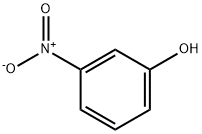
3-Nitrophenol
- CAS No.
- 554-84-7
- Chemical Name:
- 3-Nitrophenol
- Synonyms
- M-NITROPHENOL;Nsc 1551;3-Nitrophe;m-Nitrofenol;3-NITROPHENOL;3-nitro-pheno;m-nitro-pheno;Phenol,3-nitro-;Phenol, m-nitro-;meta-Nitrophenol
- CBNumber:
- CB3728637
- Molecular Formula:
- C6H5NO3
- Molecular Weight:
- 139.11
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00007240
- MOL File:
- 554-84-7.mol
| Melting point | 96-98 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 194 °C/70 mmHg (lit.) |
| bulk density | 640kg/m3 |
| Density | 1,49 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.5723 (estimate) |
| Flash point | 102°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 13.5g/l insoluble |
| pka | 8.28(at 25℃) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | Yellow to brown |
| PH | 6.6-8.6 (H2O, 20℃) |
| PH Range | 6.6(colourless)-8.6(yellow/orange) |
| Water Solubility | 13.5 g/L (25 ºC) |
| λmax | 570nm |
| Merck | 14,6618 |
| BRN | 1907946 |
| Major Application | Display device, semiconductor device, sensors, high voltage capacitors, energetic materials, electrolyte batteries, inks, correction fluid, detergent, leak detection method, lubricants, insecticide, food storage, inhibition of amyloidoses, detect bacterialinfection, drugs, material for evaluating dental caries activity |
| InChIKey | RTZZCYNQPHTPPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 554-84-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | T6P4T52V9W |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol, 3-nitro-(554-84-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | m-Nitrophenol (554-84-7) |
| UNSPSC Code | 12352104 |
| NACRES | NA.22 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS05,GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H318 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P280-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-38-41-36/37/38-33-20/21/22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37-45-36/37/39-22-28 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1663 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | SM1925000 | |||||||||
| F | 8 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 400 °C | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Harmful/Irritant | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29089000 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 554-84-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in mice, rats: 1414, 933 mg/kg, K. C. Back et al., Reclassification of Materials Listed as Transportation Health Hazards (TSA-20-72-3; PB214-270, 1972) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
3-Nitrophenol Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
yellow to brown crystalline powder
Uses
3-Nitrophenol is a chemical reagent used in various organic syntheses. Used in the synthesis of RAGE inhibitors via the etherification of phenols. Also used in the synthesis of kinase inhibitors against epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation.
Uses
As indicator in 0.3% solution in 50% alcohol. pH: 6.8 colorless, 8.6 yellow.
Production Methods
3-Nitroaniline is diazotized in aqueous sulfuric acid and then hydrolyzed by being added gradually to boiling dilute sulfuric acid. The crude product solidifies on cooling and is filtered off in 90 % yield.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of 3-nitrophenols that is phenol in which one of the hydrogens that is meta to the hydroxy group has been replaced by a nitro group.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 36, p. 5117, 1995 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(95)00963-D
General Description
Colorless to pale yellow crystalline solid. Sinks in and mixes with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water insoluble.
Reactivity Profile
3-Nitrophenol is a light-yellow, crystalline material, toxic and irritant. When heated to decomposition 3-Nitrophenol emits toxic fumes of oxides of nitrogen [Lewis, 3rd ed., 1993, p. 941]. Phenols do not behave as organic alcohols, as one might guess from the presence of a hydroxyl (-OH) group in their structure. Instead, they react as weak organic acids. Phenols and cresols are much weaker as acids than common carboxylic acids (phenol has Ka = 1.3 x 10^[-10]). These materials are incompatible with strong reducing substances such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. Flammable gas (H2) is often generated, and the heat of the reaction may ignite the gas. Heat is also generated by the acid-base reaction between phenols and bases.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
INHALATION: Inhalation or ingestion causes headaches, drowsiness, nausea, and blue color in lips, ears, and finger nails (cyanosis). EYES: Contact with eyes causes irritation. SKIN: Can be absorbed through intact skin to give same symptoms as for inhalation.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Dangerous toxic fumes of NO x
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. A skin and severe eye irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also other nitrophenol entries.
Purification Methods
Crystallise 3-nitrophenol from water, CHCl3, CS2, EtOH or pet ether (b 80-100o), and dry it under vacuum over P2O5 at room temperature. It can also be distilled at low pressure. The 4-nitrobenzoate had m 174o (from EtOH). [Beilstein 6 IV 1269.]