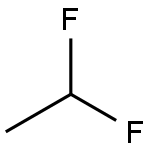
Difluoroethane
- CAS No.
- 75-37-6
- Chemical Name:
- Difluoroethane
- Synonyms
- F152A;R152A;R 152a;FC-152A;CH3CHF2;FKW152a;HFA152a;HFC-152A;dymel152;Fron152a
- CBNumber:
- CB3854228
- Molecular Formula:
- C2H4F2
- Molecular Weight:
- 66.05
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00000449
- MOL File:
- 75-37-6.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | -117 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | -25 °C |
| Density | 0.966 |
| vapor density | 2.28 (vs air) |
| refractive index | 1.2434 |
| solubility | Soluble 1 in 357 parts of water at 25°C. |
| Water Solubility | 5.37g/L(0 ºC) |
| LogP | 0.750 |
| Indirect Additives used in Food Contact Substances | 1,1-DIFLUOROETHANE |
| FDA 21 CFR | 178.3010; 701.30 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-37-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | 0B1U8K2ME0 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethane, 1,1-difluoro-(75-37-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | HFC-152a (75-37-6) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS04 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H220-H280 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P377-P381-P410+P403 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,F+ | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 11-12 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 16-33-36-38 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1030 2.1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | KI1410000 | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Flammable | |||||||||
| DOT Classification | 2.1 (Flammable gas) | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 2.1 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2903392500 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LC50 inhalation in mouse: 977gm/m3/2H | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Difluoroethane Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
liquefied colourless gas under pressure
Chemical Properties
Difluoroethane is a liquefied gas and exists as a liquid at room temperature when contained under its own vapor pressure, or as a gas when exposed to room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The liquid is practically odorless and colorless. Difluoroethane is noncorrosive and nonirritating.
Uses
HFC 152a is a specialty liquified hydrofluorocarbon gas. It is used as an intermediate in the production of fluorinated polymers, as an aerosol propellant in some specialty applications, and as a component in some refrigerant blends.
Production Methods
Difluoroethane is prepared from ethyne by the addition of hydrogen fluoride in the presence of a suitable catalyst. The difluoroethane formed is purified to remove all traces of water, as well as traces of the starting materials.
General Description
Difluoroethane is colorless, odorless gas shipped as a liquefied gas under its vapor pressure. Contact with the liquid can cause frostbite. Difluoroethane is easily ignited. Its vapors are heavier than air and a flame can travel back to the source of leak very easily. This leak can be either a liquid or vapor leak. Difluoroethane can asphyxiate by the displacement of air. Under prolonged exposure to fire or heat the containers may rupture violently and rocket.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable.
Reactivity Profile
Halogenated aliphatic compounds, such as Difluoroethane, are moderately or very reactive. Reactivity generally decreases with increased degree of substitution of halogen for hydrogen atoms. Low molecular weight haloalkanes are highly flammable and can react with some metals to form dangerous products. Materials in this group are incompatible with strong oxidizing and reducing agents. Also, they are incompatible with many amines, nitrides, azo/diazo compounds, alkali metals, and epoxides. The reaction of aluminum with various halogenated hydrocarbons produces a self-sustaining reaction with sufficient heat to melt aluminum pieces, examples of other halogenated hydrocarbons are fluorotrichloromethane, dichlorodifluoromethane, chlorodifluoromethane, tetrafluoromethane. The vigor of the reaction appears to be dependent on the combined degree of fluorination and the vapor pressure, [Chem. Eng. News 39(27):44(1961)].
Health Hazard
Inhalation of concentrated gas will cause suffocation. Contact with liquid can damage eyes because of low temperature. Frostbite may result from contact with liquid.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Difluoroethane, a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC), is an aerosol propellant used in topical pharmaceutical formulations. Difluoroethane may be used as a vehicle for dispersions and emulsions.
Since difluoroethane does not contain chlorine, there are no environmental controls on the use of this material as a propellant, since it does not deplete the ozone layer and is not a greenhouse gas.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by inhalation. Mutation data reported. Narcotic in high concentration. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidzing materials. See also FLUORIDES.
Safety
Difluoroethane may be used as an aerosol propellant in topical pharmaceutical formulations. It is generally regarded as an essentially nontoxic and nonirritant material.
Deliberate inhalation of excessive quantities of this propellant may result in death, and the following ‘warning’ statements must appear on the label of all aerosols:
WARNING: Avoid inhalation. Keep away from eyes or other mucous membranes.
WARNING: Do not inhale directly; deliberate inhalation of contents can cause death.
WARNING: Use only as directed; intentional misuse by deliberately concentrating and inhaling the contents can be harmful or fatal.
WARNING: Do not inhale directly; deliberate inhalation of contents can cause death.or
WARNING: Use only as directed; intentional misuse by deliberately concentrating and inhaling the contents can be harmful or fatal.
WARNING: Contents under pressure. Do not puncture or incinerate container. Do not expose to heat or store at room temperature above 120°F (49°C). Keep out of the reach of children.
When propellants are used in topical aerosols they may cause a chilling effect on the skin, although this effect has been somewhat overcome by the use of vapor-tap valves. The propellants quickly vaporizefromtheskin,andarenonirritating whenusedasdirected.
storage
Difluoroethane is a nonreactive and stable material. The liquefied gas is stable when used as a propellant and should be stored in a metal cylinder in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Compatible with the usual ingredients used in the formulation of pharmaceutical aerosols.
Regulatory Status
Accepted in the USA, by the FDA, for use as a topical aerosol propellant.
Difluoroethane Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
Preparation Products
Related articles
- 1,1-Difluoroethane: Properties, Production process and Uses
- According to different raw materials, the processes for manufacture of 1,1-difluoroethane include two routes: fluorination of ....
- Mar 20,2024
75-37-6(Difluoroethane)Related Search:
1of4