of oxygen atoms surrounding each titanium atom. In such distorted octahedral structures, two oxygen atoms are relatively closer to titanium than the other four oxygen atoms. Anatase is more stable than the rutile form by about 8 to 12 kJ/mol (Cotton, F.A., Wilkinson, G., Murillo, C.A and M Bochmann. 1999. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th ed, p. 697, New York: John Wiley & Sons) Other physical properties are: density 4.23g/cm3; Mohs hardness 5.8 g/cm3 ( anatase and brookite) and 6.2 g/cm3 ( rutile); index of refraction 2.488 (anatase), 2.583 (brookite) and 2.609 (rutile); melts at 1,843°C; insoluble in water and dilute acids; soluble in concentrated acids.
Occurrence
Titanium dioxide occurs in nature in the crystalline forms rutile, anatase,
and brookite. Rutile and anatase are manufactured in large quantities, which are
primarily used as pigments, but also as catalysts and in ceramics.
Verwenden
Titanium dioxide is an extreme white and bright compound with high index of refraction. In paints it is a white pigment and an opacifying agent.It is in house paints, water paints, lacquers, enamels, paper filling and coating, rubber, plastics, printing ink, synthetic fabrics, floor coverings, and shoe whiteners. Also, it is used in colorants for ceramics and coatings for welding rods. A rutile form of the dioxide is used in synthetic gem stones.
synthetische
Titanium dioxide is mined from natural deposits. It also is produced from other titanium minerals or prepared in the laboratory. Pigment-grade dioxide is produced from the minerals, rutile and ilmenite. Rutile is converted to pigment grade rutile by chlorination to give titanium tetrachloride, TiCl4. Anhydrous tetrachloride is converted back to purified rutile form by vapor phase oxidation.
Anatase form is obtained by hydrolytic precipitation of titanium(IV) sulfate on heating. The mineral ilmenite is treated with concentrated sulfuric acid. Heating the sulfate solution precipitates hydrous titanium oxide. The precipitate is calcined to expel all water.
Titanium dioxide also can be prepared by heating Ti metal in air or oxygen at elevated temperatures.
Vorbereitung Methode
Titanium dioxide occurs naturally as the minerals rutile (tetragonal
structure), anatase (tetragonal structure), and brookite (orthorhombic
structure).
Titanium dioxide may be prepared commercially by either the
sulfate or chloride process. In the sulfate process a titanium
containing ore, such as ilemenite, is digested in sulfuric acid. This
step is followed by dissolving the sulfates in water, then precipitating
the hydrous titanium dioxide using hydrolysis. Finally, the
product is calcinated at high temperature. In the chloride process,
the dry ore is chlorinated at high temperature to form titanium
tetrachloride, which is subsequently oxidized to form titanium
dioxide.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Two main physico-chemically distinct polymorphs of TiO
2 are anatase and rutile. Anatase has a higher photocatalytic activity than rutile but is thermodynamically less stable.
Hazard
Lower respiratory tract irritant. Possible
carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Titanium dioxide is a mild pulmonary
irritant and is generally regarded as a
nuisance dust.
Pharmazeutische Anwendungen
Titanium dioxide is widely used in confectionery, cosmetics, and
foods, in the plastics industry, and in topical and oral pharmaceutical
formulations as a white pigment.
Owing to its high refractive index, titanium dioxide has lightscattering
properties that may be exploited in its use as a white
pigment and opacifier. The range of light that is scattered can be
altered by varying the particle size of the titanium dioxide powder.
For example, titanium dioxide with an average particle size of
230nm scatters visible light, while titanium dioxide with an average particle size of 60nm scatters ultraviolet light and reflects visible
light.
In pharmaceutical formulations, titanium dioxide is used as a
white pigment in film-coating suspensions, sugar-coated tablets,
and gelatin capsules. Titanium dioxide may also be admixed with
other pigments.
Titanium dioxide is also used in dermatological preparations
and cosmetics, such as sunscreens.
Sicherheitsprofil
A nuisance dust. A
human skin irritant. Questionable
carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic,
neoplastigenic, and tumorigenic data.
Violent or incandescent reaction with metals
at high temperatures (e.g., aluminum,
calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium,
zinc, lithium). See also TITANIUM
COMPOUNDS.
