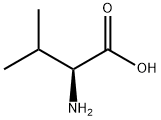
L-Valine
- CAS No.
- 72-18-4
- Chemical Name:
- L-Valine
- Synonyms
- H-VAL-OH;L-Val;L-Val-OH;Valin;2-AMINO-3-METHYLBUTANOIC ACID;L-VALINE (13C5, 99%);(S)-ALPHA-AMINOISOVALERIC ACID;(s)-2-amino-3-methylbutyricacid;(S)-alpha-Aminoisovaleric acid, (L)-2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid;-VaL
- CBNumber:
- CB3381690
- Molecular Formula:
- C5H11NO2
- Molecular Weight:
- 117.15
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00064220
- MOL File:
- 72-18-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 295-300 °C (subl.) (lit.) |
|---|---|
| alpha | 28 º (c=8, 6N HCl) |
| Boiling point | 213.6±23.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.23 |
| refractive index | 28 ° (C=8, HCl) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 25 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.29(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 5.5-6.5 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | odorless |
| Odor Type | odorless |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +27.0±0.5°, c = 5% in 5 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | 85 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax |
λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.15 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.1 |
| Merck | 14,9909 |
| BRN | 1721136 |
| InChIKey | KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N |
| LogP | 0.29 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 72-18-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| FDA 21 CFR | 172.320; 582.5925; 172.320; 310.545 |
| Substances Added to Food (formerly EAFUS) | L-VALINE |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | HG18B9YRS7 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Valine(72-18-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Valine (72-18-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 40 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 24/25-36-22 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | YV9361000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29224995 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 72-18-4(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 intraperitoneal in rat: 5390mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
L-Valine price More Price(78)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.16006 | (S)-(+)-Valine for synthesis | 72-18-4 | 25g | $54.5 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.16006 | (S)-(+)-Valine for synthesis | 72-18-4 | 100g | $86.2 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 50848 | L-Valine certified reference material, TraceCERT | 72-18-4 | 100mg | $134 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 1708503 | L-Valine United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard | 72-18-4 | 200mg | $519 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| TCI Chemical | V0014 | L-Valine >98.0%(T) | 72-18-4 | 25g | $30 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
L-Valine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Amino acids
L-Valine is a kind of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA). Animal cannot synthesize it by itself. It must be obtained from the diet to meet their nutritional needs. Therefore L-valine belongs to the essential amino acids.
Amino acids are the basic structural unit of protein synthesis, and the predecessor of other amines that metabolism needs. They are indispensable materials in our life. At present, it is known that there are 20 to 30 amino acids. Some of them can be synthesized in the human body, which are known as non-essential amino acids. And some, called essential amino acids, cannot be synthesized in the human body that should be supplemented from the outside. Mammal cells need twelve essential amino acids: L-arginine, L-cystine, L-histidine, L-leucine, L-isoleucine, L-lysine, L-methionine, L-phenylalanine, L-threonine, L-tryptophan, L-tyrosine, L-valine. These amino acids are all laevoisomer, and some non-essential amino acids of dextroisomer may have inhibitory effect on cultured cells.
L-amino acids can easier to be absorbed than D-amino acids. And the absorption of D, L-methionine has no difference. There is competition between the body transport of amino acids. The transporting of an amino acid can be suppressed by the presence of another amino acid. For example, L-valine and L-methionine can inhibit the absorption of L-leucine. Excessive lysine in dietary can inhibit the absorption of arginine. High concentration (100mM) of L-valine has no effect on the absorption of L-methionine. Because it can be transported through another route.
Content Analysis
About 200mg sample is accurately weighed, dissolved in 3ml formic acid and 50ml glacial acetic acid. Add 2 drops of crystal violet test solution (TS-74), then use 0.1mol/L perchloric acid to titrate the solution to green or blue disappear entirely. Each Ml0.1mol/L perchloric acid is equivalent to 11.72mg L-valine (C5H11NO2).
Chemical property
White crystal or crystalline powder, odorless, bitter taste. Soluble in water, solubility in water of 8.85% at 25℃. Almost insoluble in ethanol, ether, acetone. melting point(decomposition point) 315℃, isoelectric point 5.96, [α]25D+28.3 (C = 1-2g/ml, in 5mol/L HCl).
Uses
- Amino acids drugs, nutritional supplements. It can be used as the main component of aminophenol transfusion and synthesize aminophenol. L-Valine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids. It is essential amino acid. It can be used to treat liver failure and central nervous system dysfunction.
- L-Valine is essential amino acid. The requirement for men is 10mg/(kg·d). Physiological effects of the L-form is 2 times of the D-type. L-Valine deficiency can cause neurological disorders, blastocolysis, loss of weight, anemia and the like. As nutritional supplements, it can be used to prepare aminophenol transfusion and synthesize aminophenol with other essential amino acid infusion. Valine added to metric pastry (1g/kg) can make the products aroma of sesame. L-Valine used in bread can also improve the flavor.
- L-Valine is the essential amino acid. It can be used as one of pharmaceutical composition of amino acid infusion to synthesize drugs. It also can be used as food additives.
- Nutritional supplements. It can be used to prepare aminophenol transfusion and synthesize aminophenol with other essential amino acid infusion.Valine added to metric pastry (1g/kg) can make the products aroma of sesame. L-Valine used in bread can also improve the flavor.
