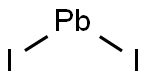
Lead(II) iodide
- CAS No.
- 10101-63-0
- Chemical Name:
- Lead(II) iodide
- Synonyms
- PbI2;Super PbI2;Lead(II) diiodide;LT-S9147;diiodolead;LEAD IODIDE;Lead lodi de;LEAD DIIODIDE;LEAD(+2)IODIDE;plumbousiodide
- CBNumber:
- CB2771616
- Molecular Formula:
- I2Pb
- Molecular Weight:
- 461.01
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00011163
- MOL File:
- 10101-63-0.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 402 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 954 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 6.16 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Flash point | 954°C |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | Soluble in concentrated solutions of alkali iodides and sodium thiosulfate. Insoluble in alcohol and cold hydrochloric acid. |
| form | beads |
| color | Yellow to orange |
| Specific Gravity | 6.16 |
| Water Solubility | Partially soluble in water. Freely soluble in sodium thiosulfate solution. Soluble in concentrated solutions of alkali iodides. Insoluble in alcohol and cold HCl.Soluble in concentrated solutions of alkali iodides and sodium thiosulfate. Insoluble in alcohol and cold hydrochloric acid. |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 0: forms stable aqueous solutions |
| λmax | 539nm(neat)(lit.) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,5411 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 8.01 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 0.05 mg/m3; TWA 0.01 ppm NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 0.050 mg/m3 |
| Stability | Stable. May discolour upon exposure to light. |
| InChIKey | RQQRAHKHDFPBMC-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10101-63-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| FDA UNII | OTL90F2GLT |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Lead diiodide(10101-63-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead(II) iodide (10101-63-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302+H332-H360Df-H373-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P202-P273-P301+P312-P304+P340+P312-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 61-20/22-33-50/53-62 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2291 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| F | 8 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28276000 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Lead(II) iodide price More Price(38)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | 211168 | Lead(II) iodide 99% | 10101-63-0 | 50g | $61.7 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 203602 | Lead(II) iodide 99.999% trace metals basis | 10101-63-0 | 50g | $188 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| TCI Chemical | L0279 | Lead(II) Iodide (99.99%, trace metals basis) [for Perovskite precursor] >98.0%(T) | 10101-63-0 | 1g | $22 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| TCI Chemical | L0279 | Lead(II) Iodide (99.99%, trace metals basis) [for Perovskite precursor] >98.0%(T) | 10101-63-0 | 5g | $54 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Alfa Aesar | 012724 | Lead(II) iodide, 99.9985% (metals basis) | 10101-63-0 | 25g | $109 | 2023-06-20 | Buy |
Lead(II) iodide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Lead (II) iodide (chemical formula: PbI) is a kind of inorganic salt. It appears as a bright yellow crystalline solid. It has some special applications such as the manufacture of solar cells, X-rays, and gamma-ray detectors. In addition, it can also be used as a paint pigment for being used in art for bronzing and in gold-like mosaic tiles. It can be commonly synthesized through a double displacement reaction between potassium iodide KI and lead (II) nitrate Pb(NO3)2 in water solution. Lead (II) acetate and sodium iodide can also be used as the substitute of lead nitrate and potassium iodide, respectively. Alternatively, it can be manufactured through the reaction between iodine vapor and the molten lead. It is also used in printing and photography. However, it is hazard to the environment, and should be taken care of to limit spread to the environment.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead(II)_iodide
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lead_II__iodide#section=Top
Chemical Properties
Lead(II) iodide, also known as Lead Iodide, is a heavy, bright yellow, odorless powder. Photoelectrons are emitted when exposed to ultraviolet light, which is readily decomposed by light in the air. It is slightly soluble in hot water, slightly soluble in cold water and hot aniline, easily soluble in sodium thiosulfate solution, soluble in concentrated potassium iodide and concentrated sodium acetate solution, and insoluble in ethanol and cold concentrated hydrochloric acid. It reacts with sodium sulfide solution to form a lead sulfide precipitate. It reacts with alkali metal and alkaline earth metal carbonate solution to obtain lead carbonate precipitate.
Physical properties
Yellow hexagonal crystals; density 6.16 g/cm3; melts at 402°C; vaporizes at 954°C; decomposes at 180°C when exposed to green light; slightly soluble in water (0.44 g/L at 0°C and 0.63 g/L at 20°C); Ksp 8.49x10-9 at 25°C; partially soluble in boiling water (4.1 g/L at 100°C); insoluble in ethanol; soluble in alkalis and alkali metal iodide solutions.
Uses
Lead(II) iodide is used as a detector material for high energy photons including x-rays and gamma rays. It is used in photography, printing, mosaic gold, and bronzing. It exhibits ferroelastic properties and has efficiency in stopping X-ray and gamma ray, which provides excellent environmental stability.
