Dibenzothiophen Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-Sätze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitsschädlich beim Verschlucken.
R20/21/22:Gesundheitsschädlich beim Einatmen,Verschlucken und Berührung mit der Haut.
S-Sätze Betriebsanweisung:
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
Beschreibung
Dibenzothiophene (DBT) is an organosulfur compound found in crude oil and petroleum. It is a colourless solid that is chemically somewhat similar to anthracene. Dibenzothiophene is used as a chemical intermediate in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals (NLM, 2006).It is used to investigate the effect of sulfur compounds in gasoline range during the fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) process.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Dibenzothiophene is a yellow-green, crystalline solid with an mp of 99.5°C and a bp of 332.5°C. It is soluble in ethanol, benzene, chloroform, and methanol but insoluble in water. Its dipole moment is 0.83 D. It is quite stable under normal temperature and pressure.
History
Dibenzothiophene was first synthesized in 1870 by Stemhouse by heating biphenyl with iron scrap, but the assigned incorrect structure was corrected by Graebe. The natural dibenzothiophene was isolated from coal tar by Kruber. Besides this, various alkylated dibenzothiophenes have also been isolated from the crude oil, but it was difficult to desulfurize them catalytically. The presence of sulfur in the fuel produces sulfur dioxide when burnt and causes air pollution.
Dibenzothiophene is a thermally stable compound and resistant to mild oxidizing agents. Depending on the nature of the oxidizing agent it is oxidized to corresponding sulfoxide and sulfone. There are numerous protocols for the construction of dibenzothiophene but some of them are limited to the synthesis of specific compounds due to noncompatibility of functional groups.
Verwenden
Dibenzothiophene is used to investigate the effect of sulfur compounds in the gasoline range during the fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) process. It can also be used as:
A starting material for the synthesis of corresponding sulfoxide and sulfone by oxidative desulfurization using various catalysts.
A template for the synthesis of surface molecular imprinted polymer (SMIP). SMIP is applicable for the removal of dibenzothiophene during desulfurization of the gasoline.
A precursor for the synthesis of DBT based π-conjugating polymers.
Definition
ChEBI: Dibenzothiophene is a mancude organic heterotricyclic parent that consists of a thiophene ring flanked by two benzene rings ortho-fused across the 2,3- and 4,5-positions. It has a role as a keratolytic drug. It is a member of dibenzothiophenes and a mancude organic heterotricyclic parent.
Application
Dibenzothiophene is an important representative of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Kinetics of hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene on presulflded molybdenaalumina catalyst has been studied in a high-pressure-flow microreactor. Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by selective cleavage of carbon sulphur bonds by a thermophilic bacterium Bacillus subtilis WU-S2B has been reported.
Dibenzothiophene was employed as heavy model sulfur compound to investigate the effect of heavy sulfur compounds on the percentage of sulfur in gasoline range during the Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) process.
synthetische
Dibenzothiophene is prepared by the reaction of biphenyl with sulfur dichloride in the presence of aluminium chloride.
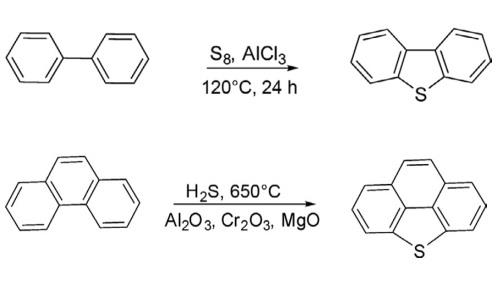
The parent dibenzothiophene has been synthesized by heating a mixture of biphenyl with sulfur at 120°C for 24 h in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 in 79% yields. This methodology is useful for the synthesis of substituted dibenzothiophenes.
An alternative new protocol has been developed for the synthesis of dibenzothiophene and bridged dibenzothiophene by heating diphenyl and phenanthrene separately with H2S in the presence of mixed metal oxides (Al2O3, Cr2O3, and MgO) at 650°C.
Reaktionen
Reduction with lithium results in scission of one C-S bond. S-oxidation occurs to give the sulfone, which is more labile than the parent dibenzothiophene. With butyllithium, this heterocycle undergoes stepwise lithiation at the 4- and 6- positions.
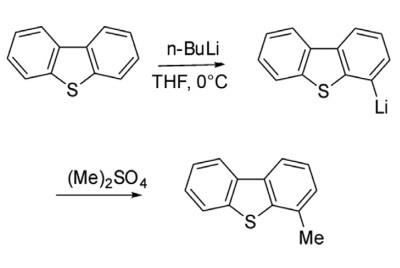
Alkylation of dibenzothiophene through Friedel-Crafts catalysis is not very facile and ends up with a complex mixture. However, alkylation of dibenzothiophene has been achieved through lithiation strategy. Thus 4-lithiated dibenzothiophene on reaction with dimethyl sulfate gave 4-methyl dibenzothiophene.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Dibenzothiophene is an important representative of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Kinetics of hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene on presulflded molybdenaalumina catalyst has been studied in a high-pressure-flow microreactor. Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by selective cleavage of carbon sulphur bonds by a thermophilic bacterium
Bacillus subtilis WU-S2B has been reported.
Chemische Reaktivität
Dibenzothiophene is heteroaromatic in nature and undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions smoothly. Mostly, electrophilic substitution occurs at position 2 of dibenzothiophene offering 2-substituted dibenzothiophene, provided position 2 is not preoccupied.
läuterung methode
Purify dibenzothiophene by chromatography on alumina with pet ether, in a darkened room. Recrystallise it from water or EtOH. [Beilstein 17 V 239.]
Einzelnachweise
[1] KARINA TACIANA SILVA. DBT- and DBTO2-Induced Dysplasia and Their Associated Proteomic Alterations in the Small Intestines of Wistar Rats[J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2014, 14 1: 385-396. DOI:
10.1021/pr5009459.
[2] MASATOSHI NAGAI Toshiaki K. Selectivity of molybdenum catalyst in hydrodesulfurization, hydrodenitrogenation, and hydrodeoxygenation: Effect of additives on dibenzothiophene hydrodesulfurization[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1983, 81 2: Pages 440-449. DOI:
10.1016/0021-9517(83)90182-3.
[3] KOHTARO KIRIMURA. Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and its derivatives through the selective cleavage of carbon-sulfur bonds by a moderately thermophilic bacterim Bacillus subtilis WU-S2B[J]. Journal of bioscience and bioengineering, 2001, 91 3: Pages 262-266. DOI:
10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80131-6.
[4] KE LI Xiangtai M Aimin Yu. Synthesis of Dibenzothiophene and 1,4-Dihydrodibenzothiophene Derivatives via Allylic Phosphonium Salt Initiated Domino Reactions[J]. Organic Letters, 2018, 20 4: 1106-1109. DOI:
10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00028.
[5] AVISIKTA SINHA Mangalampalli R. Synthesis and Properties of Dibenzothiophene Embedded Heteroporphyrins[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 86 9: 6100-6110. DOI:
10.1021/acs.joc.0c02937.
Dibenzothiophen Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