- L-Valine can be used for biochemical research, the preparation of tissue culture media. It also used as amino acids nutritional drugs in medicine.
Description
Valine (abbreviated as Val or V) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)2. L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. Human dietary sources are any proteinaceous foods such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes.
Along with leucine and isoleucine, valine is a branched-chain amino acid. It is named after the plant valerian. In sickle-cell disease, valine substitutes for the hydrophilic amino acid glutamic acid in hemoglobin. Because valine is hydrophobic, the hemoglobin is prone to abnormal aggregation.
Chemical Properties
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, soluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohol.
Uses
L-Valine is an essential amino acid and one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. L-Valine cannot be manufactured by the body and must be acquired through diet or supplementation. L-valine is found in grains, dairy products, mushrooms, meats, peanuts and soy proteins. L-Valine has been used in studies to attenuate arrhythmias and induce hypotensive effects.
Uses
valine is an amino acid used as a skin-conditioning and odor-masking agent. It is more commonly used in hair care preparations than in skin care.
Definition
ChEBI: The L-enantiomer of valine.
Biosynthesis
Valine is an essential amino acid, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. It is synthesized in plants via several steps starting from pyruvic acid. The initial part of the pathway also leads to leucine. The intermediate α-ketoisovalerate undergoes reductive amination with glutamate. Enzymes involved in this biosynthesis include :
Acetolactate synthase
Acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase
Dihydroxyacid dehydratase
Valine aminotransferase.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 22, p. 2411, 1981 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)82922-1
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 23, p. 167, 1975 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.23.167
General Description
Valine is an essential amino acid, involved in the biosynthesis of glutamine and alanine. Valine being a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA), maintains a balance among the BCAAs. L-Valine serves as an energy fuel.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Valine is an essential amino acid, involved in the biosynthesis of glutamine and alanine. Valine being a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) maintains a balance among the BCAAs. L-Valine serves as an energy fuel. Long term deficiency of L-Valine leads to growth failure, organ damage and loss of muscle mass.
Side effects
L-valine is a natural substance that is necessary for our health. As such, it generally does not have any side effects. However, taking large quantities of L-valine can cause fatigue, nausea, and a lack of muscle coordination.
Extremely high doses of L-valine can be dangerous. Excessive levels of L-valine can cause your body to produce excess ammonia which is toxic.
Extremely high levels of L-valine can cause your skin to tingle and can lead to hallucinations.
Safety Profile
Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Synthesis
Racemic valine can be synthesized by bromination of isovaleric acid followed by amination of the α-bromo derivative
HO2CCH2CH(CH3)2 + Br2 → HO2CCHBrCH(CH3)2 + HBr
HO2CCHBrCH(CH3)2 + 2 NH3 → HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)2 + NH4Br
.
Purification Methods
Crystallise L-valine from water by addition of EtOH. It sublimes at 178-188o/0.03mm with 99.3% recovery and unracemised [Gross & Gradsky J Am Chem Soc 77 1678 1955]. [Perrin J Chm Soc 3125 1958, Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2368-23771961, Beilstein 4 IV 2659.]
Nomenclature
According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming valine are numbered sequentially starting from 1 denoting the carboxyl carbon, whereas 4 and 4' denote the two terminal methyl carbons.
L-Valine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hangzhou Qiwei Pharmatech Co.,Ltd | 13282840061 | mw@qwpharmatech.com | China | 109 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 | abby@weibangbio.com | China | 8806 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-81148696 +86-15536356810 | 1022@dideu.com | China | 3882 | 58 |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 | sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12830 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 | sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5889 | 58 |
| Suzhou Sanyi Polymer Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. | +8615571922873 | 15571922873@163.com | China | 102 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +undefined18602966907 | qinhe02@xaltbio.com | China | 997 | 58 |
| Across Biotech Jinan Co LTD | +8613031735486 | frank@acrossbiotech.com | China | 105 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Franta Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86-13082019107 +86-13082019107 | admin@flanderff.com | China | 244 | 58 |
| Hebei Saisier Technology Co., LTD | +86-18400010335 +86-18034520335 | admin@hbsaisier.cn | China | 1015 | 58 |
Related articles
- The benefits and side effects of L-Valine
- L-valine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids essential for animal health and important in metabolism.
- Nov 15,2023
- L-Valine: Applications, metabolism and medical significance
- L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classifie....
- Jul 18,2023
- Biological activity of L-Valine
- L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classifie....
- Oct 16,2019
View Lastest Price from L-Valine manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2025-01-18 | L-Valine
72-18-4
|
US $10.00 / kg | 1kg | 99.9% | 10000 | Hebei Miaoyin Technology Co.,Ltd | |
 |
2025-01-17 | L-Valine
72-18-4
|
US $0.00 / Kg/Drum | 1KG | 98.5%-101.5% | 10 Tons | WUHAN FORTUNA CHEMICAL CO., LTD | |
 |
2025-01-17 | L-Valine
72-18-4
|
US $0.00 / Kg/Drum | 1KG | 99% | 200mt | Jinan Finer Chemical Co., Ltd |
72-18-4(L-Valine)Related Search:
1of4