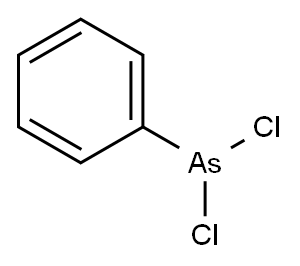
PHENYL DICHLOROARSINE
- CAS No.
- 696-28-6
- Chemical Name:
- PHENYL DICHLOROARSINE
- Synonyms
- TL 69;NA 1556;Fenyldichlorarsin;Fenildicloroarsina;Dichlor-fenylarsin;Phenyl dichlorarsine;Dichlorophenylarsine;Dichlorophenylarsenic;Rcra waste number P036;dichloro(phenyl)arsane
- CBNumber:
- CB4512323
- Molecular Formula:
- C6H5AsCl2
- Molecular Weight:
- 222.93
- MDL Number:
- MOL File:
- 696-28-6.mol
| Melting point | -19°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 255°C |
| Density | 1.652 |
| refractive index | 1.6386 |
| form | liquid |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | KK93BBF49U |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dichlorophenylarsine (696-28-6) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| RIDADR | 1556 |
|---|---|
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | I |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 696-28-6(Hazardous Substances Data) |
PHENYL DICHLOROARSINE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Phenyldichloroarsine is a colorless or light yellow liquid or gas. Odorless.
General Description
A colorless odorless liquid. Density 1.654 g / cm3. Used as a lachrymator poison gas. Toxic by inhalation and skin absorption.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts with water or with moist air to form hydrochloric acid [AAR 1991].
Reactivity Profile
PHENYL DICHLOROARSINE is incompatible with acids and bases. A reducing agents and therefore generally incompatible with oxidizing agents.
Health Hazard
Median lethal dosage 2600 mg-minute/m3. Mean incapacitating dosage 16 mg-minute/m3 as a vomiting agent and 1800 mg-minute/m3 as a blistering agent. 633 mg-minute/m3 produces eye injury. Poisonous; may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Strong irritant to eyes, skin, and issue.
Fire Hazard
PHENYL DICHLOROARSINE may burn but does not ignite readily. Containers may explode in heat of fire. Fire and runoff from fire control water may produce irritating or poisonous gases. Upon decomposition hydrogen chloride and phenylarsenious oxide are emitted. Unstable. Decomposed by water.
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation, ingestion, skin contact, and intravenous routes. See also ARSENIC. A lachrymator type of dtary poison gas. When exposed to heat, water, or steam it reacts to produce corrosive fumes of Cl-. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of arsenic.
Potential Exposure
Phenyldichloroarsine is an organoarsenic compound used in organic synthesis and as a solvent. PD has been used as a military tear gas, vesicant and blister agent.
Shipping
UN3280 Organoarsenic compound, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required, Potential Inhalation Hazard (Special Provision 5). UN1556 Arsenic compounds, liquid, n.o.s. inorganic, including arsenates, n.o.s.; arsenites, n.o.s.; arsenic sulfides, n.o.s.; and organic compounds of arsenic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. Military driver shall be given full and complete information regarding shipment and conditions in case of emergency. AR 50-6 deals specifically with the shipment of chemical agents. Shipments of agent will be escorted in accordance with AR 740-32.
Incompatibilities
Contact with water forms HCl. Heat produces fumes of arsenic and chlorine. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Attacks some metals in the presence of moisture