Uses
Used in bronzing, printing, photography, gold pencils, and mosaic gold.
Preparation
Lead diiodide is prepared by mixing aqueous solutions of lead nitrate or lead acetate with an aqueous solution of potassium or sodium iodide or hydriodic acid, followed by crystallization. The product is purified by recrystallization.
Pb2+(aq) + 2Iˉ (aq) → PbI2(s).
General Description
Lead iodide appears as a yellow crystalline solid. Insoluble in water and denser than water. Primary hazard is threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. Used in printing and photography, to seed clouds and other uses.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Lead(II) iodide has weak oxidizing or reducing powers. Redox reactions can however still occur. The majority of compounds in this class are slightly soluble or insoluble in water. If soluble in water, then the solutions are usually neither strongly acidic nor strongly basic. These compounds are not water-reactive. Light sensitive
Hazard
Lead diiodide is toxic if ingested. The symptoms are those of lead poisoning.
Health Hazard
Early symptoms of lead intoxication via inhalation or ingestion are most commonly gastrointestinal disorders, colic, constipation, etc.; weakness, which may go on to paralysis, chiefly of the extensor muscles of the wrists and less often the ankles, is noticeable in the most serious cases. Ingestion of a large amount causes local irritation of the alimentary tract. Pain, leg cramps, muscle weakness, paresthesias, depression, coma, and death may follow in 1 or 2 days. Contact with eyes causes irritation.
Potential Exposure
Lead iodide is used in bronzing, gold pencils; mosaic gold; printing, and photography
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Antidotes and special procedures for lead: Persons with significant lead poisoning are sometimes treated with CaEDTA while hospitalized. This “chelating” drug causes arush of lead from the body organs into the blood and kidneys, and thus has its own hazards, and must be administered only by highly experienced medical personnel undercontrolled conditions and careful observation. Ca EDTA orsimilar drugs should never be used to prevent poisoningwhile exposure continues or without strict exposure control,as severe kidney damage can result.Note to physician: For severe poisoning BAL [British AntiLewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol (C3H8OS2)] has beenused to treat toxic symptoms of certain heavy metals poisoning. In the case of lead poisoning it may have SOMEvalue. Although BAL is reported to have a large margin ofsafety, caution must be exercised, because toxic effects maybe caused by excessive dosage. Most can be prevented bypremedication with 1-ephedrine sulfate (CAS: 134-72-5).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Lead iodide must be stored to avoid contact withoxidizers (such as perchlorates, peroxides, permanganates,chlorates, and nitrates) and chemically active metals (suchas potassium, sodium, magnesium, and zinc), since violentreactions occur. A regulated, marked area should be established where this chemical is handled, used, or stored incompliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045. Lead iodide isregulated by an OSHA Standard, 1910.1025. All requirements of the standard must be followed.
Shipping
UN3288 Toxic solids, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
It crystallises from a large volume of water. The solubility in H2O is 1.1% at ~10o, and 3.3% at ~ 100o.
Incompatibilities
Lead iodide has weak oxidizing or reducing powers. Redox reactions can however still occur. The majority of compounds in this class are slightly soluble or insoluble in water. If soluble in water, then the solutions are usually neither strongly acidic nor strongly basic. These compounds are not water-reactive. Light sensitive Contact with oxidizers or active metals may cause violent reaction
Lead(II) iodide Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 | info@fdachem.com | China | 20287 | 58 |
| Shanghai Daken Advanced Materials Co.,Ltd | +86-371-66670886 | info@dakenam.com | China | 18779 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21634 | 55 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | sales@coreychem.com | China | 29884 | 58 |
| City Chemical LLC | 2039322489 | sales@citychemical.com | United States | 168 | 58 |
| QINGDAO HONG JIN CHEMCIAL CO.,LTD. | 532-83657313 | hjt@hong-jin.com | China | 228 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 | linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-6139-8061 +86-86-13650506873 | sales@chemdad.com | China | 39894 | 58 |
| Richest Group Ltd | 18017061086 | oled@richest-group.com | CHINA | 5600 | 58 |
| Antai Fine Chemical Technology Co.,Limited | 18503026267 | info@antaichem.com | CHINA | 9636 | 58 |
View Lastest Price from Lead(II) iodide manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-03-26 | Lead(II) iodide
10101-63-0
|
US $34.00-1.40 / kg | 1kg | 99% | g-kg-tons, free sample is available | Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | |
 |
2019-07-06 | Lead(II) iodide
10101-63-0
|
US $20.00 / KG | 1KG | 99% | customise | Career Henan Chemical Co |
-
- Lead(II) iodide
10101-63-0
- US $34.00-1.40 / kg
- 99%
- Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd
-

- Lead(II) iodide
10101-63-0
- US $20.00 / KG
- 99%
- Career Henan Chemical Co