Ammoniumformiat Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-Sätze Betriebsanweisung:
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
S-Sätze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
S37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
CH5NO2. Farblose Kristalle, die schwach nach Ameisensäure riechen.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Reizt die Augen, Atmungsorgane und die Haut. Führt nach Aufnahme grösserer Mengen zu Muskelbeschwerden, Tremor, Übelkeit und Psychosen.
Nicht mit starken Oxidationsmitteln und starken Säuren in Berührung bringen.
LD
50 (oral, Maus): 2250 mg/kg
Schutzmaßnahmen und Verhaltensregeln
Schutzhandschuhe als kurzzeitiger Staubschutz.
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Trocken aufnehmen. Der Entsorgung zuführen.
Auf Umgebung abstimmen.
Im Brandfall können gefährliche Gase freigesetzt werden.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser abwaschen.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser bei geöffnetem Lidspalt mindestens 15 Minuten ausspülen. Sofort Augenarzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Einatmen: Frischluft. Sofort Arzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Verschlucken: Reichlich Wasser trinken. Sofort Arzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung entfernen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
Gelöst als halogenfreie, organische Lösemittelabfälle.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Ammonium formate, NH4HCO2, is the ammonium salt of formic acid. It is a colorless, hygroscopic, crystalline solid. It can be synthesized through treating ammonium carbonate with 85% formic acid. It is widely used in many organic reactions such as Leuckart reaction which is the reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones. It can also be used as a buffer in HPLC and LC/MS test. Moreover, it is also used in palladium on carbon (Pd/C) reduction of functional group. It can also be used for the preparation of formic acid in situ as well as being used to store formic acid.
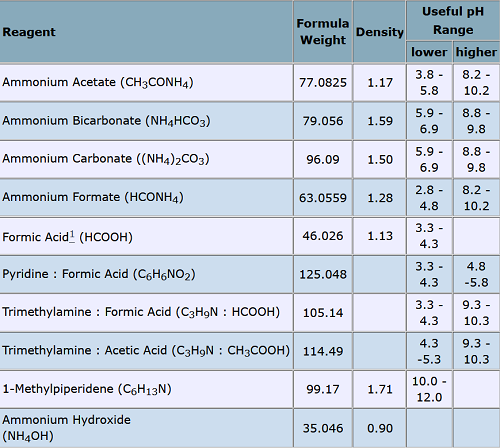
Common HPLC Buffers: Ammonium formate (2.7<PH<3.7) does a fairly good job of filling the gap at the low-pH end.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
White monoclinic deliquescent crystals or granules; density 1.280 g/cm
3; melts at 116°C; highly soluble in water (102 g/100 g at 0°C), solubility rapidly increasing with temperature (i.e., 531 g/100 g at 80°C); soluble in liquid ammonia, alcohol and ether.
Verwenden
Pure ammonium formate decomposes into formamide and water when heated, and this is its primary use in industry. Formic acid can also be obtained by reacting ammonium formate with a dilute acid, and since ammonium formate is also produced from formic acid, it can serve as a way of storing formic acid.
In chemical analysis, especially to ppt base metals from salts of the "noble" metals. Ammonium formate can also be used in palladium on carbon (Pd / C) reduction of functional groups. In the presence of Pd / C, ammonium formate decomposes to hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and ammonia.
Ammonium formate can be used for reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones (Leuckart reaction)
Ammonium formate can be used as a buffer in high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and is suitable for use with liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS). .
Definition
ChEBI: Ammonium formate is the ammonium salt of formic acid. It has a role as a buffer. It is functionally related to a formic acid.
Reaktionen
When heated, ammonium formate eliminates water, forming formamide. Upon further heating it forms to HCN and H
2O. A side reaction of this is the decomposition of formamide to CO and NH
3.
Air & Water Reaktionen
Ammonium formate is generally soluble in water.
Reaktivität anzeigen
Salts, basic, such as Ammonium formate, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes irritation of nose and throat. Ingestion irritates mouth and stomach. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation.
Brandgefahr
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating ammonia and formic acid gases may form in fire.
Sicherheitsprofil
Moderately toxic by ingestion andintravenous routes. When heated to decomposition itemits toxic fumes of NOx and NH3.
läuterung methode
Heat the solid in NH3 vapour and dry it in a vacuum till the NH3 odour is faint (note that it can evaporate completely in a vacuum). Recrystallise it from absolute EtOH and then keep it in a desiccator over 99% H2SO4 in vacuo. It is very hygroscopic. It exists in two forms, stable needles and less stable plates. It also forms acid salts, i.e. HCO2NH4.3HCO2H and HCO2NH4.HCO2H. [Kensall & Adler J Am Chem Soc 43 1473 1921, Beilstein 2 IV 18.]
Einzelnachweise
[1] http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=CV2P0503
[2] https://www.alfa.com/zh-cn/catalog/014517/
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ammonium_formate
[4] GAO X, MA Y, ZHOU F, et al. Promotion Mechanism of Ammonium Formate in Ammonium Salt Leaching Process for Weathered Crust Elution-Deposited Rare Earth Ores[J]. Minerals, 2023, 1 1: 0. DOI:10.3390/min13101286.
[5] A. S. KORNILOV. Uranium Stripping with Ammonium Acetate and Formate[J]. Radiochemistry, 2024, 65 1 supplement: S172-S176. DOI:10.1134/S1066362223070159.
[6] ISHANI BORTHAKUR, SABUJ KUNDU* Reductive Aminomethylation Using Ammonium Formate and Methanol as N1 and C1 Source: Direct Synthesis of Mono- and Di-Methylated Amines[J]. ACS Catalysis , 2024, 14 8: 5847-5857. DOI:
10.1021/acscatal.4c00346.
Ammoniumformiat Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
3-Azetidinecarboxylic acid
4-(Trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid
(R)-(-)-2-AMINOHEPTANE
5-Fluoro-2-picolinic acid
(1,3,5-TRIMETHYL-1H-PYRAZOL-4-YL)METHYLAMINE
1-N-Boc-3-hydroxyazetidine
C-(1-METHYL-PIPERIDIN-2-YL)-METHYLAMINE
4-METHYL-1,3-OXAZOLE-5-CARBOXYLIC ACID
1,2,4-Triazol
2,6-Dihydroxyisonicotinsure
4-METHYLOXAZOLE-5-CARBONYL CHLORIDE
3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzylamin
5-(AMINOMETHYL)-2,3-DIHYDROBENZO[B]FURAN
4-CHLORO-7-METHYLTHIENO[3,2-D]PYRIMIDINE
Teicoplanin A2
3-Chlorbenzylamin
DL-α-Methylbenzylamin
4-Aminotetrahydropyran
5-CHLORO-1H-INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID
4-CHLORO-2-METHYLBENZYLAMINE
7-Methylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
(4S)-HYDROXY-3-METHYL-2-(2-PROPENYL)-2-CYCLOPENTENE-1-ONE
3-(4-Morpholinyl)aniline
5-amino-1H-Indole-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
5-Azaindole
(1H-INDAZOL-3-YL)-ACETIC ACID
4-Aminomethyl-2-methoxyphenolhydrochlorid
3-Amino-5-fluoropyridine
1-Phenylethylamin (1)
1-(4-Chlorphenoxy)-3,3-dimethyl-1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butanon
ETHYL 5-AMINO-1H-INDOLE-2-CARBOXYLATE
3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylamine
3-Amino-p-anissaeure
2,5-Dimethoxybenzylamine