Sicherheit(Safety)
Titanium dioxide is widely used in foods and oral and topical
pharmaceutical formulations. It is generally regarded as an
essentially nonirritant and nontoxic excipient.
mögliche Exposition
Titanium dioxide is a white pigment used as a pigment in paint; in the rubber, plastics, ceramics, paint, and varnish industries, in dermatological preparations; and is used as a starting material for other titanium compounds; as a gem; in curing concrete; and in coatings for welding rods. It is also used in paper and cardboard manufacture.
Carcinogenicity
Carcinogenesis. In a 1985 study, rats (CD) were
exposed to graded airborne concentrations (0, 10, 50, and
250mg/m
3) of TiO2 6 h/day, 5 days/week, for 2 years. The
majority of the particles were in the respirable range (84%
≤13 mmMMD). All responses were confined to the lungs. At
the lowest dose, the histopathological evaluation of the lungs
revealed dust-laden macrophages in the alveolar ducts and
adjacent alveoli with pneumocyte hyperplasia. At the two
highest concentrations, there were increases in lung weight,
accumulation of dust in the macrophages, foamy macrophage
responses, type II pneumocyte hyperplasia, alveolar proteinosis,
alveolar bronchiolization, cholesterol granulomas, focal
pleurisy, and dust deposition in the tracheobronchiolar lymph
nodes. At the 250mg/m
3 exposure concentration, bronchiole
alveolar adenomas (males: control 2/79, 250mg/m
3 12/79;
females: control 0/79, 250mg/m
3 13/79) increased.
Additionally, 13/79 females at the 250mg/m
3 dose showed squamous cell carcinoma, compared with none in 79 controls.
Theauthorsnoted that this responsemight have little biological
relevance to humans because of the overload of respiratory
clearance mechanisms and also pointed out that the type,
location, and development of the tumors were different from
those in human lung tumors. It is not clear that the nasal
cavity epithelium was examined. However, the nasal cavity
load would be expected to be higher in the rats because of
anatomic structure, whereas the lung deposition should be
higher in humans because we are, in part, mouth breathers.
Lager
Titanium dioxide is extremely stable at high temperatures. This is
due to the strong bond between the tetravalent titanium ion and the
bivalent oxygen ions. However, titanium dioxide can lose small,
unweighable amounts of oxygen by interaction with radiant energy.
This oxygen can easily recombine again as a part of a reversible
photochemical reaction, particularly if there is no oxidizable
material available. These small oxygen losses are important because
they can cause significant changes in the optical and electrical
properties of the pigment.
Titanium dioxide should be stored in a well-closed container,
protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Forms and nomenclature
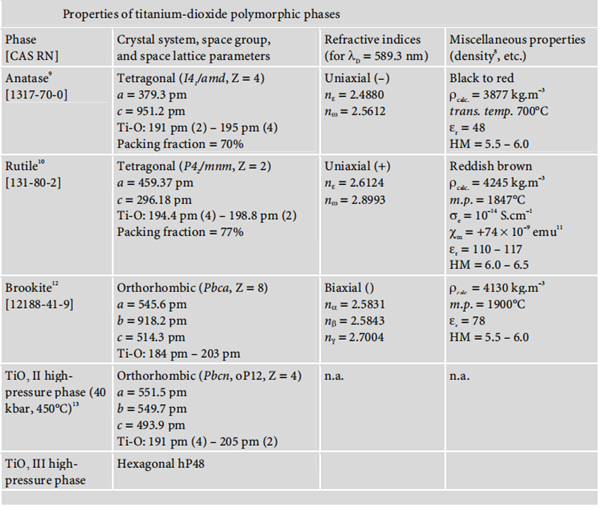
Titanium dioxide occurs in nature in three polymorphic crystal forms: anatase, rutile, and brookite.
Moreover, under high pressure, the structure of all three polymorphs of titanium dioxide
may be converted into that of α-PbO2. The following diagram summarises the main properties of these three polymorphisms:
Inkompatibilitäten
Titanium dioxide is incompatible with strong oxidizers and strong acids. Violent or incandescent reactions may occur with metals (e.g., aluminum, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc, and lithium).
Waste disposal
Land fill.
Regulatory Status
Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive
Ingredients Database (dental paste; intrauterine suppositories; ophthalmic preparations; oral capsules, suspensions, tablets; topical
and transdermal preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines
licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of
Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Titandioxid Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

